Hut Forty Two internal documentation.
This is the multi-page printable view of this section. Click here to print.
Documentation
- 1: Platforms
- 1.1: Heroku
- 1.2: Elastic Beanstalk
- 1.2.1: Amazon Linux 2023 v4.9.0
- 1.2.2: Amazon Linux 2023 v4.8.0
- 1.2.3: Amazon Linux 2023
- 2: Applications
- 2.1: Adrian Flux
- 2.1.1: buying-service-al202339-live
- 2.1.2: flix-epa-data312-live
- 2.1.3: flux-callme-service-al39
- 2.1.4: flux-exchange-service-al239
- 2.1.5: flux-qab-service-live
- 2.1.6: flux-quote-service-311-live
- 2.1.7: fluxlite-service38-live
- 2.1.8: goahead-testsuite
- 2.1.9: landscape-311-live
- 2.1.10: short-term-api-live
- 2.1.11: sterling-breakdown38-live
- 2.1.12: tgsl-data-service312
- 2.1.13: bikesure-affiliates
- 2.1.14: fakertrail
- 2.1.15: flux-bannerclick-app
- 2.1.16: flux-buying-pages-tour-caravan
- 2.1.17: flux-callback-service
- 2.1.18: flux-customer-portal
- 2.1.19: flux-epa
- 2.1.19.1: Incompletes
- 2.1.20: flux-epa-laravel-car
- 2.1.21: flux-epa-laravel-car-docker
- 2.1.22: flux-epa-laravel-laid-bike
- 2.1.23: flux-epa-laravel-laid-bike-doc
- 2.1.24: flux-epa-laravel-van
- 2.1.25: flux-epa-laravel-van-docker
- 2.1.26: flux-epa-learner
- 2.1.27: flux-epa-learner-docker
- 2.1.28: flux-epa-prd
- 2.1.29: flux-epa-service-new
- 2.1.30: flux-geo-service
- 2.1.31: flux-geodata-service
- 2.1.32: flux-handler-service
- 2.1.33: flux-jaf
- 2.1.34: flux-jam
- 2.1.35: flux-policy-documents-service
- 2.1.36: flux-redirects-service
- 2.1.37: flux-regabi-data-live
- 2.1.38: flux-shorturl-app
- 2.1.39: flux-sitedata-service
- 2.1.40: flux-sources-service
- 2.1.41: flux-worker-service
- 2.1.42: hut-app-launcher
- 2.1.43: proxy-bikesure
- 2.1.44: proxy-flux
- 2.1.45: proxy-sterling
- 2.1.46: sterling-epa-laravel-car
- 2.1.47: sterling-epa-laravel-car-docke
- 2.1.48: sterling-epa-laravel-van
- 2.1.49: sterling-epa-laravel-van-docke
- 2.2: WordPress
- 2.2.1: aahadleightran
- 2.2.2: adrianflux1
- 2.2.3: adrianfluxcomp
- 2.2.4: afcustomers
- 2.2.5: afdubtales
- 2.2.6: afguernsey
- 2.2.7: afjersey
- 2.2.8: aflearnerdrive
- 2.2.9: afmotorsport
- 2.2.10: afownersclubs
- 2.2.11: afreferral
- 2.2.12: afsupercars
- 2.2.13: afvictorianhom
- 2.2.14: bangerrally
- 2.2.15: bikesurecomps
- 2.2.16: bksbikesure
- 2.2.17: bksblog
- 2.2.18: bkscustomers
- 2.2.19: bksdigipr
- 2.2.20: bksextinction
- 2.2.21: bksforeverbike
- 2.2.22: bkskawasakiins
- 2.2.23: bksmanufacture
- 2.2.24: bksmotorcycles
- 2.2.25: bksquadbikeloc
- 2.2.26: bksreferral
- 2.2.27: bkssuzukiinsur
- 2.2.28: bkstriumphinsu
- 2.2.29: bksultimatebik
- 2.2.30: carextinction
- 2.2.31: cultclassics
- 2.2.32: datacapturedoc
- 2.2.33: driverlesscars
- 2.2.34: fluxcapacitor
- 2.2.35: fluxposure
- 2.2.36: forevercars
- 2.2.37: fuellingaround
- 2.2.38: fullchat
- 2.2.39: hondainsurance
- 2.2.40: intelligentins
- 2.2.41: kawasakiinsura
- 2.2.42: meganchallenge
- 2.2.43: noboxins
- 2.2.44: silverstonecl1
- 2.2.45: stcustomers
- 2.2.46: sterblog
- 2.2.47: sterlingcomps
- 2.2.48: sterlinginsni
- 2.2.49: sterlinginsure
- 2.2.50: ststerlingins1
- 2.2.51: suzukiinsuranc
- 2.2.52: top10cars
- 2.2.53: trinitylane
- 2.2.54: triumphinsuran
- 2.2.55: ukuscarparts
- 3: External
- 3.1: Google
- 3.1.1: Google Maps API
- 4: Memos
- 5: Frameworks
- 5.1: Django
- 5.1.1: Django 2.2 LTS
- 5.1.2: Django 3.0
- 5.1.3: Django 3.1
- 5.1.4: Django 3.2 LTS
- 5.1.5: Django 4.0
- 5.1.6: Django 4.1
- 5.1.7: Django 4.2 LTS
- 5.1.8: Django 5.0
- 5.1.9: Django 5.1
- 5.1.10: Django 5.2 LTS
- 6: Libraries
- 6.1: bannerclick
- 6.2: django-bulk-redirects
- 6.3: django-cardutils
- 6.4: django-cors-headers-model
- 6.5: django-drf-extensions
- 6.6: django-hut-python-validators
- 6.7: django-hut-theme
- 6.8: django-microservice
- 6.9: django-rest-cereal
- 6.10: django-simpleaudit
- 6.11: epa-data-client
- 6.12: flux-callme-sdk
- 6.13: flux-exchange-handler-sdk
- 6.14: flux-go
- 6.15: flux-goahead
- 6.16: flux-handler-sdk
- 6.17: flux-jobs
- 6.18: flux-sagepay
- 6.19: flux-sitedata
- 6.20: flux-sitedata-v2-shim
- 6.21: flux-tgsl-endpoints
- 6.22: flux-tgsl-listdata
- 6.23: hut-django-models
- 6.24: hut-python-cardutils
- 6.25: hut-python-validators
- 6.26: regabi-client
- 6.27: sources-client
- 6.28: tgsl
- 6.29: tgsl-metadata
- 7: Proposals
- 7.1: Edge Department Info Service Migration
- 7.2: Edge Sources Service Migration
- 7.3: Migrate Applications from Elastic Beanstalk to AWS Fargate
- 7.4: Migrate Applications from Heroku to AWS Fargate
- 7.5: Migrate Applications from Heroku to Cloudflare
- 7.6: Migrate Exchange REST API to Serverless
- 7.7: Migrate QAB Buy Web Services to Serverless
- 7.8: Migrate QAB Quoting Web Services to Serverless
- 7.9: Serverless Callbacks Migration
- 7.10: Universal Geo Service Migration
- 7.11: Remove Fakertrail Application
- 7.12: Provider Agnostic Geo Lookup Library
- 8: Example Page
1 - Platforms
Documentation for the various platforms and infrastructure stacks used across our applications.
1.1 - Heroku
Heroku is a cloud platform that enables companies to build, deliver, monitor and scale apps. This section covers the different Heroku stacks (runtime environments) and their support lifecycles.
Stack Overview
Heroku stacks are the different runtime environments available for applications. Each stack is based on a specific Ubuntu LTS version and has a defined support lifecycle.
Current Stacks
- Heroku-24: Default stack (Ubuntu 24.04) - Supported until April 2029
- Heroku-22: Active (Ubuntu 22.04) - Supported until April 2027
- Heroku-20: End of Life (April 30, 2025)
- Heroku-18: End of Life (April 30, 2023)
- Heroku-16: End of Life (May 1, 2021)
1.1.1 - heroku-24
Overview
Heroku-24 is the current default stack for new Heroku applications, based on Ubuntu 24.04 LTS.
Support Timeline
- General Availability: June 2024
- Default Stack: December 2024
- End of Life: April 2029
Key Features
Base Image Optimizations
- Reduced base image size by removing less frequently used packages (Bazaar, Mercurial)
- Build tools (GCC, Make, Git, system Python) available only at build time, not at runtime
- More efficient resource utilization
Multi-Architecture Support
- Published images support both amd64 and arm64 architectures
- Default Linux user changed from
roottoheroku
Build and Runtime Changes
- Git available only at build time (not at runtime)
- Limited locale support: C, C.utf8, POSIX, and en_US.utf8 only
- APT sources list uses new deb822 format at
/etc/apt/sources.list.d/ubuntu.sources - Reduced timezone data (only geographical regions and city names)
Fir Apps
- Only
heroku/builder:24is supported for Fir apps - Heroku-24 is the exclusive base image for new Fir applications
Upgrading to Heroku-24
Applications should be upgraded to Heroku-24 to benefit from the latest security updates, performance improvements, and extended support timeline.
References
1.1.2 - heroku-22
Overview
Heroku-22 is based on Ubuntu 22.04 LTS and is currently in active support.
Support Timeline
- Release: June 2022
- Superseded by: Heroku-24 (June 2024)
- End of Life: April 2027
Key Changes from Heroku-20
OpenSSL Version
- Ships with OpenSSL 3.0
- OpenSSL 1.1 is not available as a runtime library
- Applications depending on OpenSSL 1.1 must be updated
Ubuntu Base
- Based on Ubuntu 22.04 (Jammy Jellyfish)
- Upgraded from Ubuntu 20.04 in Heroku-20
Migration Considerations
Applications should plan migration to Heroku-24 before April 2027 to ensure continued security updates and support.
References
1.1.3 - heroku-20
⚠️ End of Life Notice
Heroku-20 reached end of life on April 30, 2025.
Overview
Heroku-20 was based on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS.
Support Timeline
- Release: 2020
- Deprecated: June 2024
- End of Life: April 30, 2025
- Build Cutoff: Approximately May 30, 2025
Post-EOL Status
- Existing apps continue to run at customer’s own risk
- No security updates provided
- No new builds/deployments allowed after build cutoff
- Limited technical support available
Required Action
All applications on Heroku-20 must be upgraded to Heroku-22 or Heroku-24 immediately.
Running applications on an end-of-life stack exposes them to security vulnerabilities and compliance risks.
Migration Path
- Test application on Heroku-24 (recommended) or Heroku-22
- Update dependencies and configurations as needed
- Deploy to new stack
- Monitor for any runtime issues
References
1.1.4 - heroku-18
⚠️ End of Life Notice
Heroku-18 reached end of life on April 30, 2023.
Overview
Heroku-18 was based on Ubuntu 18.04 LTS (Bionic Beaver).
Support Timeline
- Release: 2018
- Deprecated: June 22, 2022
- End of Life: April 30, 2023
- Build Cutoff: May 1, 2023
Post-EOL Status
- Existing apps continue to run at customer’s own risk
- No security updates since April 30, 2023
- No new builds/deployments allowed since May 1, 2023
- No technical support available
Critical Action Required
All applications still on Heroku-18 are severely outdated and must be upgraded immediately.
This stack has been unsupported for over 2 years and poses significant security and compliance risks.
Migration Path
Applications on Heroku-18 should be upgraded directly to Heroku-24 to ensure the longest support timeline.
References
1.1.5 - heroku-16
⚠️ End of Life Notice
Heroku-16 reached end of life on May 1, 2021.
Overview
Heroku-16 was based on Ubuntu 16.04 LTS (Xenial Xerus).
Support Timeline
- Release: 2016
- Deprecated: December 11, 2020
- End of Life: May 1, 2021
- Build Cutoff: June 1, 2021
Post-EOL Status
- Existing apps continue to run at customer’s own risk
- No security updates since May 1, 2021
- No new builds/deployments allowed since June 1, 2021
- No technical support available
Critical Action Required
Applications on Heroku-16 are critically outdated (4+ years unsupported) and represent a severe security risk.
Immediate upgrade to Heroku-24 is essential for security, compliance, and operational stability.
Migration Path
Direct upgrade to Heroku-24 is strongly recommended. Given the age of this stack, significant application updates will likely be required.
References
1.2 - Elastic Beanstalk
AWS Elastic Beanstalk is a fully managed service for deploying and scaling web applications and services.
These pages document the various Elastic Beanstalk platform versions used across our applications.
1.2.1 - Amazon Linux 2023 v4.9.0
Overview
Amazon Linux 2023 v4.9.0 is an Elastic Beanstalk platform version for running Python applications on 64-bit Amazon Linux 2023.
Platform Timeline
- Created: December 15, 2025
- Last Updated: December 16, 2025
- Lifecycle State: Recommended (Current recommended version)
- Status: Ready
Note: AWS does not publish specific EOL dates for Elastic Beanstalk platforms. Platform versions typically receive 90-day retirement notices when end-of-life is planned. Check the Python Platform History for updates.
Platform Details
Base System
- Operating System: Amazon Linux 2023
- Architecture: 64-bit (x86_64)
- Platform Version: 4.9.0
Python Support
This platform version supports Python applications. Common Python versions available:
- Python 3.12
- Python 3.11
- Python 3.9
The specific Python version is determined by your application’s configuration.
Key Features
Amazon Linux 2023 Benefits
- Security-focused: Regular security updates and long-term support
- Optimized for AWS: Built specifically for AWS environments
- Modern tooling: Updated system packages and build tools
- Performance: Optimized for cloud workloads
Elastic Beanstalk Integration
- Managed platform updates
- Auto-scaling capabilities
- Integrated monitoring with CloudWatch
- Load balancing
- Rolling deployments
Framework Support
This platform is commonly used for:
- Django applications
- Flask applications
- FastAPI applications
- Generic WSGI/ASGI applications
Configuration
Applications on this platform can be configured through:
- Environment variables
.ebextensionsconfiguration files- Platform-specific settings in the EB console
References
1.2.2 - Amazon Linux 2023 v4.8.0
Overview
Amazon Linux 2023 v4.8.0 is an Elastic Beanstalk platform version for running Python applications on 64-bit Amazon Linux 2023.
Platform Timeline
- Created: November 20, 2025
- Last Updated: December 16, 2025
- Lifecycle State: Available (Superseded by v4.9.0)
- Status: Ready
Note: AWS does not publish specific EOL dates for Elastic Beanstalk platforms. Platform versions typically receive 90-day retirement notices when end-of-life is planned. Check the Python Platform History for updates.
Platform Details
Base System
- Operating System: Amazon Linux 2023
- Architecture: 64-bit (x86_64)
- Platform Version: 4.8.0
Python Support
This platform version supports Python applications. Common Python versions available:
- Python 3.12
- Python 3.11
- Python 3.9
The specific Python version is determined by your application’s configuration.
Key Features
Amazon Linux 2023 Benefits
- Security-focused: Regular security updates and long-term support
- Optimized for AWS: Built specifically for AWS environments
- Modern tooling: Updated system packages and build tools
- Performance: Optimized for cloud workloads
Elastic Beanstalk Integration
- Managed platform updates
- Auto-scaling capabilities
- Integrated monitoring with CloudWatch
- Load balancing
- Rolling deployments
Framework Support
This platform is commonly used for:
- Django applications
- Flask applications
- FastAPI applications
- Generic WSGI/ASGI applications
Configuration
Applications on this platform can be configured through:
- Environment variables
.ebextensionsconfiguration files- Platform-specific settings in the EB console
Migration Considerations
Applications on this platform should plan to upgrade to v4.9.0 or later to benefit from the latest security patches and platform improvements.
References
1.2.3 - Amazon Linux 2023
Overview
Amazon Linux 2023 is the base platform for Elastic Beanstalk Python applications running on 64-bit architecture.
Support Timeline
- Initial Release: May 2023 (Platform v4.0.0)
- Current Recommended: v4.9.0 (December 2025)
- Amazon Linux 2023 Support: 5 years from release (through 2028)
- Update Frequency: Monthly security and feature updates
Note: AWS provides a 90-day notice before retiring platform versions. Active environments continue to run on their selected platform version, but new features and security updates are only available on current versions. Monitor the Python Platform History for announcements.
Platform Details
Base System
- Operating System: Amazon Linux 2023
- Architecture: 64-bit (x86_64)
Python Support
Amazon Linux 2023 supports multiple Python versions for Elastic Beanstalk applications:
- Python 3.12
- Python 3.11
- Python 3.9
- Python 3.8
Key Features
Amazon Linux 2023 Benefits
- Next-generation AL2: Successor to Amazon Linux 2
- Security-focused: SELinux enabled by default
- Deterministic updates: Predictable release schedule every 2 years
- Standard support: 5 years of support
- Modern tooling: Updated system packages and development tools
- Performance: Kernel and system optimizations for AWS
Elastic Beanstalk Advantages
- Fully managed: AWS handles provisioning, load balancing, scaling
- Auto-scaling: Automatically scales based on application demand
- Monitoring: Integrated CloudWatch metrics and logging
- Rolling updates: Zero-downtime deployments
- Multi-environment: Easy management of dev, staging, and production
Framework Support
Amazon Linux 2023 on Elastic Beanstalk supports:
- Django: Full-featured web framework
- Flask: Lightweight WSGI web application framework
- FastAPI: Modern async web framework
- Pyramid: Flexible web framework
- Custom WSGI/ASGI applications
Platform Versions
For specific platform version details, see:
Configuration Options
Environment Variables
- Set via EB console, CLI, or configuration files
- Accessible to your application at runtime
.ebextensions
- Configuration files for customizing EB environment
- Install packages, run commands, configure services
Procfile
- Define custom processes to run in your application
Best Practices
- Use specific platform versions for production stability
- Pin dependencies in requirements.txt
- Configure health checks for reliable auto-scaling
- Use environment variables for configuration
- Enable enhanced health reporting for better monitoring
References
2 - Applications
2.1 - Adrian Flux
2.1.1 - buying-service-al202339-live
Links
| URI | Type | |
|---|---|---|
| https://buying-service-al202339-live.eba-r3mwqfca.eu-west-1.elasticbeanstalk.com | elastic beanstalk url |
Environment Variables
Configuration variables for this application:
ADMIN_PATHALLOW_BROWSABLE_RENDERERAWS_ACCESS_KEY_IDAWS_S3TRACEFILE_ACCESS_KEY_IDAWS_S3TRACEFILE_BUCKET_NAMEAWS_S3TRACEFILE_REGION_NAMEAWS_S3TRACEFILE_SECRET_ACCESS_KEYAWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEYAWS_STORAGE_BUCKET_NAMEBUYING_COOKIE_DOMAINDATABASE_URLENABLE_DRF_LOGGINGENVIRONMENTFRONTEND_GENERIC_ERROR_URLFURY_AUTHPOLICY_PRECHECK_ENDPOINTPOST_3D_REDIRECT_URLPYTHONPATHSENTRY_DSNSENTRY_ENVIRONMENT
2.1.2 - flix-epa-data312-live
Links
| URI | Type | |
|---|---|---|
| https://flix-epa-data312-live.eba-pp3hhz3t.eu-west-1.elasticbeanstalk.com | elastic beanstalk url |
Environment Variables
Configuration variables for this application:
ADMIN_PATHBROKER_URLDATABASE_URLENVIRONMENTFLUX_MONITOR_TOPIC_ARNFURY_AUTHINCOMPLETES_SNS_TOPIC_ARNPYTHONPATHQAB_WEBHOOK_REPLY_TOPIC_ARNSECRET_KEYSENTRY_DSNSITE_ID
2.1.3 - flux-callme-service-al39
Links
| URI | Type | |
|---|---|---|
| https://flux-callme-service-al39.rcqs4fy6wv.eu-west-1.elasticbeanstalk.com | elastic beanstalk url |
Environment Variables
Configuration variables for this application:
ADMIN_PATHDATABASE_URLDATABASE_URL_CALLMEWEBDATABASE_URL_CALLMEWEB_READ_REPLICAPYTHONPATHSENTRY_DSNSENTRY_ENVIRONMENT
2.1.4 - flux-exchange-service-al239
Links
| URI | Type | |
|---|---|---|
| https://flux-exchange-service-al239.3p44hjsmmn.eu-west-1.elasticbeanstalk.com | elastic beanstalk url |
Environment Variables
Configuration variables for this application:
ADMIN_PATHAPI_URLBIKESURE_TRUSTPILOT_LINKCW_ACCESS_KEY_IDCW_SECRET_ACCESS_KEYDATABASE_URLDATABASE_URL_EXCHANGE_PRIVATEDEFAULT_FROM_EMAILEMAIL_HOSTEMAIL_HOST_PASSWORDEMAIL_HOST_USEREMAIL_PORTEMAIL_USE_TLSEXCHANGE_ENCRYPTION_KEYFD_TRUSTPILOT_LINKFLUX_TRUSTPILOT_LINKFURY_AUTHHIC_TRUSTPILOT_LINKINSTILLER_API_URLINSTILLER_BIKESURE_API_IDINSTILLER_BIKESURE_API_KEYINSTILLER_FLUX_API_IDINSTILLER_FLUX_API_KEYINSTILLER_INFLUX_API_IDINSTILLER_INFLUX_API_KEYLEGACY_ADRIANFLUX_SUBSCRIBE_TOKENPURE_360_SUBSCRIBE_ENDPOINTPYTHONPATHSECURE_SSL_HOSTSENTRY_DSNSENTRY_ENVIRONMENTSTERLING_TRUSTPILOT_LINKUSE_X_FORWARDED_HOSTUSE_X_FORWARDED_PORT
2.1.5 - flux-qab-service-live
Links
| URI | Type | |
|---|---|---|
| https://flux-qab-service-live.eba-pqpbj2ty.eu-west-1.elasticbeanstalk.com | elastic beanstalk url |
Environment Variables
Configuration variables for this application:
ADMIN_PATHBROKER_URLDATABASE_URLENVIRONMENTEXCHANGE_ENDPOINTEXCHANGE_ENDPOINT_FLUX_CAREXCHANGE_ENDPOINT_FLUX_CAR_LEARNEREXCHANGE_ENDPOINT_STERLING_CAREXCHANGE_TOKENPYTHONPATHSECRET_KEYSENTRY_DSNSITE_IDSOURCES_ENDPOINTTGSL_AF_CAR_QUOTE_ENDPOINTTGSL_BIKE_QUOTE_ENDPOINTTGSL_BUY_ENDPOINTTGSL_QUOTE_ENDPOINTTGSL_STERLING_CAR_ENDPOINT
2.1.6 - flux-quote-service-311-live
Links
| URI | Type | |
|---|---|---|
| https://flux-quote-service-311-live.3cg4gnpw8u.eu-west-1.elasticbeanstalk.com | elastic beanstalk url |
Environment Variables
Configuration variables for this application:
ADMIN_PATHBROKER_URLDATABASE_URLDEFAULT_FROM_EMAILEMAIL_HOSTEMAIL_HOST_PASSWORDEMAIL_HOST_USEREMAIL_USE_TLSENVIRONMENTEXCHANGE_SERVICEEXCHANGE_SERVICE_PASSWORDEXCHANGE_SERVICE_TOKENEXCHANGE_SERVICE_USERFLUX_AGG_SERVICEFURY_AUTHHIC_AGG_SERVICEHUT_API_KEYINSTILLER_API_URLINSTILLER_MICROSERVICE_TOKENINSTILLER_MICROSERVICE_URLPYTHONPATHQUOTE_TIMEOUTSECRET_KEYSEND_QUOTE_DEBUG_MAILSENTRY_DSNSHARED_DATA_DBSHARED_DATA_HOSTSHARED_DATA_PASSWORDSHARED_DATA_USERSIRA_CLIENT_NAMESIRA_PASSWORDSIRA_USERNAMESIRA_WSDLSLACK_MONITORING_ENDPOINTZEEP_LOG_LEVEL
2.1.7 - fluxlite-service38-live
Links
| URI | Type | |
|---|---|---|
| https://fluxlite-service38-live.xygjc5t8iq.eu-west-1.elasticbeanstalk.com | elastic beanstalk url |
Environment Variables
Configuration variables for this application:
ADMIN_PATHAWS_ACCESS_KEY_IDAWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEYDATABASE_URLDEFAULT_FROM_EMAILDEFAULT_TO_EMAILEMAIL_HOSTEMAIL_HOST_PASSWORDEMAIL_HOST_USEREMAIL_PORTEMAIL_USE_TLSFURY_AUTHPYTHONPATHQUOTE_SERVICE_URLSENTRY_DSNSENTRY_ENVIRONMENT
2.1.8 - goahead-testsuite
Links
| URI | Type | |
|---|---|---|
| https://goahead-testsuite.eba-cznxb3pk.eu-west-1.elasticbeanstalk.com | elastic beanstalk url |
Environment Variables
Configuration variables for this application:
ADMIN_PATHALLOW_BROWSABLE_RENDERERAWS_S3TRACEFILE_ACCESS_KEY_IDAWS_S3TRACEFILE_BUCKET_NAMEAWS_S3TRACEFILE_REGION_NAMEAWS_S3TRACEFILE_SECRET_ACCESS_KEYBUYING_SERVICE_LIVE_CREATE_URLDATABASE_URLDEBUGENCRYPTION_KEY_2020_02FURY_AUTHPYTHONPATHSENTRY_DSNSENTRY_ENVIRONMENT
2.1.9 - landscape-311-live
Links
| URI | Type | |
|---|---|---|
| https://landscape-311-live.eba-ithywivc.eu-west-1.elasticbeanstalk.com | elastic beanstalk url |
Environment Variables
Configuration variables for this application:
ADMIN_PATHBROKER_URLDATABASE_URLENCRYPTION_KEYSENVIRONMENTENVIRONMNETHKDF_SALTPYTHONPATHSECRET_KEYSENTRY_DSNSITE_ID
2.1.10 - short-term-api-live
Links
| URI | Type | |
|---|---|---|
| https://short-term-api-live.eba-zk22fxhj.eu-west-1.elasticbeanstalk.com | elastic beanstalk url |
Environment Variables
Configuration variables for this application:
ADMIN_PATHBACKEND_PRIVATE_APIBACKEND_PUBLIC_APIBROKER_URLCF_AUDDATABASE_URLDEFAULT_FROM_EMAILEMAIL_BACKENDEMAIL_HOSTEMAIL_HOST_PASSWORDEMAIL_HOST_USEREMAIL_PORTEMAIL_USE_TLSENVIRONMENTFURY_AUTHGEOSERVICE_PROXY_TOKENGEOSERVICE_PROXY_URLPASSWORD_RESET_DOMAINPYTHONPATHREGSERVICE_PROXY_TOKENREGSERVICE_PROXY_URLSECRET_KEYSENTRY_DSNTRUSTPILOT_BUSINESS_UNIT_IDTRUSTPILOT_KEYTRUSTPILOT_URL
2.1.11 - sterling-breakdown38-live
Links
| URI | Type | |
|---|---|---|
| https://sterling-breakdown38-live.yk9bkntgfj.eu-west-1.elasticbeanstalk.com | elastic beanstalk url |
Environment Variables
Configuration variables for this application:
ADMIN_PATHAGENT_IDAWS_ACCESS_KEY_IDAWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEYCC_PAYMENT_PLAN_IDCELERY_TASK_ALWAYS_EAGERCLIENT_REF_PREFIXCOMPARISON_CREATOR_REAL_TIME_SALES_ENDPOINTCREATED_BYDATABASE_URLDEFAULT_FROM_EMAILEMAIL_HOSTEMAIL_HOST_PASSWORDEMAIL_HOST_USEREMAIL_PORTEMAIL_USE_TLSEXCHANGE_SERVICE_TOKENEXCHANGE_SERVICE_URLFURY_AUTHGOOGLE_TAG_MANAGERHIC_EXCHANGE_SERVICE_TOKENHIC_EXCHANGE_SERVICE_URLPAYMENT_ERROR_PHONE_NUMBERPAYMENT_PLAN_IDPOLICY_NUMBER_PREFIXPOLICY_NUMBER_PREFIX_COMPARISONPORTFOLIO_KEYPRODUCT_IDPRODUCT_TYPEPYCURL_SSL_LIBRARYPYTHONPATHREGABI_APIREGABI_AUTH_TOKENREGABI_SERVICE_URLSAGEPAY_3D_CALLBACK_URLSAGEPAY_DIRECT_3D_SECURE_URLSAGEPAY_DIRECT_URLSAGEPAY_VENDORSCHEMASCHEME_TABLE_IDSEND_MAIL_ON_GENERATESENTRY_DSNSENTRY_ENVIRONMENTSESSION_EXPIRE_AT_BROWSER_CLOSESESSION_KEY_ENCRYPTION_KEYSOURCE_BUSINESS_IDSUBAGENT_IDTHEMETRANSACTOR_URLURL_PREPEND
2.1.12 - tgsl-data-service312
Links
| URI | Type | |
|---|---|---|
| https://tgsl-data-service312.eba-bz4yw6se.eu-west-1.elasticbeanstalk.com | elastic beanstalk url |
Environment Variables
Configuration variables for this application:
ADMIN_PATHBROKER_URLDATABASE_URLENVIRONMENTODBC_DRIVERPYTHONPATHSECRET_KEYSENTRY_DSNTGSL_DB_HOSTTGSL_DB_NAMETGSL_DB_PASSWORDTGSL_DB_USER
2.1.13 - bikesure-affiliates
Links
| URI | Type | |
|---|---|---|
| https://8e0de5fbadee4176a467eae0a014ff8f.bikesure.co.uk | frontend | |
| https://bikesure-affiliates-a4ab7315b191.herokuapp.com | heroku url | |
| https://www.bikesure.co.uk/directory/dealers/ | frontend |
Environment Variables
Configuration variables for this application:
ADMIN_PATHCF_AUDCSRF_TRUSTED_ORIGINSDEALER_ENQUIRY_EMAILSDEFAULT_FROM_EMAILEMAIL_BACKENDEMAIL_HOSTEMAIL_HOST_PASSWORDEMAIL_HOST_USEREMAIL_PORTEMAIL_USE_TLSENVIRONMENTFURY_AUTHGOOGLE_MAPS_API_KEYPROXY_DIRSECRET_KEYSENTRY_DSN
2.1.14 - fakertrail
Application URLs
| https://fakertrail.herokuapp.com | heroku url | should not be used or shared publically |
| https://zugd76r23tzfezte653fzdssds.insurergate.co.uk | frontend |
Overview
This was intended as a universal logger for Qab type services.
Deprecation
This app can be gracefully removed as it is self-contained on Heroku/Heroku-postgres. Feature flags on flux-quote-service and flux-buying-service to enable this.
2.1.15 - flux-bannerclick-app
Application URLs
| https://flux-bannerclick-app.herokuapp.com | heroku url | should not be used or shared publically |
| https://bannerclick.hut42.co.uk | service url | |
| https://bannerclick-app.adrianflux.co.uk | service url | |
| https://flux-bannerclick-app.herokuapp.com/DG9HV30L/ | admin url |
Overview
This is a simple redirecting application. Main user is nancy@mazemedia.co.uk . A “link” is added that will redirect to an endpoint such as “https://www.adrianflux.co.uk/?utm_source=Website&utm_medium=Banner&utm_id=FreeLocalNewsBanner" . The “link” will be used to redirect to the appropriate Adrian Flux page.
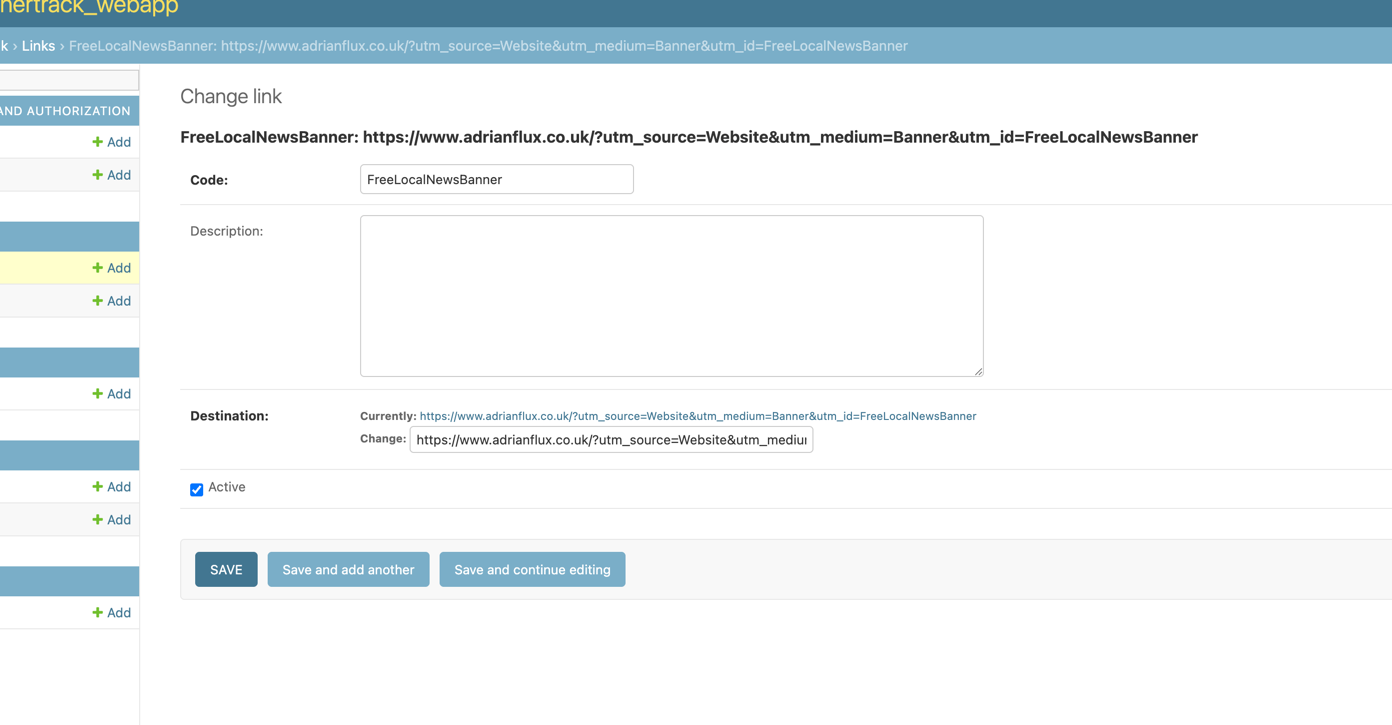
Known issues
This is “Yet Another Redirection App” and should probably be placed into a unified service.
Deprecation
Since this is a simple redirection type app then it could fall under the “Web/Redirects” proposal. However, I can see no reason why the links that it is redirecting to be used directly.
Propose we scope out current usage patterns with Maze in order to figure out the deprecation path.
2.1.18 - flux-customer-portal
Links
Environment Variables
Configuration variables for this application:
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_IDAWS_S3DUMP_ACCESS_KEY_IDAWS_S3DUMP_BUCKET_LOCATIONAWS_S3DUMP_BUCKET_NAMEAWS_S3DUMP_REGION_NAMEAWS_S3DUMP_SECRET_ACCESS_KEYAWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEYAWS_STORAGE_BUCKET_NAMECAPTCHA_REQUIREDCLOUDFRONT_URLEXCHANGE_AUTH_TOKENEXCHANGE_SERVICEEXCHANGE_SERVICE_TOKENEXHANGE_SERVICE_URLFURY_AUTHHANDLER_SERVICE_URLPAPERTRAIL_API_TOKENPGBOUNCER_MAX_CLIENT_CONNRECAPTCHA_PRIVATE_KEYRECAPTCHA_PUBLIC_KEYS3DIRECT_REGIONSATISFACTION_THRESHOLDSENTRY_DSNSENTRY_ENVIRONMENTTALKATIVE_BIKESURE_DEFAULT_QUEUE_CALLOUTTALKATIVE_FLUX_DEFAULT_QUEUE_CALLOUTTALKATIVE_VERSIONWEB_CONCURRENCY
2.1.19 - flux-epa
Links
| URI | Type | |
Environment Variables
Configuration variables for this application:
ADMIN_PATHAWS_ACCESS_KEY_IDAWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEYBROKER_URLCSRF_TRUSTED_ORIGINSENVIRONMENTEPA_DATA_SERVICE_TOKENEPA_DATA_SERVICE_URLFONTAWESOME_NPM_AUTH_TOKENIGATE_API_KEYPAPERTRAIL_API_TOKENPIP_EXTRA_INDEX_URLQAB_SERVICE_ENDPOINTQAB_SERVICE_TOKENQUOTE_LOG_SNS_TOPIC_ARNREDIS_MAX_CONNECTIONSREGSERVICE_PROXY_TOKENREGSERVICE_PROXY_URLSECRET_KEYSENTRY_DSNSOURCES_ENDPOINTSQS_QUEUE_NAME
2.1.19.1 - Incompletes
Overview
This page documents the handling of incomplete quotes in the flux-epa application.
What are Incompletes?
Incomplete quotes are quote journeys that users have started but not completed. These represent potential conversions and are valuable for follow-up and marketing purposes.
Incomplete Quote Data
Information captured for incomplete quotes typically includes:
- Quote uuid
- Contact information (email, phone)
- Vehicle/property details entered
- Quote stage reached
- Timestamp of last activity
Epa Data Logging
At the start of an EPA quote session (“first page”, typically containing the vehicle lookup) the session data object for that epa is sent to flux-epa-data . On subsequent postbacks, this telemetry data is passed to the data service. The quote uuid is used as the identifying key. Non-postback events may also be logged for things like link/button clicks, lookup states entered, etc.
This data is captured within flux-epa-data in epa logs as an EpaLog object. These are single post / event data captures with the quote uuid being the link in the individual quote journey.
When an EpaLog is created for the first time in a quote journey (i.e. the first time that quote uuid has been sent to the epa log) a QuoteLog is created. This is a singular object with the same quote uuid as the primary key. On subsequent EpaLog entries to that quote uuid, the QuoteLog object is updated to reflect the current (data) state. This means that many EpaLogs for that quote uuid will only ever have one QuoteLog.
This QuoteLog holds critical information about the current completion status of the quote.
Incomplete definition
Follow-up Process
[Document the process for following up on incomplete quotes]
Retention Policy
[Document how long incomplete quote data is retained]
Technical Implementation
[Document technical details about how incompletes are stored and processed]
2.1.20 - flux-epa-laravel-car
Links
| URI | Type | |
|---|---|---|
| https://flux-epa-laravel-car.herokuapp.com | heroku url | |
| https://quotes-car.adrianflux.co.uk | frontend |
Environment Variables
Configuration variables for this application:
ADDRESS_APIADRIANFLUX_CAR_GOOGLE_TAGMANAGERAPP_ENVAPP_KEYAPP_URLCALLBACK_URLCDN_URLEPA_APPLICATIONEPA_TYPEHelpLOG_CHANNELMETADATA_APIMETADATA_AUTH_TOKENPAPERTRAIL_API_TOKENQUOTE_APIREGABI_APIREGABI_AUTH_TOKENSENTRY_DSNSESSION_HTTP_ONLYSESSION_SECURE_COOKIE
2.1.21 - flux-epa-laravel-car-docker
Links
| URI | Type | |
|---|---|---|
| https://flux-epa-laravel-car-docker-c06df0942647.herokuapp.com | heroku url | |
| https://qc.adrianflux.co.uk | frontend |
Environment Variables
Configuration variables for this application:
ADDRESS_APIADRIANFLUX_CAR_GOOGLE_TAGMANAGERAPP_ENVAPP_KEYAPP_URLCALLBACK_URLCDN_URLEPA_APPLICATIONEPA_TYPEHelpLOG_CHANNELMETADATA_APIMETADATA_AUTH_TOKENPAPERTRAIL_API_TOKENQUOTE_APIREGABI_APIREGABI_AUTH_TOKENSENTRY_DSNSESSION_HTTP_ONLYSESSION_SECURE_COOKIE
2.1.22 - flux-epa-laravel-laid-bike
Links
| URI | Type | |
|---|---|---|
| https://flux-epa-laravel-laid-bike.herokuapp.com | heroku url | |
| https://quotes-laid.bikesure.co.uk | frontend |
Environment Variables
Configuration variables for this application:
ADDRESS_APIAPP_ENVAPP_KEYAPP_URLEPA_APPLICATIONEPA_TYPEHELPLOG_CHANNELMETADATA_APIMETADATA_AUTH_TOKENPAPERTRAIL_API_TOKENQUOTE_APIREGABI_APIREGABI_AUTH_TOKENSENTRY_LARAVEL_DSNSESSION_SECURE_COOKIE
2.1.23 - flux-epa-laravel-laid-bike-doc
Links
| URI | Type | |
|---|---|---|
| https://qd.bikesure.co.uk | frontend | |
| https://flux-epa-laravel-laid-bike-doc-745078615d70.herokuapp.com | heroku url |
Environment Variables
Configuration variables for this application:
ADDRESS_APIAPP_ENVAPP_KEYAPP_URLEPA_APPLICATIONEPA_TYPEHELPLOG_CHANNELMETADATA_APIMETADATA_AUTH_TOKENPAPERTRAIL_API_TOKENQUOTE_APIREGABI_APIREGABI_AUTH_TOKENSENTRY_LARAVEL_DSNSESSION_SECURE_COOKIE
2.1.24 - flux-epa-laravel-van
Links
| URI | Type | |
|---|---|---|
| https://flux-epa-laravel-van.herokuapp.com | heroku url | |
| https://quotes-van.adrianflux.co.uk | frontend |
Environment Variables
Configuration variables for this application:
ADDRESS_APIADRIANFLUX_VAN_GOOGLE_TAGMANAGERAPP_ENVAPP_KEYAPP_URLCALLBACK_URLCDN_URLEPA_APPLICATIONEPA_TYPEHELPLOG_CHANNELMETADATA_APIMETADATA_AUTH_TOKENPAPERTRAIL_API_TOKENQUOTE_APIREGABI_APIREGABI_AUTH_TOKENSESSION_SECURE_COOKIETHEME
2.1.25 - flux-epa-laravel-van-docker
Links
| URI | Type | |
|---|---|---|
| https://flux-epa-laravel-van-docker-827aa6265d32.herokuapp.com | heroku url | |
| https://qv.adrianflux.co.uk | frontend |
Environment Variables
Configuration variables for this application:
ADDRESS_APIADRIANFLUX_VAN_GOOGLE_TAGMANAGERAPP_ENVAPP_KEYAPP_URLCALLBACK_URLCDN_URLEPA_APPLICATIONEPA_TYPEHELPLOG_CHANNELMETADATA_APIMETADATA_AUTH_TOKENPAPERTRAIL_API_TOKENQUOTE_APIREGABI_APIREGABI_AUTH_TOKENSESSION_SECURE_COOKIETHEME
2.1.26 - flux-epa-learner
Links
| URI | Type | |
|---|---|---|
| https://quotes-learner.adrianflux.co.uk | frontend | |
| https://flux-epa-learner.herokuapp.com | heroku url |
Environment Variables
Configuration variables for this application:
ADDRESS_APIADRIANFLUX_LEARNER_GOOGLE_TAGMANAGERAPP_DEBUGAPP_ENVAPP_KEYAPP_URLCDN_URLEPA_APPLICATIONEPA_TYPEGOOGLE_ANALYTICSHANDLER_REDIRECTHELPLOG_CHANNELMETADATA_APIMETADATA_AUTH_TOKENPAPERTRAIL_API_TOKENQUOTE_APIREGABI_APIREGABI_AUTH_TOKENSENTRY_LARAVEL_DSNSESSION_SECURE_COOKIETHEME
2.1.27 - flux-epa-learner-docker
Links
| URI | Type | |
|---|---|---|
| https://ql.adrianflux.co.uk | frontend | |
| https://flux-epa-learner-docker-803877447f91.herokuapp.com | heroku url |
Environment Variables
Configuration variables for this application:
ADDRESS_APIADRIANFLUX_LEARNER_GOOGLE_TAGMANAGERAPP_DEBUGAPP_ENVAPP_KEYAPP_URLCDN_URLEPA_APPLICATIONEPA_TYPEGOOGLE_ANALYTICSHELPLOG_CHANNELMETADATA_APIMETADATA_AUTH_TOKENPAPERTRAIL_API_TOKENQUOTE_APIREGABI_APIREGABI_AUTH_TOKENSENTRY_LARAVEL_DSNSESSION_SECURE_COOKIETHEME
2.1.28 - flux-epa-prd
Links
| URI | Type | |
|---|---|---|
| https://quotes3.adrianflux.co.uk | frontend | |
| https://quotes3.sterling-insurance.co.uk | frontend | |
| https://flux-epa-prd-203eafc4b020.herokuapp.com | heroku url |
Environment Variables
Configuration variables for this application:
ADMIN_PATHAWS_ACCESS_KEY_IDAWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEYCACHE_KEY_PREFIXCF_MIDDLEWARE_CF_AUDCSRF_TRUSTED_ORIGINSENVIRONMENTFONTAWESOME_NPM_AUTH_TOKENFURY_AUTHIGATE_API_KEYQAB_SERVICE_ENDPOINTQAB_WEBHOOK_REPLY_TOPIC_ARNQUOTE_LOG_SNS_TOPIC_ARNREDIS_MAX_CONNECTIONSREGSERVICE_PROXY_TOKENREGSERVICE_PROXY_URLSECRET_KEYSENTRY_DSNSOURCES_ENDPOINT
2.1.29 - flux-epa-service-new
Links
| URI | Type | |
|---|---|---|
| https://flux-epa-service-new.herokuapp.com | heroku url | |
| https://brannigan.insurergate.co.uk | frontend |
Environment Variables
Configuration variables for this application:
ADMIN_PATHCF_AUDMETADATEN_API_LOGGINGPAPERTRAIL_API_TOKENPIP_EXTRA_INDEX_URLSENTRY_DSNSENTRY_ENVIRONMENT
2.1.30 - flux-geo-service
Links
| URI | Type | |
| —— |
| — |
| https://flux-geo-service.herokuapp.com |
| https://geoaddress-service.adrianflux.co.uk |
| https://geo-service.insurergate.co.uk |
| https://geo-service.adrianflux.co.uk |
Environment Variables
Configuration variables for this application:
ADDRESS_IO_APIADDRESS_IO_API_KEYADMIN_PATHCSRF_TRUSTED_ORIGINSENVIRONMENTPAPERTRAIL_API_TOKENPIP_EXTRA_INDEX_URLSECRET_KEYSENTRY_DSNSITE_ID
2.1.31 - flux-geodata-service
Links
| URI | Type | |
|---|---|---|
| https://flux-geodata-service-90a9459c132a.herokuapp.com | heroku url | |
| https://geo.insurergate.co.uk | frontend |
Environment Variables
Configuration variables for this application:
ADMIN_PATHCACHE_BACKENDCSRF_TRUSTED_ORIGINSFIELD_ENCRYPTION_KEYPIP_EXTRA_INDEX_URLSECRET_KEY
2.1.32 - flux-handler-service
Links
| URI | Type | |
Environment Variables
Configuration variables for this application:
ADMIN_PATHFURY_AUTHPAPERTRAIL_API_TOKENPIP_EXTRA_INDEX_URLSECURE_SSL_REDIRECTSENTRY_DSNSENTRY_ENVIRONMENTSOURCES_SERVICESOURCES_SERVICE_ENDPOINT
2.1.33 - flux-jaf
Links
| URI | Type | |
|---|---|---|
| https://apply2.adrianflux.co.uk | frontend | |
| https://apply.sterling-insurance.co.uk | frontend | |
| https://flux-jaf-7367d32e97e8.herokuapp.com | heroku url |
Environment Variables
Configuration variables for this application:
ADMIN_PATHCSRF_TRUSTED_ORIGINSENVIRONMENTEXCHANGE_API_KEYEXCHANGE_URLIGATE_API_KEYPAPERTRAIL_API_TOKENPIP_EXTRA_INDEX_URLSECRET_KEYSENTRY_DSNTURNSTILE_SECRETTURNSTILE_SITEKEY
2.1.34 - flux-jam
Links
| URI | Type | |
| —— |
| — |
| https://flux-jam-5d1d2152f6b1.herokuapp.com |
| https://jam.sterling-insurance.co.uk |
| https://jam.adrianflux.co.uk |
Environment Variables
Configuration variables for this application:
ADMIN_PATHCSRF_TRUSTED_ORIGINSDEFAULT_FROM_EMAILEMAIL_HOSTEMAIL_HOST_PASSWORDEMAIL_HOST_USEREMAIL_PORTEMAIL_USE_TLSFONTAWESOME_NPM_AUTH_TOKENPAPERTRAIL_API_TOKENPIP_EXTRA_INDEX_URLSECRET_KEYWEBHOOK_TOKEN
2.1.35 - flux-policy-documents-service
Links
| URI | Type | |
| —— |
| — |
| https://flux-policy-documents-service.herokuapp.com |
Environment Variables
Configuration variables for this application:
ADMIN_PATHAWS_ACCESS_KEY_IDAWS_S3_REGION_NAMEAWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEYAWS_STORAGE_BUCKET_NAMECLOUDFRONT_URLCORS_ORIGIN_WHITELISTDATABASE_URL_CUSTOMER_PORTALDEBUGFURY_AUTHSECRET_KEY
2.1.36 - flux-redirects-service
Links
| URI | Type | |
| —— |
| — |
| https://redirects-service.insurergate.co.uk |
| https://flux-redirects-service.herokuapp.com |
Environment Variables
Configuration variables for this application:
ADMIN_PATHCLOUDFLARE_ACCOUNTCLOUDFLARE_TOKENCSRF_TRUSTED_ORIGINSENVIRONMENTPAPERTRAIL_API_TOKENPIP_EXTRA_INDEX_URLSECRET_KEYSENTRY_DSNSITE_ID
2.1.37 - flux-regabi-data-live
Links
| URI | Type | |
|---|---|---|
| https://flux-regabi-data-live.herokuapp.com | heroku url | |
| https://zoidberg.insurergate.co.uk | frontend |
Environment Variables
Configuration variables for this application:
ADMIN_PATHAWS_ACCESS_KEY_IDAWS_S3_ENDPOINT_URLAWS_S3_HOSTAWS_S3_REGION_NAMEAWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEYAWS_STORAGE_BUCKET_NAMECARWEBUK_CLIENTDESCCARWEBUK_CLIENTREFCARWEBUK_KEY1CARWEBUK_PASSWORDCARWEBUK_URLCARWEBUK_USERNAMECARWEBUK_VERSIONCSRF_TRUSTED_ORIGINSENVIRONMENTFURY_AUTHPAPERTRAIL_API_TOKENPIP_EXTRA_INDEX_URLSENTRY_DSNWEB_CONCURRENCY
2.1.38 - flux-shorturl-app
Links
| URI | Type | |
|---|---|---|
| https://blog.hertsinsurance.com | frontend | |
| https://flux-shorturl-app.herokuapp.com | heroku url | |
| https://hicrides.com | frontend | |
| https://www.hicrides.com | frontend | |
| https://ster.lv | frontend | |
| https://flux.cx | frontend | |
| https://hicrides.co.uk | frontend | |
| https://docs.trinitylane.co.uk | frontend | |
| https://bikesu.re | frontend | |
| https://hic.cx | frontend | |
| https://shorturl.hut42.co.uk | frontend | |
| https://www.hicrides.co.uk | frontend |
Environment Variables
Configuration variables for this application:
ADMIN_PATHENVIRONMENTPAPERTRAIL_API_TOKENPIP_EXTRA_INDEX_URLREDIRECT_URL_POLICY_BOOKSECRET_KEYSENTRY_DSN
2.1.39 - flux-sitedata-service
Links
| URI | Type | |
Environment Variables
Configuration variables for this application:
ADMIN_PATHCACHE_BACKENDCACHE_LOCATIONCORS_ALLOWED_ORIGINS"https://www.sterling-insurance.co.uk","https://adrianflux.co.uk","https://www.adrianflux.co.uk","https://customers.adrianflux.co.uk","https://bikesure.co.uk","https://www.bikesure.co.uk","https://customers.bikesure.co.uk","https://hertsinsurance.com","https://www.hertsinsurance.com","https://customers.hertsinsurance.com","https://influx.co.uk","https://www.influx.co.uk","https://fluxdirect.co.uk","https://www.fluxdirect.co.uk","https://chartwellinsurance.co.uk","https://www.chartwellinsurance.co.uk","https://flux-sitedata-client.pages.dev","https://www.adrianflux.gg","https://www.adrianflux.je","https://www.trinitylane.co.uk"]CSRF_TRUSTED_ORIGINSDEFERRED_LOGENVIRONMENTFIELD_ENCRYPTION_KEYPAPERTRAIL_API_TOKENPIP_EXTRA_INDEX_URLSECRET_KEYSENTRY_DSN
2.1.40 - flux-sources-service
Links
| URI | Type | |
| —— |
| — |
| https://flux-sources-service.herokuapp.com |
| https://sources-service.insurergate.co.uk |
Environment Variables
Configuration variables for this application:
ADMIN_PATHAPIREQUESTLOG_RETENTION_HOURSPIP_EXTRA_INDEX_URLSECURE_SSL_REDIRECTSENTRY_ENVIRONMENT
2.1.41 - flux-worker-service
Links
| URI | Type | |
| —— |
| — |
| https://flux-app.af-test.co.uk |
| https://sterling-app.af-test.co.uk |
| https://flux-worker-service.herokuapp.com |
| https://worker-service.insurergate.co.uk |
Overview
This is a Django based app with no frontend. It’s primary purpose is to provide a backend interface (Django Admin) to provide metadata type variable values such as “FLUX_HOME_INSURANCE_SAVING_PERCENTAGE” to inject into Adrian Flux brand pages.
The db stored values (postgres) sync up with a Cloudflare KV store, which a Cloudflare Worker uses to do shortcode style replacements like [[ FLUX_HOME_INSURANCE_SAVING_PERCENTAGE ]] which do the actual replacement in usually, Wordpress content pages.
Environment Variables
Configuration variables for this application:
ADMIN_PATHCLOUDFLARE_ACCOUNT_IDCLOUDFLARE_API_KEYDEBUGFURY_AUTHSECRET_KEY
2.1.42 - hut-app-launcher
Links
| URI | Type | |
| —— |
| — |
| https://apps.insurergate.co.uk |
| https://hut-app-launcher.herokuapp.com |
Environment Variables
Configuration variables for this application:
ADMIN_PATHAWS_ACCESS_KEY_IDAWS_S3_REGION_NAMEAWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEYAWS_STORAGE_BUCKET_NAMECSRF_TRUSTED_ORIGINSPAPERTRAIL_API_TOKENPIP_EXTRA_INDEX_URLSECRET_KEYWPENGINE_PASSWORDWPENGINE_USER_ID
2.1.43 - proxy-bikesure
Links
| URI | Type | |
|---|---|---|
| https://dashboard.heroku.com/apps/proxy-bikesure | deployment | |
| https://proxy-bikesure.herokuapp.com | heroku url | should not be used or shared publically |
| https://www.bikesure.co.uk | frontend | Main public front end |
| https://adrianflux.co.uk | frontend | To be removed: nominally Cloudflare will redirect this to www |
Overview
This runs dyno(s) on Heroku that act as a reverse proxy for the various applications running under the www.bikesure.co.uk domain.
For example:
https://www.bikesure.co.uk > Main WP on WP Engine
https://www.bikesure.co.uk/blog > Bikesure blog on WP Engine
The proxys work with a proxy_pass to a subdomain, e.g blog.bikesure.co.uk. Cloudflare DNS for blog.bikesure.co.uk will point directly to the site on WP Engine. www.bikesure.co.uk will point to this proxy on Heroku and that will do the routing.
Known Issues
There are limitations regarding this kind of proxying. These can be summarised as:
- Client makes a request to a WP proxied site, i.e. https://www.bikesure.co.uk/blog
- WP Engine is slow to return the response, blocking the NGINX worker
- This worker block affects all requests hitting the
www.bikesure.co.ukdomain, including the main page and other critical pages such as callback. - This problem is exaggerated on cache-misses on WP Engine which happens a lot on requests such as https://www.bikesure.co.uk/blog?some-tracking-code=somerandomsttring as these will always cause a cache miss
- Can cause 2-5 second delays on main site, which blocks the workers again and a negative feedback cycle ensues
Environment Variables
Configuration variables for this application:
PAPERTRAIL_API_TOKEN
2.1.44 - proxy-flux
Links
| URI | Type | |
|---|---|---|
| https://dashboard.heroku.com/apps/proxy-flux | deployment | |
| https://proxy-flux.herokuapp.com | heroku url | should not be used or shared publically |
| https://www.adrianflux.co.uk | frontend | Main public front end |
| https://adrianflux.co.uk | frontend | To be removed: nominally Cloudflare will redirect this to www |
Overview
This runs dyno(s) on Heroku that act as a reverse proxy for the various applications running under the www.adrianflux.co.uk domain.
For example:
https://www.adrianflux.co.uk > Main WP on WP Engine
https://www.adrianflux.co.uk/blog > Fluxposure on WP Engine
https://www.adrianflux.co.uk/uk-us-car-part-names > UK v US on WP Engine
The proxys work with a proxy_pass to a subdomain, e.g blog.adrianflux.co.uk. Cloudflare DNS for blog.adrianflux.co.uk will point directly to the site on WP Engine. www.adrianflux.co.uk will point to this proxy on Heroku and that will do the routing.
Known Issues
There are limitations regarding this kind of proxying. These can be summarised as:
- Client makes a request to a WP proxied site, i.e. https://www.adrianflux.co.uk/blog
- WP Engine is slow to return the response, blocking the NGINX worker
- This worker block affects all requests hitting the
www.adrianflux.co.ukdomain, including the main page and other critical pages such as callback. - This problem is exaggerated on cache-misses on WP Engine which happens a lot on requests such as https://www.adrianflux.co.uk/blog?some-tracking-code=somerandomsttring as these will always cause a cache miss
- Can cause 2-5 second delays on main site, which blocks the workers again and a negative feedback cycle ensues
Environment Variables
Configuration variables for this application:
PAPERTRAIL_API_TOKEN
2.1.45 - proxy-sterling
Links
| URI | Type | |
|---|---|---|
| https://dashboard.heroku.com/apps/proxy-sterling | deployment | |
| https://proxy-sterling.herokuapp.com | heroku url | should not be used or shared publically |
| https://www.sterling-insurance.co.uk | frontend | Main public front end |
| https://adrianflux.co.uk | frontend | To be removed: nominally Cloudflare will redirect this to www |
Overview
This runs dyno(s) on Heroku that act as a reverse proxy for the various applications running under the www.sterling-insurance.co.uk domain.
For example:
https://www.sterling-insurance.co.uk > Main WP on WP Engine
https://www.sterling-insurance.co.uk/blog > Sterling blog on WP Engine
The proxys work with a proxy_pass to a subdomain, e.g blog.sterling.co.uk. Cloudflare DNS for blog.sterling.co.uk will point directly to the site on WP Engine. www.sterling-insurance.co.uk will point to this proxy on Heroku and that will do the routing.
Known Issues
There are limitations regarding this kind of proxying. These can be summarised as:
- Client makes a request to a WP proxied site, i.e. https://www.sterling-insurance.co.uk/blog
- WP Engine is slow to return the response, blocking the NGINX worker
- This worker block affects all requests hitting the
www.sterling-insurance.co.ukdomain, including the main page and other critical pages such as callback. - This problem is exaggerated on cache-misses on WP Engine which happens a lot on requests such as https://www.sterling-insurance.co.uk/blog?some-tracking-code=somerandomsttring as these will always cause a cache miss
- Can cause 2-5 second delays on main site, which blocks the workers again and a negative feedback cycle ensues
Environment Variables
Configuration variables for this application:
PAPERTRAIL_API_TOKEN
2.1.46 - sterling-epa-laravel-car
Links
| URI | Type | |
|---|---|---|
| https://quotes.sterling-insurance.co.uk | frontend | |
| https://sterling-epa-laravel-car.herokuapp.com | heroku url |
Environment Variables
Configuration variables for this application:
ADDRESS_APIAPP_ENVAPP_KEYAPP_URLCDN_URLEPA_APPLICATIONEPA_TYPEHANDLER_DEPARTMENTHANDLER_REDIRECTHELPLOG_CHANNELMETADATA_APIMETADATA_AUTH_TOKENMETADATA_SOURCEPAPERTRAIL_API_TOKENQUOTE_APIREGABI_APIREGABI_AUTH_TOKENSESSION_SECURE_COOKIESTERLING_GOOGLE_TAGMANAGERTHEME
2.1.47 - sterling-epa-laravel-car-docke
Links
| URI | Type | |
|---|---|---|
| https://qc.sterling-insurance.co.uk | frontend | |
| https://sterling-epa-laravel-car-docke-8090fe679347.herokuapp.com | heroku url |
Environment Variables
Configuration variables for this application:
ADDRESS_APIAPP_ENVAPP_KEYAPP_URLCDN_URLEPA_APPLICATIONEPA_TYPEHANDLER_DEPARTMENTHELPLOG_CHANNELMETADATA_APIMETADATA_AUTH_TOKENMETADATA_SOURCEPAPERTRAIL_API_TOKENQUOTE_APIREGABI_APIREGABI_AUTH_TOKENSESSION_SECURE_COOKIESTERLING_GOOGLE_TAGMANAGERTHEME
2.1.48 - sterling-epa-laravel-van
Links
| URI | Type | |
|---|---|---|
| https://sterling-epa-laravel-van.herokuapp.com | heroku url | |
| https://quotes-van.sterling-insurance.co.uk | frontend |
Environment Variables
Configuration variables for this application:
ADDRESS_APIAPP_ENVAPP_KEYAPP_URLCDN_URLEPA_APPLICATIONEPA_TYPEHANDLER_DEPARTMENTHANDLER_REDIRECTHELPLOG_CHANNELMETADATA_APIMETADATA_AUTH_TOKENMETADATA_SOURCEPAPERTRAIL_API_TOKENQUOTE_APIREGABI_APIREGABI_AUTH_TOKENSESSION_SECURE_COOKIESTERLING_VAN_GOOGLE_TAGMANAGERTHEME
2.1.49 - sterling-epa-laravel-van-docke
Links
| URI | Type | |
|---|---|---|
| https://qv.sterling-insurance.co.uk | frontend | |
| https://sterling-epa-laravel-van-docke-f02a122fa86e.herokuapp.com | heroku url |
Environment Variables
Configuration variables for this application:
ADDRESS_APIAPP_ENVAPP_KEYAPP_URLCDN_URLEPA_APPLICATIONEPA_TYPEHANDLER_DEPARTMENTHELPLOG_CHANNELMETADATA_APIMETADATA_AUTH_TOKENMETADATA_SOURCEPAPERTRAIL_API_TOKENQUOTE_APIREGABI_APIREGABI_AUTH_TOKENSESSION_SECURE_COOKIESTERLING_VAN_GOOGLE_TAGMANAGERTHEME
2.2 - WordPress
2.2.1 - aahadleightran
Overview
WordPress site aahadleightran hosted on WP Engine.
Links
| URL | Type |
|---|---|
| https://www.hadleighbreakdown.co.uk | Primary Domain |
| https://aahadleightran.wpengine.com | WP Engine URL |
Site Information
Site Name: HB | Hadliegh Breakdown
Install Name: aahadleightran
WordPress Version: 6.8.3
Environment: production
PHP Version: 8.2
Status: active
Multisite: No
Created: 2023-11-09
Tags
- Hadleigh Breakdown
Plugins & Themes
Plugin and theme information is not available via WP Engine API. This section can be manually updated with active plugins and theme details.
WP Engine Details
- Install ID:
14cf3790-23ce-40f3-bd8c-1f9bbc2fe9b1 - Site ID:
2ee3a06f-6f92-47a3-9721-86ad7453f927 - Account ID:
1df5f442-982f-4ded-b8a8-ff64bf4f5c6b
2.2.2 - adrianflux1
Overview
WordPress site adrianflux1 hosted on WP Engine.
Links
| URL | Type |
|---|---|
| https://wpe.adrianflux.co.uk | Primary Domain |
| https://adrianflux1.wpengine.com | WP Engine URL |
Site Information
Site Name: Adrian Flux
Install Name: adrianflux1
WordPress Version: 6.8.3
Environment: production
PHP Version: 8.4
Status: active
Multisite: No
Created: 2025-02-28
Tags
- Adrian Flux
- Instant Callback
- Scheduled Callback
Plugins & Themes
Plugin and theme information is not available via WP Engine API. This section can be manually updated with active plugins and theme details.
WP Engine Details
- Install ID:
d9333181-d1f8-47b9-ad6a-6e3f46ceacff - Site ID:
7914e381-fff9-40a7-ad98-8dbe545bd9fb - Account ID:
d7fb8db5-7276-4093-b390-bab079dada24
2.2.3 - adrianfluxcomp
Overview
WordPress site adrianfluxcomp hosted on WP Engine.
Links
| URL | Type |
|---|---|
| https://competitions.adrianflux.co.uk | Primary Domain |
| https://adrianfluxcomp.wpengine.com | WP Engine URL |
Site Information
Site Name: AF | Competitions
Install Name: adrianfluxcomp
WordPress Version: 6.8.3
Environment: production
PHP Version: 8.4
Status: active
Multisite: No
Created: 2022-04-30
Tags
- Adrian Flux
- WP Forms
Plugins & Themes
Plugin and theme information is not available via WP Engine API. This section can be manually updated with active plugins and theme details.
WP Engine Details
- Install ID:
2bb49253-7dd3-457f-b65b-c7425443558d - Site ID:
1bd04bae-6184-4eb0-bb86-07ef825203eb - Account ID:
67f3426d-ea0c-4d81-a2c6-cbdf3fd91900
2.2.4 - afcustomers
Overview
WordPress site afcustomers hosted on WP Engine.
Links
| URL | Type |
|---|---|
| https://customers.adrianflux.co.uk | Primary Domain |
| https://afcustomers.wpengine.com | WP Engine URL |
Site Information
Site Name: AF | Adrian Flux Customers
Install Name: afcustomers
WordPress Version: 6.9
Environment: production
PHP Version: 8.4
Status: active
Multisite: No
Created: 2023-11-10
Tags
- Customer Sites
Plugins & Themes
Plugin and theme information is not available via WP Engine API. This section can be manually updated with active plugins and theme details.
WP Engine Details
- Install ID:
83c67f66-1cc0-4a8b-a216-8509a39a2272 - Site ID:
47ff9070-663d-497c-bf4b-32d29b018a4f - Account ID:
1df5f442-982f-4ded-b8a8-ff64bf4f5c6b
2.2.5 - afdubtales
Overview
WordPress site afdubtales hosted on WP Engine.
Links
| URL | Type |
|---|---|
| https://dubtales.adrianflux.co.uk | Primary Domain |
| https://afdubtales.wpengine.com | WP Engine URL |
Site Information
Site Name: AF | Dubtales
Install Name: afdubtales
WordPress Version: 6.8.3
Environment: production
PHP Version: 8.4
Status: active
Multisite: No
Created: 2023-07-25
Tags
- Adrian Flux
- Scheduled Callback
Plugins & Themes
Plugin and theme information is not available via WP Engine API. This section can be manually updated with active plugins and theme details.
WP Engine Details
- Install ID:
be22999d-3a5d-471b-88fd-e250dea57f5d - Site ID:
dbb0ac9f-addc-4727-b1e9-ff5247a9a188 - Account ID:
67f3426d-ea0c-4d81-a2c6-cbdf3fd91900
2.2.6 - afguernsey
Overview
WordPress site afguernsey hosted on WP Engine.
Links
| URL | Type |
|---|---|
| https://www.adrianflux.gg | Primary Domain |
| https://afguernsey.wpengine.com | WP Engine URL |
Site Information
Site Name: AF | Islands (Guernsey)
Install Name: afguernsey
WordPress Version: 6.8.3
Environment: production
PHP Version: 8.2
Status: active
Multisite: No
Created: 2023-11-10
Tags
- Adrian Flux
- Scheduled Callback
Plugins & Themes
Plugin and theme information is not available via WP Engine API. This section can be manually updated with active plugins and theme details.
WP Engine Details
- Install ID:
80de8ec6-be87-4e7b-be40-d29aa7cbebde - Site ID:
18381815-b746-44ad-aa94-ed2e9442d41c - Account ID:
1df5f442-982f-4ded-b8a8-ff64bf4f5c6b
2.2.7 - afjersey
Overview
WordPress site afjersey hosted on WP Engine.
Links
| URL | Type |
|---|---|
| https://www.adrianflux.je | Primary Domain |
| https://afjersey.wpengine.com | WP Engine URL |
Site Information
Site Name: AF | Islands (Jersey)
Install Name: afjersey
WordPress Version: 6.8.3
Environment: production
PHP Version: 8.2
Status: active
Multisite: No
Created: 2023-11-10
Tags
- Adrian Flux
- Scheduled Callback
Plugins & Themes
Plugin and theme information is not available via WP Engine API. This section can be manually updated with active plugins and theme details.
WP Engine Details
- Install ID:
0c0a06d4-3f6f-4c12-931a-7839776f8386 - Site ID:
a5721410-1811-4e55-9441-057ea807859c - Account ID:
1df5f442-982f-4ded-b8a8-ff64bf4f5c6b
2.2.8 - aflearnerdrive
Overview
WordPress site aflearnerdrive hosted on WP Engine.
Links
| URL | Type |
|---|---|
| https://learner-drivers.adrianflux.co.uk | Primary Domain |
| https://aflearnerdrive.wpengine.com | WP Engine URL |
Site Information
Site Name: AF | Learner Driver Hub
Install Name: aflearnerdrive
WordPress Version: 6.8.3
Environment: production
PHP Version: 8.4
Status: active
Multisite: No
Created: 2023-07-15
Tags
- Adrian Flux
Plugins & Themes
Plugin and theme information is not available via WP Engine API. This section can be manually updated with active plugins and theme details.
WP Engine Details
- Install ID:
8b43afe6-abf0-474f-b8b4-717f7d647e95 - Site ID:
1901cbc0-5c79-48a7-ac6b-42d20df1fc22 - Account ID:
67f3426d-ea0c-4d81-a2c6-cbdf3fd91900
2.2.9 - afmotorsport
Overview
WordPress site afmotorsport hosted on WP Engine.
Links
| URL | Type |
|---|---|
| https://motorsport.adrianflux.co.uk | Primary Domain |
| https://afmotorsport.wpengine.com | WP Engine URL |
Site Information
Site Name: AF | Motorsport
Install Name: afmotorsport
WordPress Version: 6.8.3
Environment: production
PHP Version: 8.4
Status: active
Multisite: No
Created: 2022-05-10
Tags
- Adrian Flux
- Scheduled Callback
Plugins & Themes
Plugin and theme information is not available via WP Engine API. This section can be manually updated with active plugins and theme details.
WP Engine Details
- Install ID:
d25786f4-e627-4973-91ec-53bec9918774 - Site ID:
612812f0-9e7d-484f-910c-29bfbe3e6b5b - Account ID:
67f3426d-ea0c-4d81-a2c6-cbdf3fd91900
2.2.10 - afownersclubs
Overview
WordPress site afownersclubs hosted on WP Engine.
Links
| URL | Type |
|---|---|
| https://oci.adrianflux.co.uk | Primary Domain |
| https://afownersclubs.wpengine.com | WP Engine URL |
Site Information
Site Name: AF | Owners Clubs
Install Name: afownersclubs
WordPress Version: 6.8.3
Environment: production
PHP Version: 8.4
Status: active
Multisite: No
Created: 2024-02-06
Tags
- Adrian Flux
- Instant Callback
Plugins & Themes
Plugin and theme information is not available via WP Engine API. This section can be manually updated with active plugins and theme details.
WP Engine Details
- Install ID:
e1cf0d35-ac14-48fa-bb5e-c2378d74f851 - Site ID:
5933cffe-c848-444a-9af6-0a42cef5e8a2 - Account ID:
1df5f442-982f-4ded-b8a8-ff64bf4f5c6b
2.2.11 - afreferral
Overview
WordPress site afreferral hosted on WP Engine.
Links
| URL | Type |
|---|---|
| https://referral-scheme.adrianflux.co.uk | Primary Domain |
| https://afreferral.wpengine.com | WP Engine URL |
Site Information
Site Name: AF | Referral Scheme
Install Name: afreferral
WordPress Version: 6.8.3
Environment: production
PHP Version: 8.4
Status: active
Multisite: No
Created: 2023-11-10
Tags
- Adrian Flux
Plugins & Themes
Plugin and theme information is not available via WP Engine API. This section can be manually updated with active plugins and theme details.
WP Engine Details
- Install ID:
59d89e7a-2487-4914-9faa-c79eae3fae2d - Site ID:
7c0fd93c-56ee-4b2e-bd15-9c7b415a6370 - Account ID:
1df5f442-982f-4ded-b8a8-ff64bf4f5c6b
2.2.12 - afsupercars
Overview
WordPress site afsupercars hosted on WP Engine.
Links
| URL | Type |
|---|---|
| https://supercars.adrianflux.co.uk | Primary Domain |
| https://afsupercars.wpengine.com | WP Engine URL |
Site Information
Site Name: AF | Supercars
Install Name: afsupercars
WordPress Version: 6.8.3
Environment: production
PHP Version: 8.4
Status: active
Multisite: No
Created: 2022-05-09
Tags
- Adrian Flux
Plugins & Themes
Plugin and theme information is not available via WP Engine API. This section can be manually updated with active plugins and theme details.
WP Engine Details
- Install ID:
c8729817-8220-40e6-86f2-bd2250b837d7 - Site ID:
a2f54b49-f137-47db-9f4a-502a20fd4660 - Account ID:
67f3426d-ea0c-4d81-a2c6-cbdf3fd91900
2.2.13 - afvictorianhom
Overview
WordPress site afvictorianhom hosted on WP Engine.
Links
| URL | Type |
|---|---|
| https://victorian-homes.adrianflux.co.uk | Primary Domain |
| https://afvictorianhom.wpengine.com | WP Engine URL |
Site Information
Site Name: AF | Victorian Homes
Install Name: afvictorianhom
WordPress Version: 6.8.3
Environment: production
PHP Version: 8.4
Status: active
Multisite: No
Created: 2023-08-16
Tags
- Adrian Flux
- Scheduled Callback
Plugins & Themes
Plugin and theme information is not available via WP Engine API. This section can be manually updated with active plugins and theme details.
WP Engine Details
- Install ID:
59b0a8f6-9a22-4fec-82f8-bc63b45c21e6 - Site ID:
ad4c4df4-a6a9-4a93-ad1c-b71a6e1403d8 - Account ID:
67f3426d-ea0c-4d81-a2c6-cbdf3fd91900
2.2.14 - bangerrally
Overview
WordPress site bangerrally hosted on WP Engine.
Links
| URL | Type |
|---|---|
| https://banger-rally-guide.sterling-insurance.co.uk | Primary Domain |
| https://bangerrally.wpengine.com | WP Engine URL |
Site Information
Site Name: ST | Sterling Insurance Banger Rally
Install Name: bangerrally
WordPress Version: 6.8.3
Environment: production
PHP Version: 8.2
Status: active
Multisite: No
Created: 2024-02-06
Tags
- Sterling Insurance
- Scheduled Callback
Plugins & Themes
Plugin and theme information is not available via WP Engine API. This section can be manually updated with active plugins and theme details.
WP Engine Details
- Install ID:
f88a87df-f193-46ca-9f19-9062dda99bd9 - Site ID:
6eeec0ed-097a-413e-9bfd-c5c82efc6cd2 - Account ID:
67f3426d-ea0c-4d81-a2c6-cbdf3fd91900
2.2.15 - bikesurecomps
Overview
WordPress site bikesurecomps hosted on WP Engine.
Links
| URL | Type |
|---|---|
| https://competitions.bikesure.co.uk | Primary Domain |
| https://bikesurecomps.wpengine.com | WP Engine URL |
Site Information
Site Name: BKS | Competitions
Install Name: bikesurecomps
WordPress Version: 6.8.3
Environment: production
PHP Version: 8.2
Status: active
Multisite: No
Created: 2022-04-30
Tags
- Bikesure
Plugins & Themes
Plugin and theme information is not available via WP Engine API. This section can be manually updated with active plugins and theme details.
WP Engine Details
- Install ID:
d64d1a9e-b49e-45ee-bbd5-72833784a366 - Site ID:
0062bbd4-8520-482b-9b16-5b300356ae80 - Account ID:
67f3426d-ea0c-4d81-a2c6-cbdf3fd91900
2.2.16 - bksbikesure
Overview
WordPress site bksbikesure hosted on WP Engine.
Links
| URL | Type |
|---|---|
| https://bikesure.bikesure.co.uk | Primary Domain |
| https://bksbikesure.wpengine.com | WP Engine URL |
Site Information
Site Name: BKS | Bikesure
Install Name: bksbikesure
WordPress Version: 6.8.3
Environment: production
PHP Version: 8.4
Status: active
Multisite: No
Created: 2023-11-11
Tags
- Bikesure
- Instant Callback
- Scheduled Callback
Plugins & Themes
Plugin and theme information is not available via WP Engine API. This section can be manually updated with active plugins and theme details.
WP Engine Details
- Install ID:
c9c0313e-d694-4e27-a802-a4491fe6a540 - Site ID:
8d3d1ab2-3f1c-45f0-a948-350f857101bf - Account ID:
1df5f442-982f-4ded-b8a8-ff64bf4f5c6b
2.2.17 - bksblog
Overview
WordPress site bksblog hosted on WP Engine.
Links
| URL | Type |
|---|---|
| https://bikesureblog.bikesure.co.uk | Primary Domain |
| https://bksblog.wpengine.com | WP Engine URL |
Site Information
Site Name: BKS | Blog
Install Name: bksblog
WordPress Version: 6.8.3
Environment: production
PHP Version: 8.2
Status: active
Multisite: No
Created: 2023-04-26
Tags
- Bikesure
Plugins & Themes
Plugin and theme information is not available via WP Engine API. This section can be manually updated with active plugins and theme details.
WP Engine Details
- Install ID:
5716a101-0360-4840-af16-88dd15394a1c - Site ID:
13cf8867-3393-4863-a595-801c62e40bd1 - Account ID:
67f3426d-ea0c-4d81-a2c6-cbdf3fd91900
2.2.18 - bkscustomers
Overview
WordPress site bkscustomers hosted on WP Engine.
Links
| URL | Type |
|---|---|
| https://customers.bikesure.co.uk | Primary Domain |
| https://bkscustomers.wpengine.com | WP Engine URL |
Site Information
Site Name: BKS | Bikesure Customers
Install Name: bkscustomers
WordPress Version: 6.9
Environment: production
PHP Version: 8.2
Status: active
Multisite: No
Created: 2023-11-11
Tags
- Bikesure
Plugins & Themes
Plugin and theme information is not available via WP Engine API. This section can be manually updated with active plugins and theme details.
WP Engine Details
- Install ID:
93f17f25-edd4-4f77-9a92-c70f7448afb7 - Site ID:
d346aedb-7c74-4281-bd92-49132d5bf0e8 - Account ID:
1df5f442-982f-4ded-b8a8-ff64bf4f5c6b
2.2.19 - bksdigipr
Overview
WordPress site bksdigipr hosted on WP Engine.
Links
| URL | Type |
|---|---|
| https://digital.bikesure.co.uk | Primary Domain |
| https://bksdigipr.wpengine.com | WP Engine URL |
Site Information
Site Name: BKS | Digi PR
Install Name: bksdigipr
WordPress Version: 6.8.3
Environment: production
PHP Version: 8.2
Status: active
Multisite: No
Created: 2025-05-06
Tags
- Bikesure
Plugins & Themes
Plugin and theme information is not available via WP Engine API. This section can be manually updated with active plugins and theme details.
WP Engine Details
- Install ID:
599fcd60-c7f9-43b0-9742-9fde7be61001 - Site ID:
6444423e-ee23-4978-8a13-bcee2f83438f - Account ID:
67f3426d-ea0c-4d81-a2c6-cbdf3fd91900
2.2.20 - bksextinction
Overview
WordPress site bksextinction hosted on WP Engine.
Links
| URL | Type |
|---|---|
| https://motorbike-extinction.bikesure.co.uk | Primary Domain |
| https://bksextinction.wpengine.com | WP Engine URL |
Site Information
Site Name: BKS | Extinction
Install Name: bksextinction
WordPress Version: 6.8.3
Environment: production
PHP Version: 8.2
Status: active
Multisite: No
Created: 2024-10-15
Tags
- Bikesure
Plugins & Themes
Plugin and theme information is not available via WP Engine API. This section can be manually updated with active plugins and theme details.
WP Engine Details
- Install ID:
78dbe646-d694-4510-9571-d3b8ca027233 - Site ID:
f9a03ad5-06a9-46db-ae31-0122b22274ca - Account ID:
67f3426d-ea0c-4d81-a2c6-cbdf3fd91900
2.2.21 - bksforeverbike
Overview
WordPress site bksforeverbike hosted on WP Engine.
Links
| URL | Type |
|---|---|
| https://forever-bikes.bikesure.co.uk | Primary Domain |
| https://bksforeverbike.wpengine.com | WP Engine URL |
Site Information
Site Name: BKS | Forever Bikes
Install Name: bksforeverbike
WordPress Version: 6.8.3
Environment: production
PHP Version: 8.2
Status: active
Multisite: No
Created: 2023-04-25
Tags
- Bikesure
Plugins & Themes
Plugin and theme information is not available via WP Engine API. This section can be manually updated with active plugins and theme details.
WP Engine Details
- Install ID:
5a1e9165-2c82-4ea7-90b8-dd81cd37c199 - Site ID:
3c4d6256-7989-4f0b-883a-49e42eeb49df - Account ID:
67f3426d-ea0c-4d81-a2c6-cbdf3fd91900
2.2.22 - bkskawasakiins
Overview
WordPress site bkskawasakiins hosted on WP Engine.
Links
| URL | Type |
|---|---|
| https://callback.kawasaki-insurance.com | Primary Domain |
| https://bkskawasakiins.wpengine.com | WP Engine URL |
Site Information
Site Name: BKS | Kawasaki Insurance
Install Name: bkskawasakiins
WordPress Version: 6.8.3
Environment: production
PHP Version: 8.4
Status: active
Multisite: No
Created: 2025-05-15
Plugins & Themes
Plugin and theme information is not available via WP Engine API. This section can be manually updated with active plugins and theme details.
WP Engine Details
- Install ID:
fa9f06ae-d4e9-4cd3-8134-e69fad39f3fc - Site ID:
a72d8730-8a59-4894-8c58-f8dae4daa833 - Account ID:
1df5f442-982f-4ded-b8a8-ff64bf4f5c6b
2.2.23 - bksmanufacture
Overview
WordPress site bksmanufacture hosted on WP Engine.
Links
| URL | Type |
|---|---|
| https://callback.ducati-insurance.com | Primary Domain |
| https://bksmanufacture.wpengine.com | WP Engine URL |
Site Information
Site Name: BKS | Ducati Insurance
Install Name: bksmanufacture
WordPress Version: 6.8.3
Environment: production
PHP Version: 8.2
Status: active
Multisite: No
Created: 2024-10-28
Tags
- Bikesure
- Scheduled Callback
Plugins & Themes
Plugin and theme information is not available via WP Engine API. This section can be manually updated with active plugins and theme details.
WP Engine Details
- Install ID:
3154f071-fa96-4895-b7ca-6d21ea00b0e6 - Site ID:
b863a504-9f73-4a76-a469-3f1c4d892201 - Account ID:
1df5f442-982f-4ded-b8a8-ff64bf4f5c6b
2.2.24 - bksmotorcycles
Overview
WordPress site bksmotorcycles hosted on WP Engine.
Links
| URL | Type |
|---|---|
| https://motorcycle-stunt-riders.bikesure.co.uk | Primary Domain |
| https://bksmotorcycles.wpengine.com | WP Engine URL |
Site Information
Site Name: BKS | Motorcycle Stunt Riders
Install Name: bksmotorcycles
WordPress Version: 6.8.3
Environment: production
PHP Version: 8.2
Status: active
Multisite: No
Created: 2023-04-26
Tags
- Bikesure
Plugins & Themes
Plugin and theme information is not available via WP Engine API. This section can be manually updated with active plugins and theme details.
WP Engine Details
- Install ID:
3b8f7a5a-5f33-4b4b-ada4-d806ea9d6043 - Site ID:
bf24b0f3-1b6c-4948-9416-93320f7253c0 - Account ID:
67f3426d-ea0c-4d81-a2c6-cbdf3fd91900
2.2.25 - bksquadbikeloc
Overview
WordPress site bksquadbikeloc hosted on WP Engine.
Links
| URL | Type |
|---|---|
| https://best-quad-bike-locations-world.bikesure.co.uk | Primary Domain |
| https://bksquadbikeloc.wpengine.com | WP Engine URL |
Site Information
Site Name: BKS | Quad Bike Locations
Install Name: bksquadbikeloc
WordPress Version: 6.8.3
Environment: production
PHP Version: 8.2
Status: active
Multisite: No
Created: 2023-10-30
Tags
- Bikesure
Plugins & Themes
Plugin and theme information is not available via WP Engine API. This section can be manually updated with active plugins and theme details.
WP Engine Details
- Install ID:
51a79ab7-b4b0-430c-a497-d5c8110c015b - Site ID:
b47405bb-b872-483c-bb62-226095f89558 - Account ID:
67f3426d-ea0c-4d81-a2c6-cbdf3fd91900
2.2.26 - bksreferral
Overview
WordPress site bksreferral hosted on WP Engine.
Links
| URL | Type |
|---|---|
| https://referral-scheme.bikesure.co.uk | Primary Domain |
| https://bksreferral.wpengine.com | WP Engine URL |
Site Information
Site Name: BKS | Referral Scheme
Install Name: bksreferral
WordPress Version: 6.7.4
Environment: production
PHP Version: 8.2
Status: active
Multisite: No
Created: 2023-11-10
Plugins & Themes
Plugin and theme information is not available via WP Engine API. This section can be manually updated with active plugins and theme details.
WP Engine Details
- Install ID:
a818cabc-247a-47f1-8b95-900c95c5c070 - Site ID:
26c15f82-dc02-4304-8566-a3470ce4137b - Account ID:
1df5f442-982f-4ded-b8a8-ff64bf4f5c6b
2.2.27 - bkssuzukiinsur
Overview
WordPress site bkssuzukiinsur hosted on WP Engine.
Links
| URL | Type |
|---|---|
| https://callback.suzukibikeinsurance.com | Primary Domain |
| https://bkssuzukiinsur.wpengine.com | WP Engine URL |
Site Information
Site Name: BKS | Suzuki Insurance
Install Name: bkssuzukiinsur
WordPress Version: 6.8.3
Environment: production
PHP Version: 8.2
Status: active
Multisite: No
Created: 2025-05-15
Plugins & Themes
Plugin and theme information is not available via WP Engine API. This section can be manually updated with active plugins and theme details.
WP Engine Details
- Install ID:
f9debae0-c248-4b3f-acee-d7e4114991e2 - Site ID:
12e7cccf-b516-4307-934e-52e18c56e6da - Account ID:
1df5f442-982f-4ded-b8a8-ff64bf4f5c6b
2.2.28 - bkstriumphinsu
Overview
WordPress site bkstriumphinsu hosted on WP Engine.
Links
| URL | Type |
|---|---|
| https://callback.triumph-bikeinsurance.co.uk | Primary Domain |
| https://bkstriumphinsu.wpengine.com | WP Engine URL |
Site Information
Site Name: BKS | Triumph Insurance
Install Name: bkstriumphinsu
WordPress Version: 6.8.3
Environment: production
PHP Version: 8.4
Status: active
Multisite: No
Created: 2025-05-15
Plugins & Themes
Plugin and theme information is not available via WP Engine API. This section can be manually updated with active plugins and theme details.
WP Engine Details
- Install ID:
6edd4bed-2f66-4699-950b-6b8897a93230 - Site ID:
0d5be307-f89c-4269-92b0-0c53c65fccea - Account ID:
1df5f442-982f-4ded-b8a8-ff64bf4f5c6b
2.2.29 - bksultimatebik
Overview
WordPress site bksultimatebik hosted on WP Engine.
Links
| URL | Type |
|---|---|
| https://ultimate-bike-collection.bikesure.co.uk | Primary Domain |
| https://bksultimatebik.wpengine.com | WP Engine URL |
Site Information
Site Name: BKS | Ultimate Bike Collection
Install Name: bksultimatebik
WordPress Version: 6.8.3
Environment: production
PHP Version: 8.4
Status: active
Multisite: No
Created: 2024-03-21
Tags
- Bikesure
Plugins & Themes
Plugin and theme information is not available via WP Engine API. This section can be manually updated with active plugins and theme details.
WP Engine Details
- Install ID:
ab4ec812-f653-4f3d-8f21-bf21dcf1b9d1 - Site ID:
efb673b8-30fc-436c-85c8-d34d6524fff7 - Account ID:
67f3426d-ea0c-4d81-a2c6-cbdf3fd91900
2.2.30 - carextinction
Overview
WordPress site carextinction hosted on WP Engine.
Links
| URL | Type |
|---|---|
| https://car-extinction.adrianflux.co.uk | Primary Domain |
| https://carextinction.wpengine.com | WP Engine URL |
Site Information
Site Name: AF | Extinction
Install Name: carextinction
WordPress Version: 6.8.3
Environment: production
PHP Version: 8.4
Status: active
Multisite: No
Created: 2024-07-12
Tags
- Adrian Flux
Plugins & Themes
Plugin and theme information is not available via WP Engine API. This section can be manually updated with active plugins and theme details.
WP Engine Details
- Install ID:
3a4773fd-b6e9-4589-aac4-8343753b6004 - Site ID:
f3eb883c-8d0e-4047-9b08-dfd5df21f419 - Account ID:
67f3426d-ea0c-4d81-a2c6-cbdf3fd91900
2.2.31 - cultclassics
Overview
WordPress site cultclassics hosted on WP Engine.
Links
| URL | Type |
|---|---|
| https://cult-classics.adrianflux.co.uk | Primary Domain |
| https://cultclassics.wpengine.com | WP Engine URL |
Site Information
Site Name: AF | Cult Classics
Install Name: cultclassics
WordPress Version: 6.8.3
Environment: production
PHP Version: 8.4
Status: active
Multisite: No
Created: 2023-05-25
Tags
- Adrian Flux
Plugins & Themes
Plugin and theme information is not available via WP Engine API. This section can be manually updated with active plugins and theme details.
WP Engine Details
- Install ID:
07f72c95-b228-4eb6-b932-be092a3b3c0e - Site ID:
cbf001a0-8586-460a-be35-b48bb103c5c6 - Account ID:
67f3426d-ea0c-4d81-a2c6-cbdf3fd91900
2.2.32 - datacapturedoc
Overview
WordPress site datacapturedoc hosted on WP Engine.
Links
| URL | Type |
|---|---|
| https://form-docs.af-dev.co.uk | Primary Domain |
| https://datacapturedoc.wpengine.com | WP Engine URL |
Site Information
Site Name: ZZZ | Forms Documentation
Install Name: datacapturedoc
WordPress Version: 6.8.3
Environment: production
PHP Version: 8.2
Status: active
Multisite: No
Created: 2025-02-21
Plugins & Themes
Plugin and theme information is not available via WP Engine API. This section can be manually updated with active plugins and theme details.
WP Engine Details
- Install ID:
2cd37d36-aa46-4bc7-aa07-95a8c4dc5142 - Site ID:
894de0ae-2740-4a2d-9cda-ec6a3a859649 - Account ID:
1df5f442-982f-4ded-b8a8-ff64bf4f5c6b
2.2.33 - driverlesscars
Overview
WordPress site driverlesscars hosted on WP Engine.
Links
| URL | Type |
|---|---|
| https://driverlesscars.adrianflux.co.uk | Primary Domain |
| https://driverlesscars.wpengine.com | WP Engine URL |
Site Information
Site Name: AF | Driverless Cars
Install Name: driverlesscars
WordPress Version: 6.8.3
Environment: production
PHP Version: 8.4
Status: active
Multisite: No
Created: 2022-05-04
Tags
- Adrian Flux
Plugins & Themes
Plugin and theme information is not available via WP Engine API. This section can be manually updated with active plugins and theme details.
WP Engine Details
- Install ID:
20aa3817-6d5d-4a78-a307-378d20cd3879 - Site ID:
e0a933bd-ff59-41a6-8979-30631581005c - Account ID:
67f3426d-ea0c-4d81-a2c6-cbdf3fd91900
2.2.34 - fluxcapacitor
Overview
WordPress site fluxcapacitor hosted on WP Engine.
Links
| URL | Type |
|---|---|
| https://www.flux-capacitor.co.uk | Primary Domain |
| https://fluxcapacitor.wpengine.com | WP Engine URL |
Site Information
Site Name: AF | Flux Capacitor
Install Name: fluxcapacitor
WordPress Version: 6.8.3
Environment: production
PHP Version: 8.4
Status: active
Multisite: No
Created: 2022-05-10
Tags
- Adrian Flux
Plugins & Themes
Plugin and theme information is not available via WP Engine API. This section can be manually updated with active plugins and theme details.
WP Engine Details
- Install ID:
3b5bfa68-fb4a-4887-a1db-90ee49e75dc8 - Site ID:
ec8a80e0-57e2-4ca5-8bbb-d5b3e7f2a6a6 - Account ID:
67f3426d-ea0c-4d81-a2c6-cbdf3fd91900
2.2.35 - fluxposure
Overview
WordPress site fluxposure hosted on WP Engine.
Links
| URL | Type |
|---|---|
| https://blog.adrianflux.co.uk | Primary Domain |
| https://fluxposure.wpengine.com | WP Engine URL |
Site Information
Site Name: AF | Fluxposure
Install Name: fluxposure
WordPress Version: 6.9
Environment: production
PHP Version: 8.4
Status: active
Multisite: No
Created: 2024-02-01
Tags
- Adrian Flux
- Instant Callback
Plugins & Themes
Plugin and theme information is not available via WP Engine API. This section can be manually updated with active plugins and theme details.
WP Engine Details
- Install ID:
1079b877-d9d8-4c2c-905a-a4422609364b - Site ID:
b7902e37-72dc-4169-8e14-fa7322e69f53 - Account ID:
67f3426d-ea0c-4d81-a2c6-cbdf3fd91900
2.2.36 - forevercars
Overview
WordPress site forevercars hosted on WP Engine.
Links
| URL | Type |
|---|---|
| https://forever-cars.adrianflux.co.uk | Primary Domain |
| https://forevercars.wpengine.com | WP Engine URL |
Site Information
Site Name: AF | Forever Cars
Install Name: forevercars
WordPress Version: 6.8.3
Environment: production
PHP Version: 8.4
Status: active
Multisite: No
Created: 2022-04-11
Tags
- Adrian Flux
Plugins & Themes
Plugin and theme information is not available via WP Engine API. This section can be manually updated with active plugins and theme details.
WP Engine Details
- Install ID:
4e86bc0f-00b1-484f-9e76-81f46c3f2e0f - Site ID:
4740c365-295c-4e49-9690-49855c8cfbe2 - Account ID:
67f3426d-ea0c-4d81-a2c6-cbdf3fd91900
2.2.37 - fuellingaround
Overview
WordPress site fuellingaround hosted on WP Engine.
Links
| URL | Type |
|---|---|
| https://fuelling-around.adrianflux.co.uk | Primary Domain |
| https://fuellingaround.wpengine.com | WP Engine URL |
Site Information
Site Name: AF | Fuelling Around
Install Name: fuellingaround
WordPress Version: 6.8.3
Environment: production
PHP Version: 8.4
Status: active
Multisite: No
Created: 2022-04-06
Tags
- Adrian Flux
Plugins & Themes
Plugin and theme information is not available via WP Engine API. This section can be manually updated with active plugins and theme details.
WP Engine Details
- Install ID:
33d85a40-ec51-45fd-9ce9-3826f5aedefe - Site ID:
ee7b18d5-4c1c-4935-930b-f4de646a640a - Account ID:
67f3426d-ea0c-4d81-a2c6-cbdf3fd91900
2.2.38 - fullchat
Overview
WordPress site fullchat hosted on WP Engine.
Links
| URL | Type |
|---|---|
| https://full-chat.bikesure.co.uk | Primary Domain |
| https://fullchat.wpengine.com | WP Engine URL |
Site Information
Site Name: BKS | Full Chat Podcast
Install Name: fullchat
WordPress Version: 6.8.3
Environment: production
PHP Version: 8.2
Status: active
Multisite: No
Created: 2024-04-16
Tags
- Bikesure
Plugins & Themes
Plugin and theme information is not available via WP Engine API. This section can be manually updated with active plugins and theme details.
WP Engine Details
- Install ID:
7a02b523-8fbe-402f-9d82-9a923822966b - Site ID:
d97cb978-c1d9-4d6d-805d-7e49ee21e7d4 - Account ID:
67f3426d-ea0c-4d81-a2c6-cbdf3fd91900
2.2.39 - hondainsurance
Overview
WordPress site hondainsurance hosted on WP Engine.
Links
| URL | Type |
|---|---|
| https://callback.honda-bikeinsurance.co.uk | Primary Domain |
| https://hondainsurance.wpengine.com | WP Engine URL |
Site Information
Site Name: BKS | Honda Insurance
Install Name: hondainsurance
WordPress Version: 6.8.3
Environment: production
PHP Version: 8.2
Status: active
Multisite: No
Created: 2025-03-13
Tags
- Bikesure
- Scheduled Callback
Plugins & Themes
Plugin and theme information is not available via WP Engine API. This section can be manually updated with active plugins and theme details.
WP Engine Details
- Install ID:
fe4847cf-0c87-469a-b8f3-5704a4540e61 - Site ID:
b49f2956-cbdd-41d1-8224-5d1914168936 - Account ID:
1df5f442-982f-4ded-b8a8-ff64bf4f5c6b
2.2.40 - intelligentins
Overview
WordPress site intelligentins hosted on WP Engine.
Links
| URL | Type |
|---|---|
| https://intelligent-instructor.adrianflux.co.uk | Primary Domain |
| https://intelligentins.wpengine.com | WP Engine URL |
Site Information
Site Name: AF | Intelligent Instructor
Install Name: intelligentins
WordPress Version: 6.8.3
Environment: production
PHP Version: 8.4
Status: active
Multisite: No
Created: 2023-11-09
Tags
- Adrian Flux
- Scheduled Callback
Plugins & Themes
Plugin and theme information is not available via WP Engine API. This section can be manually updated with active plugins and theme details.
WP Engine Details
- Install ID:
e8a92d05-5739-4fc1-a488-608b0df57118 - Site ID:
6ba3d253-1a23-4129-8979-d48823ea111a - Account ID:
1df5f442-982f-4ded-b8a8-ff64bf4f5c6b
2.2.41 - kawasakiinsura
Overview
WordPress site kawasakiinsura hosted on WP Engine.
Links
| URL | Type |
|---|---|
| https://kawasaki-callback.bks-test.co.uk | Primary Domain |
| https://kawasakiinsura.wpengine.com | WP Engine URL |
Site Information
Site Name: BKS | Kawasaki Insurance
Install Name: kawasakiinsura
WordPress Version: 6.8.3
Environment: staging
PHP Version: 8.2
Status: active
Multisite: No
Created: 2025-04-21
Plugins & Themes
Plugin and theme information is not available via WP Engine API. This section can be manually updated with active plugins and theme details.
WP Engine Details
- Install ID:
d5db4684-da9d-4749-b59d-f5ef38184d04 - Site ID:
a72d8730-8a59-4894-8c58-f8dae4daa833 - Account ID:
1df5f442-982f-4ded-b8a8-ff64bf4f5c6b
2.2.42 - meganchallenge
Overview
WordPress site meganchallenge hosted on WP Engine.
Links
| URL | Type |
|---|---|
| https://www.meganschallenge.co.uk | Primary Domain |
| https://meganchallenge.wpengine.com | WP Engine URL |
Site Information
Site Name: ZZZ | Megans Challenge
Install Name: meganchallenge
WordPress Version: 6.8.3
Environment: production
PHP Version: 8.2
Status: active
Multisite: No
Created: 2022-10-08
Plugins & Themes
Plugin and theme information is not available via WP Engine API. This section can be manually updated with active plugins and theme details.
WP Engine Details
- Install ID:
b8cbfc0e-5757-4df4-a2f3-c57414565d1b - Site ID:
0fc8e3e8-d768-4832-9a4f-f2d370f88eca - Account ID:
67f3426d-ea0c-4d81-a2c6-cbdf3fd91900
2.2.43 - noboxins
Overview
WordPress site noboxins hosted on WP Engine.
Links
| URL | Type |
|---|---|
| https://www.noboxinsurance.co.uk | Primary Domain |
| https://noboxins.wpengine.com | WP Engine URL |
Site Information
Site Name: NB | Nobox Insurance
Install Name: noboxins
WordPress Version: 6.8.3
Environment: production
PHP Version: 8.2
Status: active
Multisite: No
Created: 2023-11-10
Tags
- Nobox Insurance
Plugins & Themes
Plugin and theme information is not available via WP Engine API. This section can be manually updated with active plugins and theme details.
WP Engine Details
- Install ID:
51703f02-dbd4-4dcf-aaf2-2c50ed9471c9 - Site ID:
1e6355a2-c2bb-429b-859a-59cd7298e39f - Account ID:
1df5f442-982f-4ded-b8a8-ff64bf4f5c6b
2.2.44 - silverstonecl1
Overview
WordPress site silverstonecl1 hosted on WP Engine.
Links
| URL | Type |
|---|---|
| https://silverstone-festival.adrianflux.co.uk | Primary Domain |
| https://silverstonecl1.wpengine.com | WP Engine URL |
Site Information
Site Name: AF | Silverstone Festival
Install Name: silverstonecl1
WordPress Version: 6.8.3
Environment: production
PHP Version: 8.4
Status: active
Multisite: No
Created: 2022-12-12
Tags
- Adrian Flux
- Scheduled Callback
Plugins & Themes
Plugin and theme information is not available via WP Engine API. This section can be manually updated with active plugins and theme details.
WP Engine Details
- Install ID:
ff78bdaa-a561-478e-bf1a-dc1321c6d5f0 - Site ID:
77ae1250-38c0-4c0e-a000-85e747ea8fae - Account ID:
67f3426d-ea0c-4d81-a2c6-cbdf3fd91900
2.2.45 - stcustomers
Overview
WordPress site stcustomers hosted on WP Engine.
Links
| URL | Type |
|---|---|
| https://customers.sterling-insurance.co.uk | Primary Domain |
| https://stcustomers.wpengine.com | WP Engine URL |
Site Information
Site Name: ST | Sterling Insurance Customers
Install Name: stcustomers
WordPress Version: 6.9
Environment: production
PHP Version: 8.4
Status: active
Multisite: No
Created: 2024-01-23
Tags
- Sterling Insurance
Plugins & Themes
Plugin and theme information is not available via WP Engine API. This section can be manually updated with active plugins and theme details.
WP Engine Details
- Install ID:
4b23f949-23f4-4d54-8017-cd51a9d0ba4e - Site ID:
2bbc0614-4771-473c-9989-9c4887417c49 - Account ID:
1df5f442-982f-4ded-b8a8-ff64bf4f5c6b
2.2.46 - sterblog
Overview
WordPress site sterblog hosted on WP Engine.
Links
| URL | Type |
|---|---|
| https://blog.sterling-insurance.co.uk | Primary Domain |
| https://sterblog.wpengine.com | WP Engine URL |
Site Information
Site Name: ST | Sterling Insurance Blog
Install Name: sterblog
WordPress Version: 6.8.3
Environment: production
PHP Version: 8.2
Status: active
Multisite: No
Created: 2024-02-06
Tags
- Sterling Insurance
Plugins & Themes
Plugin and theme information is not available via WP Engine API. This section can be manually updated with active plugins and theme details.
WP Engine Details
- Install ID:
2037eb20-3182-44e9-9dc2-7f0ec6bc811d - Site ID:
26a4c5b8-3499-4d91-a461-4262f24c89dd - Account ID:
67f3426d-ea0c-4d81-a2c6-cbdf3fd91900
2.2.47 - sterlingcomps
Overview
WordPress site sterlingcomps hosted on WP Engine.
Links
| URL | Type |
|---|---|
| https://competitions.sterling-insurance.co.uk | Primary Domain |
| https://sterlingcomps.wpengine.com | WP Engine URL |
Site Information
Site Name: ST | Sterling Insurance Competitions
Install Name: sterlingcomps
WordPress Version: 6.8.3
Environment: production
PHP Version: 8.2
Status: active
Multisite: No
Created: 2022-04-30
Tags
- Sterling Insurance
Plugins & Themes
Plugin and theme information is not available via WP Engine API. This section can be manually updated with active plugins and theme details.
WP Engine Details
- Install ID:
dbdacfd1-fef1-42de-8e36-43c764165e89 - Site ID:
a96d229a-e6da-4732-a242-9af4d208fcde - Account ID:
67f3426d-ea0c-4d81-a2c6-cbdf3fd91900
2.2.48 - sterlinginsni
Overview
WordPress site sterlinginsni hosted on WP Engine.
Links
| URL | Type |
|---|---|
| https://northern-ireland.sterling-insurance.co.uk | Primary Domain |
| https://sterlinginsni.wpengine.com | WP Engine URL |
Site Information
Site Name: ST | Sterling Insurance Northern Ireland
Install Name: sterlinginsni
WordPress Version: 6.8.3
Environment: production
PHP Version: 8.2
Status: active
Multisite: No
Created: 2023-11-11
Tags
- Sterling Insurance
- Instant Callback
- Scheduled Callback
Plugins & Themes
Plugin and theme information is not available via WP Engine API. This section can be manually updated with active plugins and theme details.
WP Engine Details
- Install ID:
b37f38fd-fd10-46e7-8c4b-54a9449bc244 - Site ID:
a5200a7c-56b8-4007-97d6-c1ae5ec82acd - Account ID:
1df5f442-982f-4ded-b8a8-ff64bf4f5c6b
2.2.49 - sterlinginsure
Overview
WordPress site sterlinginsure hosted on WP Engine.
Links
| URL | Type |
|---|---|
| https://sterling-insurance.sterling-insurance.co.uk | Primary Domain |
| https://sterlinginsure.wpengine.com | WP Engine URL |
Site Information
Site Name: ST | Sterling Insurance
Install Name: sterlinginsure
WordPress Version: 6.8.3
Environment: production
PHP Version: 8.2
Status: active
Multisite: No
Created: 2024-03-21
Tags
- Sterling Insurance
- Instant Callback
- Scheduled Callback
Plugins & Themes
Plugin and theme information is not available via WP Engine API. This section can be manually updated with active plugins and theme details.
WP Engine Details
- Install ID:
2205b380-82b6-46e0-a1b2-4cf6a77d81bb - Site ID:
cdc4017c-3860-4766-8b7f-e9dc970ec444 - Account ID:
1df5f442-982f-4ded-b8a8-ff64bf4f5c6b
2.2.50 - ststerlingins1
Overview
WordPress site ststerlingins1 hosted on WP Engine.
Links
| URL | Type |
|---|---|
| https://sterling-insurance.ster-test.co.uk | Primary Domain |
| https://ststerlingins1.wpengine.com | WP Engine URL |
Site Information
Site Name: ST | Sterling Insurance
Install Name: ststerlingins1
WordPress Version: 6.8.3
Environment: staging
PHP Version: 8.2
Status: active
Multisite: No
Created: 2024-02-20
Tags
- Sterling Insurance
- Instant Callback
- Scheduled Callback
Plugins & Themes
Plugin and theme information is not available via WP Engine API. This section can be manually updated with active plugins and theme details.
WP Engine Details
- Install ID:
8c5d40bb-92c1-4021-8d33-d31f567c16f4 - Site ID:
cdc4017c-3860-4766-8b7f-e9dc970ec444 - Account ID:
1df5f442-982f-4ded-b8a8-ff64bf4f5c6b
2.2.51 - suzukiinsuranc
Overview
WordPress site suzukiinsuranc hosted on WP Engine.
Links
| URL | Type |
|---|---|
| https://suzuki-callback.bks-test.co.uk | Primary Domain |
| https://suzukiinsuranc.wpengine.com | WP Engine URL |
Site Information
Site Name: BKS | Suzuki Insurance
Install Name: suzukiinsuranc
WordPress Version: 6.8.3
Environment: staging
PHP Version: 8.2
Status: active
Multisite: No
Created: 2025-04-22
Plugins & Themes
Plugin and theme information is not available via WP Engine API. This section can be manually updated with active plugins and theme details.
WP Engine Details
- Install ID:
a7628976-9fc3-4147-a705-bbcb13ad1f23 - Site ID:
12e7cccf-b516-4307-934e-52e18c56e6da - Account ID:
1df5f442-982f-4ded-b8a8-ff64bf4f5c6b
2.2.52 - top10cars
Overview
WordPress site top10cars hosted on WP Engine.
Links
| URL | Type |
|---|---|
| https://top-10-cars.adrianflux.co.uk | Primary Domain |
| https://top10cars.wpengine.com | WP Engine URL |
Site Information
Site Name: AF | Top 10 Cars
Install Name: top10cars
WordPress Version: 6.8.3
Environment: production
PHP Version: 8.4
Status: active
Multisite: No
Created: 2022-05-09
Tags
- Adrian Flux
Plugins & Themes
Plugin and theme information is not available via WP Engine API. This section can be manually updated with active plugins and theme details.
WP Engine Details
- Install ID:
5e3b0389-4216-4561-93f8-9e542f036390 - Site ID:
35a7f537-be45-48f1-82b8-bc284ae0df25 - Account ID:
67f3426d-ea0c-4d81-a2c6-cbdf3fd91900
2.2.53 - trinitylane
Overview
WordPress site trinitylane hosted on WP Engine.
Links
| URL | Type |
|---|---|
| https://www.trinitylane.co.uk | Primary Domain |
| https://trinitylane.wpengine.com | WP Engine URL |
Site Information
Site Name: TL | Trinity Lane
Install Name: trinitylane
WordPress Version: 6.9
Environment: production
PHP Version: 8.2
Status: active
Multisite: No
Created: 2023-11-10
Tags
- Trinity Lane
Plugins & Themes
Plugin and theme information is not available via WP Engine API. This section can be manually updated with active plugins and theme details.
WP Engine Details
- Install ID:
6190dda4-00f5-45b1-8a88-d79efc121283 - Site ID:
95ce09c2-f1d8-437d-ba2e-37a7846f8909 - Account ID:
1df5f442-982f-4ded-b8a8-ff64bf4f5c6b
2.2.54 - triumphinsuran
Overview
WordPress site triumphinsuran hosted on WP Engine.
Links
| URL | Type |
|---|---|
| https://triumph-callback.bks-test.co.uk | Primary Domain |
| https://triumphinsuran.wpengine.com | WP Engine URL |
Site Information
Site Name: BKS | Triumph Insurance
Install Name: triumphinsuran
WordPress Version: 6.8.3
Environment: staging
PHP Version: 8.2
Status: active
Multisite: No
Created: 2025-04-22
Plugins & Themes
Plugin and theme information is not available via WP Engine API. This section can be manually updated with active plugins and theme details.
WP Engine Details
- Install ID:
0ed8f23d-ef2a-469a-bb34-429814c668e6 - Site ID:
0d5be307-f89c-4269-92b0-0c53c65fccea - Account ID:
1df5f442-982f-4ded-b8a8-ff64bf4f5c6b
2.2.55 - ukuscarparts
Overview
WordPress site ukuscarparts hosted on WP Engine.
Links
| URL | Type |
|---|---|
| https://uk-us-car-part-names.adrianflux.co.uk | Primary Domain |
| https://ukuscarparts.wpengine.com | WP Engine URL |
Site Information
Site Name: AF | UK & US Car Part Names
Install Name: ukuscarparts
WordPress Version: 6.8.3
Environment: production
PHP Version: 8.4
Status: active
Multisite: No
Created: 2022-05-10
Tags
- Adrian Flux
Plugins & Themes
Plugin and theme information is not available via WP Engine API. This section can be manually updated with active plugins and theme details.
WP Engine Details
- Install ID:
c4238792-85bc-4a56-bd8a-7bb7456a5f39 - Site ID:
95b0d464-b95c-47b2-b575-e69414778ecf - Account ID:
67f3426d-ea0c-4d81-a2c6-cbdf3fd91900
3 - External
3.1 - Google
3.1.1 - Google Maps API
Overview
The Google Maps JavaScript API is used across our applications to provide interactive mapping, geocoding, and location-based functionality.
Official Documentation
For complete API reference and guides, see the Google Maps JavaScript API Documentation .
Usage in Our Applications
- bikesure-affiliates - Bikesure Dealer Directory public frontend
Common Features
- Interactive Maps - Display dealerships and service locations
- Geocoding - Convert addresses to coordinates
- Place Search - Find nearby locations
- Custom Markers - Branded map pins and info windows
API Key Management
Google Maps API keys are configured via environment variables:
GOOGLE_MAPS_API_KEY- API key for accessing Google Maps services
API keys should be restricted to specific domains and services in the Google Cloud Console to prevent unauthorized usage.
Key Resources
Support & Billing
- Pricing: Google Maps Platform Pricing
- Usage Limits: Monitor usage in Google Cloud Console
- Support: Google Maps Platform Support
4 - Memos
Overview
This section contains technical memos and in-depth research documents covering architectural decisions, technical analyses, and comprehensive guides for complex topics.
Browse Memos
Navigate through the sidebar to explore individual memos, or use the search feature to find specific documents.
4.1 - Sample Memo
Executive Summary
This is a sample memo that demonstrates the recommended structure and format for technical memos. It provides a template that can be used as a starting point for creating new memos.
Introduction
Purpose
Explain the purpose of the memo and what problems or questions it addresses.
Scope
Define the scope of the document, including what is covered and what is explicitly out of scope.
Audience
Identify the intended audience and any prerequisite knowledge required.
Background
Provide necessary background information and context for understanding the memo content.
Current State
Describe the current situation, challenges, or problems that motivated this memo.
Requirements
List any requirements or constraints that influenced the analysis or recommendations.
Technical Analysis
Approach
Describe the methodology or approach used in the analysis.
Findings
Present the key findings from the technical analysis.
Trade-offs
Discuss the trade-offs considered and how different options were evaluated.
Recommendations
Provide specific recommendations based on the analysis.
Implementation Considerations
Discuss practical considerations for implementing the recommendations.
Risk Assessment
Identify potential risks and mitigation strategies.
Conclusion
Summarize the key points and recommendations.
References
- List relevant documentation
- External resources
- Related memos
4.2 - Viitata Tenancy Infrastructure
Executive Summary
This memo documents the strategic architecture migration for Viitata from a single-tenant-per-instance model to a multi-tenant architecture on Heroku. This migration addresses critical operational inefficiencies, enables deployment of the new Viitata version with its required worker architecture, and significantly reduces both current costs and the cost of scaling while eliminating DevOps friction for client onboarding.
Key Changes:
- Architecture: Single-tenant-per-instance → Multi-tenant shared infrastructure
- Platform: Heroku (no change)
- Application Version: Current (single worker) → New version (3 workers required)
- Cost Impact: $96/month currently → $288/month if upgraded on single-tenant → $130/month on multi-tenant
- Cost Savings: 55% reduction vs. deploying new version on single-tenant architecture
Introduction
Purpose
This document outlines the rationale, technical approach, and benefits of migrating Viitata from a distributed single-tenant-per-instance model to a consolidated multi-tenant architecture on Heroku.
Scope
This memo covers:
- Current single-tenant-per-instance architecture on Heroku
- New Viitata version requirements (3-worker architecture)
- Proposed multi-tenant architecture on Heroku
- Cost analysis and operational benefits
- Technical considerations and trade-offs
Out of scope:
- Detailed application code changes for multi-tenancy
- Specific Heroku configuration details
- Data migration procedures and implementation timeline
Audience
This document is intended for technical leadership, DevOps engineers, and stakeholders involved in infrastructure planning and decision-making.
Background
Current State: Single-Tenant-Per-Instance on Heroku
Viitata currently operates with a single-tenant-per-instance model on Heroku, consisting of:
Infrastructure per Tenant:
- 1 Heroku application instance (single worker)
- 1 PostgreSQL database
- 1 Redis cache instance
- Cost: ~$16/month per tenant
Current Deployment:
- 6 production instances running current Viitata version
- Each instance operates as a single-worker application
- Total monthly cost: ~$96 (6 instances × $16)
- Each instance requires independent CI/CD pipeline
- Each instance requires separate DevOps configuration
Important Note: The current architecture runs an older version of Viitata that does not require the 3-worker architecture. However, the new version of Viitata cannot be deployed without this infrastructure change.
Challenges with Current Architecture
1. Cost Scalability Concerns
With 6 production tenants at $16/month each, the current architecture costs approximately $96/month. While manageable at this scale, the cost scales linearly with each new tenant ($16 per additional tenant). More critically, the new version of Viitata requires a 3-worker architecture that would triple costs to approximately $288/month for the same 6 tenants.
2. DevOps Friction
Each new client onboarding requires:
- Provisioning new Heroku application
- Configuring new PostgreSQL database
- Setting up new Redis cache
- Configuring CI/CD pipeline
- Managing environment variables and secrets
- Setting up monitoring and logging
This creates substantial friction and delays in client onboarding.
3. CI/CD Maintenance Overhead
Maintaining 6 separate CI/CD pipelines creates:
- Increased complexity in deployment processes
- Higher risk of configuration drift
- Difficulty in applying updates uniformly
- Additional testing burden across instances
4. Blocking Issue: New Viitata Version Requirements
The new version of Viitata fundamentally requires three distinct worker types to function:
- Web worker: Handles HTTP requests
- Celery worker: Processes asynchronous tasks
- Celery Beat worker: Manages scheduled tasks and periodic jobs
This is not optional - the new Viitata version cannot be deployed without all three workers running.
Under the single-tenant model, deploying the new version would require:
- 18 total worker processes (6 instances × 3 workers)
- Tripling of infrastructure costs per tenant (from $16 to ~$48 per tenant)
- Total monthly cost increase from $96 to approximately $288/month
- 18 separate processes to monitor and manage
Critical Impact: The single-tenant architecture makes it economically and operationally prohibitive to deploy the new version of Viitata. Without migrating to multi-tenant, the platform cannot evolve.
Technical Analysis
Proposed Architecture: Multi-Tenant on Heroku
The new architecture consolidates all tenants into a single shared Heroku infrastructure:
Shared Infrastructure:
- 1 Heroku application (supporting 3 worker types)
- 1 Heroku PostgreSQL database (with tenant isolation)
- 1 Heroku Redis cache (with tenant namespacing)
- Estimated cost: ~$130/month total
Worker Configuration:
- 1 web worker (serving all tenants)
- 1 Celery worker (processing tasks for all tenants)
- 1 Celery Beat worker (managing schedules for all tenants)
- Total: 3 workers supporting all tenants
Cost Analysis
| Architecture Model | Viitata Version | Tenants | Workers | Monthly Cost | Cost per Tenant |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Current (Single-Tenant) | Old | 6 | 6 (1 per instance) | $96 | $16.00 |
| Single-Tenant Upgraded | New | 6 | 18 (3 per instance) | $288 | $48.00 |
| Multi-Tenant (Proposed) | New | 6 | 3 (shared) | $130 | $21.67 |
| Savings vs. Upgraded | - | - | -83% | -$158/month | -55% |
Key Insights:
- Current architecture cannot run the new Viitata version without significant cost increase
- New version’s 3-worker requirement would triple single-tenant costs ($96 → $288)
- Multi-tenant architecture enables new version deployment at 55% lower cost than single-tenant upgrade
- Marginal cost advantage: Adding tenant #7 costs $0/month (vs. $48/month in single-tenant)
- Cost efficiency improves with scale: 10 tenants = $13/tenant, 20 tenants = $6.50/tenant
Benefits
1. Cost Reduction
- 83% reduction in infrastructure costs
- Costs remain flat as tenant count grows (until scaling threshold)
- Predictable cost model
2. Operational Efficiency
- Single CI/CD pipeline for all tenants
- Unified deployment process
- Consistent configuration across all tenants
- Reduced maintenance overhead
3. Client Onboarding
- Near-instant tenant provisioning (database record vs. full infrastructure)
- Minimal DevOps involvement
- Faster time-to-value for new clients
- Reduced onboarding friction
4. Enables New Viitata Version Deployment
- Supports required 3-worker architecture (web, Celery, Celery Beat)
- 3 shared workers support all tenants (vs. 18 separate workers in single-tenant)
- Makes new version economically viable to deploy
- Simplified monitoring and management
- Better resource utilization
- Easier to scale horizontally when needed
Technical Considerations
Data Isolation
- Tenant identification at application layer
- Row-level security in PostgreSQL
- Redis key namespacing by tenant ID
- Careful query design to prevent data leakage
Performance
- Shared resources require proper resource allocation
- Connection pooling for database efficiency
- Caching strategies to prevent tenant interference
- Monitoring to identify tenant-specific performance issues
Security
- Tenant isolation at application and data layers
- Secure tenant context management
- Audit logging for compliance
- Regular security reviews of multi-tenant code paths
Scalability
- Horizontal scaling when single instance reaches capacity
- Database sharding if needed for very large tenant counts
- CDN and edge caching for static assets
- Load balancing across multiple application instances
Trade-offs
Advantages
- Dramatic cost reduction
- Simplified operations
- Faster client onboarding
- Better resource utilization
- Easier maintenance and updates
Disadvantages
- Tenant isolation complexity in application code
- Potential “noisy neighbor” issues
- Database restore impact: Currently, database snapshots can be restored per-tenant without affecting other clients. In multi-tenant architecture, a database restore would affect all tenants simultaneously, making it impossible to roll back a single client’s data due to a bug or data issue
- More complex deployment rollback scenarios
- Requires careful tenant-aware code design
- Less isolation between tenants compared to separate instances
Risk Mitigation
- Comprehensive testing of tenant isolation
- Resource limits per tenant
- Monitoring and alerting for anomalies
- Gradual migration approach
- Ability to isolate problematic tenants if needed
- Database restore mitigation:
- Implement application-level point-in-time recovery per tenant
- Maintain granular database backups with tenant-specific restore capabilities
- Use transaction logs to selectively restore tenant data
- Establish procedures for tenant-specific data rollback without full database restore
- More rigorous testing and staging processes to prevent production data issues
- Consider automated daily tenant-level logical backups (pg_dump per tenant)
Conclusion
The migration from a single-tenant-per-instance architecture to a multi-tenant architecture on Heroku represents a strategic necessity for Viitata’s evolution. This change delivers:
- Enables deployment of new Viitata version with required 3-worker architecture
- 55% cost reduction vs. deploying new version on single-tenant ($288/month → $130/month)
- Dramatic reduction in operational complexity (6 CI/CD pipelines → 1, 18 workers → 3)
- Near-zero marginal cost for new tenants ($0 vs. $48/tenant in single-tenant)
- Improving cost efficiency at scale: Cost per tenant decreases as platform grows
- Eliminates DevOps friction in client onboarding
Without this migration, deploying the new version of Viitata would nearly triple costs while adding significant operational burden. The multi-tenant architecture not only makes the new version economically viable but also positions Viitata for sustainable growth with costs that improve with scale.
While multi-tenancy introduces complexity in application design around tenant isolation and data security, the alternative—remaining on single-tenant architecture—would either block the platform’s evolution or make it financially unsustainable. The operational benefits, cost savings, and improved scalability make this migration essential for Viitata’s future.
References
4.3 - Heroku to AWS Migration
Executive Summary
This memo documents the strategic platform migration for Viitata from Heroku to AWS (Amazon Web Services). This migration addresses critical compliance requirements around UK data residency, reduces infrastructure costs, provides greater operational flexibility and control, and enables better performance and integration with additional AWS services.
Key Changes:
- Platform: Heroku → AWS ECS (Elastic Container Service)
- Region: EU-West-1 (Ireland) → EU-West-2 (London, UK)
- Primary Driver: Compliance - UK data residency and backup retention
- Additional Benefits: Cost reduction, greater control, performance improvements, AWS service ecosystem
Critical Compliance Issue: Currently on Heroku, while the primary database is in EU-West-1 (Ireland), database backups are retained in the USA. This creates compliance risks for UK data residency requirements. AWS enables full infrastructure and data containment within EU-West-2 (London).
Introduction
Purpose
This document outlines the rationale, technical approach, and benefits of migrating Viitata’s multi-tenant infrastructure from Heroku to AWS, with a focus on achieving UK data sovereignty and compliance requirements while improving operational capabilities.
Scope
This memo covers:
- Current multi-tenant architecture on Heroku
- Compliance and data residency challenges
- Proposed multi-tenant architecture on AWS ECS
- Cost analysis and operational benefits
- Technical considerations and trade-offs
Out of scope:
- Detailed AWS infrastructure-as-code configurations
- Specific containerization implementation details
- Data migration procedures and implementation timeline
- Application code changes required for AWS
Audience
This document is intended for technical leadership, compliance officers, DevOps engineers, and stakeholders involved in infrastructure planning and decision-making.
Background
Current State: Multi-Tenant on Heroku
Viitata currently operates with a multi-tenant architecture on Heroku, consisting of:
Infrastructure:
- 1 Heroku application (3 dynos: web, Celery worker, Celery Beat)
- 1 Heroku PostgreSQL database in EU-West-1 (Ireland)
- 1 Heroku Redis cache
- Current cost: ~$130/month
Current Deployment:
- Multi-tenant architecture supporting 6 production tenants
- Single CI/CD pipeline
- Heroku-managed infrastructure and scaling
- Automatic SSL, DNS, and platform maintenance
Critical Issues with Current Platform
1. Compliance and Data Residency (Primary Driver)
Database Backup Location:
- Primary database: EU-West-1 (Ireland, EU)
- Database backups: Stored in USA (Heroku’s backup infrastructure)
This creates significant compliance risks:
- UK data residency requirements cannot be met
- Backup data crosses international boundaries
- Potential violations of data protection regulations
- Risk for clients requiring UK-only data storage
- Audit and compliance reporting challenges
Regional Limitation:
- Application and database in Ireland (EU-West-1), not UK
- No option for UK-specific region on Heroku
- Cannot guarantee UK data sovereignty
2. Cost Considerations
While Heroku provides managed services, the cost includes:
- Premium for managed platform (~30-40% over raw compute)
- Limited ability to optimize resource allocation
- Dyno pricing model less flexible than AWS instance types
- Add-on costs (PostgreSQL, Redis) with limited customization
3. Limited Control and Flexibility
Infrastructure Control:
- Cannot customize underlying OS or runtime environment
- Limited control over networking and security groups
- Restricted access to infrastructure-level monitoring
- Cannot implement custom security controls
Resource Optimization:
- Fixed dyno sizes with limited granularity
- Cannot right-size resources for specific workloads
- Limited ability to use spot instances or reserved capacity
- Cannot separate worker resources by type
4. Performance Constraints
Heroku Limitations:
- Shared infrastructure with potential noisy neighbor issues
- Limited database connection pooling options
- Router timeout constraints (30 seconds)
- Limited control over caching layers
- Cannot implement custom CDN configurations
5. AWS Service Integration
Current limitations for integrating with AWS services:
- External network calls to AWS services (S3, SES, etc.)
- Additional latency for AWS service integration
- Cannot use VPC peering or private networking
- Limited IAM role-based security
- Cannot leverage AWS-native monitoring and logging
Technical Analysis
Proposed Architecture: Multi-Tenant on AWS ECS
The new architecture migrates the multi-tenant application to AWS infrastructure with a fully containerized, role-based security model.
Architecture Overview
The following diagram illustrates the proposed AWS architecture:
graph TB
subgraph Internet
Users[Users/Clients]
end
subgraph "AWS EU-West-2 (London)"
subgraph "VPC"
subgraph "Public Subnets"
ALB[Application Load Balancer<br/>HTTPS:443]
NAT[NAT Gateway]
end
subgraph "Private Subnets"
subgraph "ECS Fargate Cluster"
Web[Web Tasks<br/>nginx + gunicorn<br/>Auto-scaling]
Worker[Celery Worker Tasks<br/>Auto-scaling]
Beat[Celery Beat Task<br/>Single instance]
end
RDS[(RDS PostgreSQL<br/>Multi-AZ<br/>Automated Backups)]
Cache[(ElastiCache Valkey<br/>Redis-compatible<br/>Cache & Results)]
end
end
SQS[Amazon SQS<br/>Celery Message Broker<br/>Task Queue]
S3[S3 Bucket<br/>Media Storage]
CW[CloudWatch<br/>Logs & Metrics]
SM[Secrets Manager<br/>Credentials]
end
Users -->|HTTPS| ALB
ALB -->|Routes traffic| Web
Web -->|IAM Role| S3
Web -->|Read/Write| RDS
Web -->|Cache/Sessions| Cache
Web -->|Send tasks| SQS
Web -->|Logs| CW
Web -->|Get secrets| SM
Worker -->|IAM Role| S3
Worker -->|Read/Write| RDS
Worker -->|Receive/Delete tasks| SQS
Worker -->|Store results| Cache
Worker -->|Logs| CW
Worker -->|Get secrets| SM
Beat -->|Send scheduled tasks| SQS
Beat -->|Read/Write| RDS
Beat -->|Logs| CW
Web -.->|Outbound via| NAT
Worker -.->|Outbound via| NAT
Beat -.->|Outbound via| NAT
classDef public fill:#e1f5ff,stroke:#01579b,stroke-width:2px
classDef private fill:#f3e5f5,stroke:#4a148c,stroke-width:2px
classDef data fill:#fff3e0,stroke:#e65100,stroke-width:2px
classDef compute fill:#e8f5e9,stroke:#1b5e20,stroke-width:2px
classDef aws fill:#fff9c4,stroke:#f57f17,stroke-width:2px
class ALB,NAT public
class Web,Worker,Beat compute
class RDS,Cache data
class S3,CW,SM,SQS awsCore Infrastructure Components:
Database Layer
- Amazon RDS for PostgreSQL in EU-West-2 (London)
- Multi-AZ deployment for high availability
- Automated backups retained in EU-West-2
- Point-in-time recovery capabilities
- All tenant data with row-level isolation
Cache Layer
- Amazon ElastiCache with Valkey (Redis-compatible) in EU-West-2
- Used for session storage, application caching, and Celery result backend
- Tenant-namespaced keys for data isolation
- High-performance in-memory data store
Message Queue Layer
- Amazon SQS (Simple Queue Service) in EU-West-2
- Celery message broker for task distribution
- Fully managed, serverless message queue
- No infrastructure to maintain or scale
- Automatic message retention and delivery
- Dead letter queue for failed tasks
- FIFO queues for task ordering if needed
- Cost-effective: Pay only for messages processed
Compute Layer - ECS Fargate
Three separate ECS task definitions running on Fargate:
Task Definition 1: Web Application
- Container: nginx + gunicorn
- Receives traffic from Application Load Balancer (ALB)
- Handles HTTPS requests routed by ALB
- Auto-scaling based on CPU/memory and request count
- Appropriate resources: ~0.5-1 vCPU, 1-2GB memory
- Multiple tasks for high availability and load distribution
- ALB distributes traffic across all healthy web tasks
Task Definition 2: Celery Worker
- Container: Celery worker process
- Consumes tasks from Amazon SQS queue
- Auto-scaling based on SQS queue depth (ApproximateNumberOfMessagesVisible) and CPU utilization
- Right-sized resources: ~0.25-0.5 vCPU, 0.5-1GB memory
- Can scale independently based on task backlog in SQS
Task Definition 3: Celery Beat
- Container: Celery Beat scheduler
- Manages periodic and scheduled tasks
- Publishes scheduled tasks to SQS queue
- Fixed scaling: Single task (Beat requires single instance)
- Minimal resources: ~0.25 vCPU, 0.5GB memory
- Auto-restart on failure
Rationale for Separate Task Definitions:
- Each workload has different resource requirements
- Independent scaling policies per service type
- Web scales with traffic, workers scale with queue depth
- Cost optimization: Right-size each workload separately
- Isolation: Issues in one service don’t affect others
Auto-Scaling Configuration:
ECS provides automatic scaling that adjusts the number of running tasks based on demand, with both scale-up and scale-down capabilities:
Web Tasks Auto-Scaling:
- Metrics: CPU utilization, memory utilization, ALB request count per target
- Scale-up triggers:
- CPU > 70% for 2 minutes → Add tasks
- Requests per task > 1000/min → Add tasks
- Scale-down triggers:
- CPU < 30% for 5 minutes → Remove tasks
- Requests per task < 200/min → Remove tasks
- Min/Max tasks: 2 minimum (HA), 10 maximum
- Benefits: Handles traffic spikes from multiple tenants, scales down during low usage to save costs
Celery Worker Auto-Scaling:
- Metrics: CPU utilization, SQS ApproximateNumberOfMessagesVisible (native CloudWatch metric)
- Scale-up triggers:
- SQS queue depth > 100 messages → Add workers
- CPU > 80% for 3 minutes → Add workers
- Scale-down triggers:
- SQS queue depth < 10 messages for 10 minutes → Remove workers
- CPU < 20% for 10 minutes → Remove workers
- Min/Max tasks: 1 minimum, 5 maximum
- Benefits: SQS provides native queue metrics for accurate scaling decisions; efficiently processes task backlog, reduces to minimum during idle periods
Celery Beat Scaling:
- Fixed at 1 task (Beat scheduler requires single instance)
- Auto-restart on failure for reliability
Multi-Tenant Scaling Benefits:
Auto-scaling is particularly valuable for multi-tenant architecture:
- Unpredictable tenant activity: Different tenants have different usage patterns and peak times
- Cost efficiency: Automatically scales down during low-usage periods (nights, weekends)
- Spike handling: Automatically scales up when multiple tenants become active simultaneously
- Resource optimization: Pays only for resources actually needed at any given time
- Example scenario:
- During business hours (9am-5pm): 6-8 web tasks handle peak multi-tenant load
- During nights (11pm-6am): Scales down to 2 web tasks, saving ~$40-60/month
- Weekend spikes: Auto-scales up to handle unexpected tenant activity
Comparison to Heroku:
Scaling Feature Heroku AWS ECS Scale-up Manual or via add-ons Automatic based on metrics Scale-down Manual only Automatic (saves costs) Scaling metrics Limited (response time, throughput) Extensive (CPU, memory, custom CloudWatch metrics, ALB metrics, queue depth) Per-service scaling Requires multiple apps Built-in per task definition Cost during low usage Fixed (pays for min dynos) Dynamic (scales to minimum) Multi-tenant optimization Limited Excellent - handles variable tenant load patterns Cost Impact:
- Scale-down capability can reduce compute costs by 40-50% during off-peak hours
- For multi-tenant with variable load, average monthly compute cost drops significantly
- Example: Instead of running 6 web tasks 24/7, average 4 tasks/hour = 33% cost reduction
Networking and Load Balancing
- Application Load Balancer (ALB) as entry point for all web traffic
- Sits in public subnets
- Terminates HTTPS/SSL connections
- Routes traffic to web task definition only
- Health checks on web tasks
- Automatically distributes load across multiple web task instances
- VPC with public and private subnets across multiple Availability Zones
- Private subnets for ECS tasks, RDS, and ElastiCache (no direct internet access)
- Public subnets for ALB only
- NAT Gateway for outbound internet access from private subnets
- Security groups for service-level network isolation
- ALB security group: Allow inbound 443 from internet
- Web task security group: Allow inbound from ALB only
- Worker task security groups: No inbound internet traffic
- RDS/ElastiCache security groups: Allow access from ECS tasks only
- Application Load Balancer (ALB) as entry point for all web traffic
Security Model: Role-Based Authentication
Shift from IAM Users to IAM Roles:
- Current (Heroku): IAM user credentials stored as environment variables for AWS service access (S3, SES, etc.)
- Proposed (AWS): ECS task IAM roles with least-privilege permissions
IAM Role-Based Security Benefits:
- No stored credentials: Tasks assume roles automatically via ECS Task Role
- Dramatically reduced credential leakage risk: No long-lived access keys in environment variables or code
- Automatic credential rotation: AWS STS provides temporary credentials (auto-expire and rotate)
- Least-privilege access: Each task definition gets only required permissions
- Audit trail: CloudTrail logs all role assumption and service access
- Infrastructure-as-code: IAM roles defined in CloudFormation templates
- Centralized security: All permissions defined and version-controlled
Example Security Architecture:
- Web task role: Read S3 (media), write CloudWatch Logs
- Celery worker task role: Read/Write S3, SES send email, SQS receive/delete messages, CloudWatch Logs
- Celery Beat task role: SQS send messages, CloudWatch Logs only
- RDS access: PostgreSQL username/password from Secrets Manager (accessed via IAM role)
- SQS access: Fully controlled via IAM roles (no credentials needed)
- No IAM user access keys anywhere in the system
Additional AWS Services
- Amazon SQS for Celery message broker (fully managed queue)
- CloudWatch Logs for centralized logging
- CloudWatch Metrics for monitoring and alerting (includes native SQS metrics)
- AWS Secrets Manager for database credentials and API keys
- S3 for media file storage (UK region)
- CloudFormation for infrastructure-as-code deployment
- ECR (Elastic Container Registry) for Docker image storage
Region and Compliance:
- All resources in EU-West-2 (London, UK)
- No data transfer outside UK jurisdiction
- Estimated cost: ~$90-115/month (12-30% savings, includes SQS)
Connectivity Flow
Internet (HTTPS:443)
↓
Application Load Balancer (Public Subnet)
↓ (Routes to web tasks only)
ECS Web Tasks (nginx + gunicorn) (Private Subnet)
↓
├─→ RDS PostgreSQL (Private Subnet)
├─→ ElastiCache Valkey (Private Subnet - cache/sessions)
├─→ Amazon SQS (Send tasks via IAM role)
└─→ S3 (via IAM role)
ECS Celery Workers (Private Subnet)
↓
├─→ RDS PostgreSQL (Private Subnet)
├─→ ElastiCache Valkey (Private Subnet - result backend)
├─→ Amazon SQS (Receive/Delete tasks via IAM role)
└─→ S3 (via IAM role)
ECS Celery Beat (Private Subnet)
↓
├─→ RDS PostgreSQL (Private Subnet)
└─→ Amazon SQS (Send scheduled tasks via IAM role)
Key Points:
- Only web tasks receive traffic from ALB - Workers have no inbound internet traffic
- All three task definitions connect to RDS
- Celery uses Amazon SQS as message broker - fully managed, serverless queue
- ElastiCache Valkey used for caching, sessions, and Celery result backend
- All ECS tasks connect to AWS services (S3, SQS, CloudWatch) via IAM roles
- No stored credentials required anywhere
- SQS provides native CloudWatch metrics for auto-scaling
Infrastructure-as-Code
The entire architecture is defined in CloudFormation templates:
- VPC, subnets, route tables, security groups
- RDS database configuration
- ElastiCache cluster configuration
- SQS queues (standard and dead letter queues)
- ECS cluster, task definitions, and services
- Application Load Balancer and target groups
- IAM roles and policies
- CloudWatch alarms and dashboards
Benefits:
- Version-controlled infrastructure
- Reproducible environments (staging = production)
- No manual configuration or drift
- Peer-reviewed infrastructure changes via Git
- Disaster recovery: Rebuild from templates
CI/CD Pipeline
GitHub Actions Workflow:
The deployment pipeline is automated via GitHub Actions, providing consistent and reliable deployments:
graph LR
A[Code Push to GitHub] --> B[GitHub Actions Triggered]
B --> C[Build Docker Image]
C --> D[Push to ECR]
D --> E[Update ECS Task Definitions]
E --> F[Deploy Web Tasks]
E --> G[Deploy Celery Workers]
E --> H[Deploy Celery Beat]
style A fill:#e8f5e9
style B fill:#fff3e0
style C fill:#e1f5ff
style D fill:#f3e5f5
style E fill:#fff9c4
style F fill:#e8f5e9
style G fill:#e8f5e9
style H fill:#e8f5e9Deployment Process:
- Trigger: Code pushed to main branch or pull request merged
- Build: GitHub Actions workflow executes
- Builds single Docker image containing application code
- Runs tests (optional: can block deployment on failure)
- Tags image with commit SHA and/or semantic version
- Push to ECR: Docker image pushed to Elastic Container Registry in EU-West-2
- ECR provides secure, private Docker registry
- Images stored in same region as deployment (UK)
- Automatic image scanning for vulnerabilities (optional)
- Update Task Definitions: GitHub Actions updates ECS task definitions
- All three task definitions reference the same Docker image
- Only the container command/entrypoint differs per service:
- Web:
gunicorncommand - Celery Worker:
celery workercommand - Celery Beat:
celery beatcommand
- Web:
- Deploy: ECS performs rolling updates
- Web tasks: Rolling deployment with health checks via ALB
- Celery Workers: Rolling update, new tasks pick up from queue
- Celery Beat: Stop old task, start new task (single instance)
Single Image, Multiple Services:
All three ECS task definitions use the same Docker image from ECR. The service type is determined by the command executed:
# Example task definition differences
Web Task Definition:
Image: <ECR_URI>:latest
Command: ["gunicorn", "app.wsgi:application"]
Celery Worker Task Definition:
Image: <ECR_URI>:latest # Same image!
Command: ["celery", "-A", "app", "worker"]
Celery Beat Task Definition:
Image: <ECR_URI>:latest # Same image!
Command: ["celery", "-A", "app", "beat"]
Benefits:
- Single build: One Docker image for all services (faster builds)
- Consistency: All services run identical application code
- Simplified versioning: Single image tag tracks deployment
- Reduced storage: ECR stores one image instead of three
- Atomic deployments: All services deployed from same code version
Comparison to Heroku:
| Aspect | Heroku | AWS ECS |
|---|---|---|
| Deployment trigger | git push heroku | GitHub Actions workflow |
| Build process | Heroku buildpacks | Docker image build |
| Artifact storage | Heroku slug storage | ECR (version-controlled) |
| Deployment control | Limited (auto-deploy) | Full control (approval gates, rollback) |
| Multi-service | Separate apps or Procfile | Task definitions with same image |
| Rollback | heroku releases:rollback | ECS task definition revision or redeploy previous image tag |
Additional CI/CD Capabilities:
- Environment-specific deployments: Separate workflows for staging and production
- Approval gates: Require manual approval before production deployment
- Automated testing: Run integration tests against staging before production
- Blue-green deployments: Deploy new version alongside old, switch traffic
- Canary deployments: Gradually shift traffic to new version
- Automated rollback: Detect failures via CloudWatch alarms and auto-rollback
Cost Analysis
| Component | Heroku (Current) | AWS (Proposed) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Web Application | ~$25-50 | ~$20-35 | ECS Fargate or EC2 instances |
| Celery Worker | ~$25-50 | ~$20-35 | Right-sized for workload |
| Celery Beat | ~$25-50 | ~$10-15 | Smaller instance for scheduler |
| PostgreSQL | ~$15-20 | ~$20-25 | RDS with backups in UK |
| Redis Cache | ~$15-20 | ~$10-15 | ElastiCache (cache + result backend) |
| SQS Message Queue | Included in dyno | ~$1-3 | Pay per million requests, negligible cost |
| Load Balancer | Included | ~$15-20 | ALB costs |
| Total | ~$130/month | ~$90-115/month | 12-30% savings |
Cost Optimization Opportunities:
- Auto-scaling with scale-down: Automatically reduce running tasks during low-usage periods (40-50% compute savings during off-peak)
- Reserved instances for baseline workloads (up to 50% additional savings)
- Spot instances for Celery workers (up to 70% savings on compute)
- S3 storage tiers for media files
- CloudWatch log retention policies
- Right-sizing based on actual usage patterns
Multi-Tenant Auto-Scaling Impact: The auto-scaling capability is particularly valuable for multi-tenant architecture where tenant usage patterns vary throughout the day. Instead of paying for peak capacity 24/7 (as with Heroku), ECS automatically scales down during low-usage periods, significantly reducing average compute costs.
Important Note: Cost savings are secondary to compliance requirements. Even if costs were equivalent, the migration would be necessary for UK data residency.
Benefits
1. Compliance and Data Sovereignty (Primary Benefit)
- UK data residency: All infrastructure and data in EU-West-2 (London)
- Backup compliance: Database backups remain in UK
- Audit trail: Full control and visibility over data location
- Regulatory compliance: Meets UK data protection requirements
- Client confidence: Can guarantee UK-only data storage
- Reduced legal risk: Eliminates cross-border data transfer concerns
2. Cost Efficiency
- 15-30% immediate cost reduction (~$130 → ~$90-110/month)
- Automatic scale-down during low usage: 40-50% additional compute savings during off-peak hours
- Multi-tenant load optimization: Auto-scaling handles variable tenant usage patterns efficiently
- Additional savings opportunities with reserved/spot instances
- More granular resource allocation (no paying for unused capacity)
- Flexible pricing models (on-demand, reserved, spot)
- Pay only for actual resource consumption, not fixed capacity
3. Greater Control and Flexibility
Infrastructure Control:
- Full control over container images and runtime environment
- Custom networking and security group configuration
- Direct access to infrastructure-level metrics
- Ability to implement custom security controls
- VPC configuration for network isolation
Operational Flexibility:
- Choose instance types optimized for workload
- Separate scaling policies per service
- Custom monitoring and alerting
- Advanced deployment strategies (blue/green, canary)
Infrastructure-as-Code:
- 100% version-controlled infrastructure using CloudFormation templates
- Entire infrastructure stack defined as code (VPC, ECS, RDS, ElastiCache, ALB, etc.)
- Git-based workflow for infrastructure changes (review, approve, deploy)
- Reproducible environments (staging matches production exactly)
- Disaster recovery: Rebuild entire infrastructure from templates
- Change tracking and audit trail for infrastructure modifications
- Team collaboration on infrastructure changes via pull requests
- No manual ClickOps or undocumented configuration drift
Heroku Limitation: On Heroku, infrastructure is configured via web UI or CLI commands that aren’t easily version-controlled. App configuration can be tracked, but the underlying platform infrastructure (databases, dynos, add-ons) requires manual provisioning and documentation.
4. Performance Improvements
AWS Performance Advantages:
- Dedicated compute resources (no noisy neighbors)
- Auto-scaling for traffic spikes: Automatically adds capacity when multiple tenants become active
- Dynamic resource allocation: Scales up/down based on actual demand (CPU, memory, request count, queue depth)
- Advanced connection pooling (RDS Proxy)
- No 30-second timeout constraints
- Custom CDN configuration (CloudFront)
- Private networking between services (reduced latency)
- Better database performance tuning options
- Independent scaling per service type (web vs. workers)
5. AWS Service Ecosystem
Native Integration:
- Amazon SQS for Celery message broker: Fully managed, serverless queue with no infrastructure to maintain
- S3 for media and static file storage (same region)
- SES for email services
- Lambda for serverless functions
- CloudWatch for comprehensive monitoring (includes native SQS metrics for auto-scaling)
- AWS Secrets Manager for credential management
- IAM roles for secure, passwordless service access
- VPC endpoints for private AWS service access
SQS-Specific Benefits:
- Zero infrastructure management: No Redis/ElastiCache broker to maintain or scale
- Native CloudWatch metrics: ApproximateNumberOfMessagesVisible metric for accurate worker auto-scaling
- Reliability: Built-in message durability and delivery guarantees
- Dead letter queues: Automatic handling of failed tasks
- Cost-effective: Pay only for messages processed (~$0.40 per million requests)
- Unlimited scalability: No capacity planning required
- IAM-based security: No broker credentials to manage
Technical Considerations
Containerization
ECS Container Setup:
- Dockerize Django application (web, Celery, Beat)
- Use ECR (Elastic Container Registry) for image storage
- Multi-stage builds for optimized image sizes
- Health checks for container orchestration
- Environment-based configuration
Database Migration
RDS PostgreSQL:
- Similar to Heroku Postgres (based on PostgreSQL)
- Enhanced monitoring and performance insights
- Automated backups with configurable retention
- Multi-AZ deployment for high availability
- Parameter groups for fine-tuned configuration
- RDS Proxy for connection pooling
Networking and Security
VPC Configuration:
- Private subnets for database and cache
- Public subnets for load balancer
- Security groups for service isolation
- NAT Gateway for outbound traffic from private subnets
- VPC endpoints for AWS services (S3, Secrets Manager)
Security Enhancements:
- IAM roles instead of static credentials
- Secrets Manager for sensitive configuration
- AWS WAF (Web Application Firewall) for web protection
- CloudTrail for audit logging
- Encryption at rest and in transit
Monitoring and Observability
CloudWatch Integration:
- Application logs aggregation
- Custom metrics and dashboards
- Alerting for critical events
- Performance monitoring
- Cost tracking and budgets
X-Ray (Optional):
- Distributed tracing
- Performance bottleneck identification
- Request flow visualization
High Availability
AWS HA Features:
- Multi-AZ RDS deployment
- ECS service auto-recovery
- Application Load Balancer health checks
- Automated backups and snapshots
- Cross-AZ redundancy
Trade-offs
Advantages
- UK data residency and compliance (eliminates critical blocker)
- Cost savings (15-30%)
- 100% infrastructure-as-code with CloudFormation (version control, reproducibility, no drift)
- Greater infrastructure control
- Better performance and scalability
- AWS service ecosystem integration
- More flexible resource allocation
- Enhanced security capabilities
- Better monitoring and observability
Disadvantages
- Increased operational responsibility (less managed than Heroku)
- Steeper learning curve for AWS services
- More complex infrastructure management
- Need for AWS expertise in team
- Infrastructure-as-code maintenance overhead
- More components to monitor and maintain
- Deployment complexity (ECS vs. git push heroku)
Risk Mitigation
- Training and documentation: Invest in AWS training for team
- Infrastructure-as-code: Use Terraform or CloudFormation for reproducibility
- Gradual migration: Test thoroughly in staging environment
- Monitoring from day one: Comprehensive CloudWatch setup before go-live
- AWS support plan: Consider AWS Business Support for expert guidance
- Runbooks and procedures: Document common operational tasks
- Disaster recovery testing: Regular restore testing from backups
Compliance Requirements
UK Data Residency
Requirements Met:
- All compute resources in EU-West-2 (London)
- Database and backups in EU-West-2 (London)
- Redis cache in EU-West-2 (London)
- Application logs in EU-West-2 (CloudWatch Logs)
- S3 storage in EU-West-2 (if used)
Audit Trail:
- CloudTrail logs all API calls and data access
- Resource tagging for compliance tracking
- IAM policies enforce regional restrictions
- AWS Organizations for governance controls
Data Protection Compliance
GDPR/UK GDPR Alignment:
- Data processing within UK jurisdiction
- No cross-border data transfers to USA
- Right to erasure (tenant deletion capabilities)
- Data encryption at rest and in transit
- Audit logs for data access
Conclusion
The migration from Heroku to AWS ECS represents a strategic necessity for Viitata, driven primarily by UK data residency and compliance requirements. The current Heroku architecture creates unacceptable compliance risk due to database backups being retained in the USA, making it impossible to guarantee UK-only data storage.
This migration delivers:
- Resolves critical compliance issue: UK data residency with backups in EU-West-2 (London)
- Eliminates USA data transfer: All data and backups remain in UK
- Cost savings: 15-30% base reduction + 40-50% additional savings from auto-scaling during off-peak
- Auto-scaling with scale-down: Handles multi-tenant traffic spikes automatically while reducing costs during low-usage periods
- 100% version-controlled infrastructure: CloudFormation templates for entire stack, eliminating manual configuration and drift
- Greater operational control: Full infrastructure flexibility and customization
- Performance improvements: Dedicated resources, auto-scaling for spikes, and advanced AWS features
- AWS service ecosystem: Native integration with SQS (message broker), S3, CloudWatch, IAM, and other services
- Serverless message queue: SQS eliminates need to manage message broker infrastructure
- Enhanced security: VPC isolation, IAM roles, Secrets Manager, and encryption
While AWS requires greater operational expertise compared to Heroku’s managed platform, the compliance requirements make this migration essential. The additional benefits of cost savings, performance improvements, and operational flexibility provide further justification beyond the compliance imperative.
Without this migration, Viitata cannot serve clients with UK data residency requirements and remains exposed to compliance risks associated with cross-border backup storage.
References
5 - Frameworks
Overview
This section documents the various frameworks and libraries we use across our application portfolio.
Available Frameworks
Django
Python web framework used for building web applications. We use multiple versions across different projects.
Other Frameworks
Additional framework documentation will be added as needed.
5.1 - Django
Overview
Django is a high-level Python web framework that encourages rapid development and clean, pragmatic design. We use various Django versions across our application portfolio.
Official Documentation
Django Versions in Use
- buying-service-al202339-live - REST based service for caravan buying
- flix-epa-data312-live - EPA logger for metrics/incompletes
- flux-callme-service-al39 - Django REST based service for Callback table inserts in private VPC
- flux-exchange-service-al239 - Django REST based Web Service for Exchange Message workflows
- flux-qab-service-live - Django REST based webservice for TGSL quotes to (new) EPA forms
- flux-quote-service-311-live - Django REST based webservice for TGSL quotes to legacy Laravel EPA forms
- fluxlite-service38-live - Django REST based backend service for Fluxlite mobile app.
- goahead-testsuite - TGSL request / response logger for TGSL service development
- landscape-311-live - Infrastructure graph generator for Adrian Flux applications
- short-term-api-live - Django REST based web service for Short Term Mobile app backend
- sterling-breakdown38-live - Fullstack Django Application for breakdown purchasing
- tgsl-data-service312 - Django based backend for TGSL data synchronisation
- bikesure-affiliates - Bikesure Dealer Directory public frontend
- fakertrail - Django based HTTP Python Logger
- flux-bannerclick-app - Simple custom URL redirects
- flux-callback-service - Django REST based web service for callback sending
- flux-customer-portal - Legacy Policy Documents service for Customer Portal
- flux-epa-learner-docker - Legacy PHP EPA (Adrianflux/learner) - container version
- flux-epa-prd - EPA version 2.0 (Adrian Flux Leaner, Sterling Learner)
- flux-epa-service-new - Metadata data service for Legacy Laravel EPAs
- flux-geo-service - Django REST based web service for GeoData lookups
- flux-geodata-service - Django REST based web service for GeoData lookups ("legacy" apps)
- flux-handler-service - Django REST based web service for Department Info (opening times etc.) lookups
- flux-jaf - Adrian Flux (public) Job Application Form (JAF)
- flux-jam - Job Application Management (JAM) backend for Adrian Flux job applications
- flux-policy-documents-service - Django REST based web service for Sterling Policy Documents
- flux-redirects-service - Redirects manager for Adrian Flux brands URLs
- flux-regabi-data-live - Django REST based web service for car registration / information lookups
- flux-shorturl-app - Simple custom URL redirects for "short" Flux brand URLs
- flux-sitedata-service - Django REST based service for Metadata management Adrian Flux brand sites
- flux-sources-service - Django REST based web service for Flux source code lookups
- flux-worker-service - Worker service for Adrian Flux brand content variables.
- hut-app-launcher - Application Launcher for Adrian Flux brand backends
Version-Specific Documentation
Browse documentation for specific Django versions we use:
- Django 2.2 - LTS (Long Term Support)
- Django 3.0
- Django 3.1
- Django 3.2 - LTS (Long Term Support)
- Django 4.0
- Django 4.1
- Django 4.2 - LTS (Long Term Support)
- Django 5.0
- Django 5.1
- Django 5.2
Key Features
- ORM (Object-Relational Mapping) - Database abstraction layer
- Admin Interface - Auto-generated admin panel
- URL Routing - Clean URL design
- Template Engine - Built-in templating system
- Security - Built-in protections against common vulnerabilities
- Forms & Validation - Robust form handling
5.1.1 - Django 2.2 LTS
Overview
Django 2.2 LTS is a Python web framework release. This is a Long Term Support (LTS) release with extended security updates.
Official Documentation
Applications Using Django 2.2
- buying-service-al202339-live - REST based service for caravan buying
- flux-exchange-service-al239 - Django REST based Web Service for Exchange Message workflows
- fluxlite-service38-live - Django REST based backend service for Fluxlite mobile app.
- sterling-breakdown38-live - Fullstack Django Application for breakdown purchasing
- fakertrail - Django based HTTP Python Logger
- flux-callback-service - Django REST based web service for callback sending
Key Information
- Python Compatibility: Check official docs for supported Python versions
- Support Status: LTS - Extended security support
- End of Support: Check Django Roadmap
Resources
5.1.2 - Django 3.0
Overview
Django 3.0 is a Python web framework release.
Official Documentation
Applications Using Django 3.0
No applications currently using this framework.
Key Information
- Python Compatibility: Check official docs for supported Python versions
Resources
5.1.3 - Django 3.1
Overview
Django 3.1 is a Python web framework release.
Official Documentation
Applications Using Django 3.1
No applications currently using this framework.
Key Information
- Python Compatibility: Check official docs for supported Python versions
Resources
5.1.4 - Django 3.2 LTS
Overview
Django 3.2 LTS is a Python web framework release. This is a Long Term Support (LTS) release with extended security updates.
Official Documentation
Applications Using Django 3.2
- flux-callme-service-al39 - Django REST based service for Callback table inserts in private VPC
- goahead-testsuite - TGSL request / response logger for TGSL service development
- flux-customer-portal - Legacy Policy Documents service for Customer Portal
- flux-policy-documents-service - Django REST based web service for Sterling Policy Documents
- flux-worker-service - Worker service for Adrian Flux brand content variables.
Key Information
- Python Compatibility: Check official docs for supported Python versions
- Support Status: LTS - Extended security support
- End of Support: Check Django Roadmap
Resources
5.1.5 - Django 4.0
Overview
Django 4.0 is a Python web framework release.
Official Documentation
Applications Using Django 4.0
No applications currently using this framework.
Key Information
- Python Compatibility: Check official docs for supported Python versions
Resources
5.1.6 - Django 4.1
Overview
Django 4.1 is a Python web framework release.
Official Documentation
Applications Using Django 4.1
- flux-geodata-service - Django REST based web service for GeoData lookups ("legacy" apps)
- flux-sitedata-service - Django REST based service for Metadata management Adrian Flux brand sites
- flux-sources-service - Django REST based web service for Flux source code lookups
Key Information
- Python Compatibility: Check official docs for supported Python versions
Resources
5.1.7 - Django 4.2 LTS
Overview
Django 4.2 LTS is a Python web framework release. This is a Long Term Support (LTS) release with extended security updates.
Official Documentation
Applications Using Django 4.2
- flux-bannerclick-app - Simple custom URL redirects
- flux-jam - Job Application Management (JAM) backend for Adrian Flux job applications
- flux-redirects-service - Redirects manager for Adrian Flux brands URLs
- hut-app-launcher - Application Launcher for Adrian Flux brand backends
Key Information
- Python Compatibility: Check official docs for supported Python versions
- Support Status: LTS - Extended security support
- End of Support: Check Django Roadmap
Resources
5.1.8 - Django 5.0
Overview
Django 5.0 is a Python web framework release.
Official Documentation
Applications Using Django 5.0
No applications currently using this framework.
Key Information
- Python Compatibility: Check official docs for supported Python versions
Resources
5.1.9 - Django 5.1
Overview
Django 5.1 is a Python web framework release.
Official Documentation
Applications Using Django 5.1
- flux-qab-service-live - Django REST based webservice for TGSL quotes to (new) EPA forms
- flux-quote-service-311-live - Django REST based webservice for TGSL quotes to legacy Laravel EPA forms
- landscape-311-live - Infrastructure graph generator for Adrian Flux applications
- short-term-api-live - Django REST based web service for Short Term Mobile app backend
- flux-geo-service - Django REST based web service for GeoData lookups
- flux-jaf - Adrian Flux (public) Job Application Form (JAF)
- flux-regabi-data-live - Django REST based web service for car registration / information lookups
- flux-shorturl-app - Simple custom URL redirects for "short" Flux brand URLs
- sterling-epa-laravel-van-docke - Legacy PHP EPA (Sterling/Van) - container version
Key Information
- Python Compatibility: Check official docs for supported Python versions
Resources
5.1.10 - Django 5.2 LTS
Overview
Django 5.2 is a Python web framework release. This is a Long Term Support (LTS) release with extended security updates.
Official Documentation
Applications Using Django 5.2
- flix-epa-data312-live - EPA logger for metrics/incompletes
- bikesure-affiliates - Bikesure Dealer Directory public frontend
- flux-epa-service-new - Metadata data service for Legacy Laravel EPAs
- flux-handler-service - Django REST based web service for Department Info (opening times etc.) lookups
Key Information
- Python Compatibility: Check official docs for supported Python versions
Resources
6 - Libraries
Overview
This section contains documentation for private packages and libraries developed and maintained internally. These libraries are used across multiple applications in the ecosystem.
Browse Libraries
Navigate through the sidebar to explore individual library documentation, or use the search feature to find specific packages.
6.1 - bannerclick
Overview
Private package library used across multiple applications.
Repository
- GitHub: https://github.com/Hut42/bannerclick
- Language: Python
- Created: 2023-04-25
- Last Updated: 2023-05-01
Documentation
bannerclick
bannerclick api to set redirects and track visits
[Full documentation available in the repository README]
Usage
This library is used by 1 application(s):
- flux-redirects-service - Redirects manager for Adrian Flux brands URLs
6.2 - django-bulk-redirects
Overview
Bulk redirector
Repository
- GitHub: https://github.com/Hut42/django-bulk-redirects
- Language: Python
- Created: 2023-03-13
- Last Updated: 2023-07-18
Latest Release
- Version: 0.46
- Published: 2023-07-18
Documentation
django-bulk-redirects
Service logic to handle redirects from one service to another.
[Full documentation available in the repository README]
Usage
This library is used by 1 application(s):
- flux-redirects-service - Redirects manager for Adrian Flux brands URLs
6.3 - django-cardutils
Overview
Payment card utilities.
Repository
- GitHub: https://github.com/Hut42/hut-python-cardutils
- Language: Python
- Created: 2020-03-03
- Last Updated: 2025-02-02
Documentation
django-cardutils
Payment card utilities.
[Full documentation available in the repository README]
Usage
This library is used by 1 application(s):
- buying-service-al202339-live - REST based service for caravan buying
6.4 - django-cors-headers-model
Overview
Persistent CORS configuration restrored.
Repository
- GitHub: https://github.com/Hut42/django-cors-headers-model
- Language: Python
- Created: 2023-05-05
- Last Updated: 2023-11-22
Documentation
django-cors-headers-model
Persistent CORS configuration restrored.
[Full documentation available in the repository README]
Usage
This library is used by 4 application(s):
- flux-callme-service-al39 - Django REST based service for Callback table inserts in private VPC
- short-term-api-live - Django REST based web service for Short Term Mobile app backend
- flux-geodata-service - Django REST based web service for GeoData lookups ("legacy" apps)
- flux-sitedata-service - Django REST based service for Metadata management Adrian Flux brand sites
6.5 - django-drf-extensions
Overview
Standard extensions for Django Rest Framework.
Repository
- GitHub: https://github.com/Hut42/django-drf-extensions
- Language: Python
- Created: 2023-01-22
- Last Updated: 2024-09-12
Latest Release
- Version: 0.7
- Published: 2023-08-04
Documentation
django-drf-extensions
Standard extensions for Django Rest Framework.
[Full documentation available in the repository README]
Usage
This library is used by 10 application(s):
- bannerclick - Private package library
- django-bulk-redirects - Bulk redirector
- flux-jobs - Flux job application capture and management
- flux-sitedata - Sitedata for Flux brands.
- flux-sitedata-v2-shim - API compatibility shim for v1 clients to use v2 service.
- flix-epa-data312-live - EPA logger for metrics/incompletes
- flux-qab-service-live - Django REST based webservice for TGSL quotes to (new) EPA forms
- flux-quote-service-311-live - Django REST based webservice for TGSL quotes to legacy Laravel EPA forms
- flux-regabi-data-live - Django REST based web service for car registration / information lookups
- flux-sitedata-service - Django REST based service for Metadata management Adrian Flux brand sites
6.6 - django-hut-python-validators
Overview
extensions to hut-python-validators to allow for usage in django.
Repository
- GitHub: https://github.com/Hut42/django-hut-python-validators
- Language: Python
- Created: 2025-07-22
- Last Updated: 2025-11-07
Latest Release
- Version: v0.5
- Published: 2025-11-07
Documentation
django-hut-python-validators
extensions to hut-python-validators to allow for usage in django.
[Full documentation available in the repository README]
Usage
This library is used by 1 application(s):
- bikesure-affiliates - Bikesure Dealer Directory public frontend
6.7 - django-hut-theme
Overview
Simple Hut branded django admin theme
Repository
- GitHub: https://github.com/Hut42/django-hut-theme
- Language: CSS
- Created: 2021-04-08
- Last Updated: 2021-04-16
Documentation
django-hut-theme
Simple Hut branded django admin theme.
[Full documentation available in the repository README]
Usage
This library is used by 13 application(s):
- flix-epa-data312-live - EPA logger for metrics/incompletes
- flux-qab-service-live - Django REST based webservice for TGSL quotes to (new) EPA forms
- flux-quote-service-311-live - Django REST based webservice for TGSL quotes to legacy Laravel EPA forms
- short-term-api-live - Django REST based web service for Short Term Mobile app backend
- flux-geo-service - Django REST based web service for GeoData lookups
- flux-geodata-service - Django REST based web service for GeoData lookups ("legacy" apps)
- flux-policy-documents-service - Django REST based web service for Sterling Policy Documents
- flux-redirects-service - Redirects manager for Adrian Flux brands URLs
- flux-regabi-data-live - Django REST based web service for car registration / information lookups
- flux-shorturl-app - Simple custom URL redirects for "short" Flux brand URLs
- flux-sitedata-service - Django REST based service for Metadata management Adrian Flux brand sites
- hut-app-launcher - Application Launcher for Adrian Flux brand backends
- sterling-epa-laravel-van-docke - Legacy PHP EPA (Sterling/Van) - container version
6.8 - django-microservice
Overview
Base functionality for django based microservice
Repository
- GitHub: https://github.com/Hut42/django-microservice
- Language: Python
- Created: 2018-11-28
- Last Updated: 2023-03-15
Documentation
django-microservice
App that will install and configure Django / Django Rest Framework (DRF) with a base set of functionality and sensible defaults.
NOTE: Version 2.x has a pile of backwards-incompatible breaking changes. See CHANGELOG.md for exact details.
Requirements
- Python (3.6.8, 3.7.x)
- Django (3.2)
Installation
As the package is hosted on Gemfury, :code:FURY_AUTH should be in your environment variables with a valid deploy token.
Use pip (version > 20.0) to install.
.. code-block:: bash
pip install django-microservice --extra-index-url https://${FURY_AUTH}:@pypi.fury.io/hutfortytwo/
Or, in your :code:requirements.txt like:
.. code-block:: python
[...]
# Private requirements
--extra-index-url https://${FURY_AUTH}:@pypi.fury.io/hutfortytwo/
django-microservice>=2.0,<3.0
Add :code:'microservice' to your :code:INSTALLED_APPS setting.
.. code-block:: python
INSTALLED_APPS = [
...
'microservice',
]
Installed Apps
[Full documentation available in the repository README]
Usage
This library is used by 5 application(s):
- buying-service-al202339-live - REST based service for caravan buying
- flux-exchange-service-al239 - Django REST based Web Service for Exchange Message workflows
- goahead-testsuite - TGSL request / response logger for TGSL service development
- flux-callback-service - Django REST based web service for callback sending
- flux-policy-documents-service - Django REST based web service for Sterling Policy Documents
6.9 - django-rest-cereal
Overview
Simple dynamic serializers for DRF.
Repository
- GitHub: https://github.com/Hut42/django-rest-cereal
- Language: Python
- Created: 2021-04-19
- Last Updated: 2021-06-16
Documentation
django-rest-cereal
Simple dynamic serializers for DRF.
[Full documentation available in the repository README]
Usage
This library is used by 1 application(s):
- buying-service-al202339-live - REST based service for caravan buying
6.10 - django-simpleaudit
Overview
Private package library used across multiple applications.
Repository
- GitHub: https://github.com/Hut42/django-simpleaudit
- Language: Python
- Created: 2019-01-25
- Last Updated: 2020-03-27
Latest Release
- Version:
- Published: 2020-03-27
Documentation
django-simpleaudit
Django simple audit trail and Useful Mixin thing
[Full documentation available in the repository README]
Usage
This library is used by 2 application(s):
- flux-exchange-service-al239 - Django REST based Web Service for Exchange Message workflows
- flux-handler-service - Django REST based web service for Department Info (opening times etc.) lookups
6.11 - epa-data-client
Overview
Python client for epa-data microservice.
Repository
- GitHub: https://github.com/Hut42/epa-data-client
- Language: Makefile
- Created: 2024-09-05
- Last Updated: 2024-09-05
Documentation
{REPOSITORY_NAME}
{SHORT_DESCRIPTION}
[Full documentation available in the repository README]
Usage
This library is not currently used by any documented applications.
6.12 - flux-callme-sdk
Overview
Python SDK for flux-callme-service.
Repository
- GitHub: https://github.com/Hut42/flux-callme-sdk
- Language: Python
- Created: 2019-05-07
- Last Updated: 2019-11-07
Documentation
flux-callme-sdk
SDK for flux-callme-service.
[Full documentation available in the repository README]
Usage
This library is used by 2 application(s):
- flux-callme-service-al39 - Django REST based service for Callback table inserts in private VPC
- flux-callback-service - Django REST based web service for callback sending
6.13 - flux-exchange-handler-sdk
Overview
SDK for creation of new Exchange Message Handlers
Repository
- GitHub: https://github.com/Hut42/flux-exchange-handler-sdk
- Language: Python
- Created: 2019-11-22
- Last Updated: 2019-11-22
Documentation
package
[Full documentation available in the repository README]
Usage
This library is used by 1 application(s):
- flux-exchange-service-al239 - Django REST based Web Service for Exchange Message workflows
6.14 - flux-go
Overview
Python library for Flux policy buying transactions.
Repository
- GitHub: https://github.com/Hut42/flux-go
- Language: Python
- Created: 2025-03-08
- Last Updated: 2025-03-10
Latest Release
- Version: v2.4
- Published: 2025-03-10
Documentation
flux-go
Python library for Flux policy buying transactions.
[Full documentation available in the repository README]
Usage
This library is used by 1 application(s):
- buying-service-al202339-live - REST based service for caravan buying
6.15 - flux-goahead
Overview
Flux/TGSL policy processing library
Repository
- GitHub: https://github.com/Hut42/flux-goahead
- Language: Python
- Created: 2018-06-26
- Last Updated: 2022-11-01
Documentation
flux-goahead
Flux/TGSL policy processing library
[Full documentation available in the repository README]
Usage
This library is used by 2 application(s):
- buying-service-al202339-live - REST based service for caravan buying
- goahead-testsuite - TGSL request / response logger for TGSL service development
6.16 - flux-handler-sdk
Overview
Python SDK for flux-handler-service.
Repository
- GitHub: https://github.com/Hut42/flux-handler-sdk
- Language: Python
- Created: 2019-05-07
- Last Updated: 2019-11-26
Documentation
flux-handler-sdk
SDK for flux-handler-service.
[Full documentation available in the repository README]
Usage
This library is used by 1 application(s):
- flux-callback-service - Django REST based web service for callback sending
6.17 - flux-jobs
Overview
Flux job application capture and management
Repository
- GitHub: https://github.com/Hut42/flux-jobs-form
- Language: Python
- Created: 2023-04-28
- Last Updated: 2023-08-15
Latest Release
- Version: 0.73
- Published: 2023-07-26
Documentation
flux-jobs
Flux job application capture and management.
[Full documentation available in the repository README]
Usage
This library is used by 1 application(s):
- flux-jam - Job Application Management (JAM) backend for Adrian Flux job applications
6.18 - flux-sagepay
Overview
Payment library for Flux SagePay transactions.
Repository
- GitHub: https://github.com/Hut42/flux-sagepay
- Language: Python
- Created: 2025-03-08
- Last Updated: 2025-07-30
Latest Release
- Version: v2.7
- Published: 2025-07-30
Documentation
flux-sagepay
Payment library for Flux SagePay transactions.
[Full documentation available in the repository README]
Usage
This library is used by 2 application(s):
- buying-service-al202339-live - REST based service for caravan buying
- goahead-testsuite - TGSL request / response logger for TGSL service development
6.19 - flux-sitedata
Overview
Sitedata for Flux brands.
Repository
- GitHub: https://github.com/Hut42/flux-sitedata
- Language: Python
- Created: 2023-02-02
- Last Updated: 2023-07-17
Latest Release
- Version: 0.14
- Published: 2023-07-17
Documentation
flux-sitedata
Sitedata for Flux brands.
[Full documentation available in the repository README]
Usage
This library is used by 2 application(s):
- flux-sitedata-v2-shim - API compatibility shim for v1 clients to use v2 service.
- flux-sitedata-service - Django REST based service for Metadata management Adrian Flux brand sites
6.20 - flux-sitedata-v2-shim
Overview
API compatibility shim for v1 clients to use v2 service.
Repository
- GitHub: https://github.com/Hut42/flux-sitedata-v2-shim
- Language: Python
- Created: 2023-02-17
- Last Updated: 2023-07-17
Latest Release
- Version: 1.3
- Published: 2023-07-17
Documentation
flux-sitedata-v2-shim
API compatibility shim for v1 clients to use v2 service.
This also includes the initial metadata models - these should be removed at the earliest opportunity.
[Full documentation available in the repository README]
Usage
This library is used by 1 application(s):
- flux-sitedata-service - Django REST based service for Metadata management Adrian Flux brand sites
6.21 - flux-tgsl-endpoints
Overview
Global TGSL test/live endpoints
Repository
- GitHub: https://github.com/Hut42/flux-tgsl-endpoints
- Language: Python
- Created: 2021-05-12
- Last Updated: 2021-05-12
Documentation
flux-tgsl-endpoints
Global TGSL test/live endpoints.
[Full documentation available in the repository README]
Usage
This library is used by 1 application(s):
- buying-service-al202339-live - REST based service for caravan buying
6.22 - flux-tgsl-listdata
Overview
Flux TGSL list and system data
Repository
- GitHub: https://github.com/Hut42/flux-tgsl-listdata
- Language: Python
- Created: 2021-10-19
- Last Updated: 2022-07-07
Documentation
flux-tgsl-listdata
Flux TGSL list and system data
[Full documentation available in the repository README]
Usage
This library is used by 1 application(s):
- buying-service-al202339-live - REST based service for caravan buying
6.23 - hut-django-models
Overview
Private package library used across multiple applications.
Repository
- GitHub: https://github.com/Hut42/hut-django-models
- Language: Python
- Created: 2022-03-10
- Last Updated: 2022-12-01
Documentation
hut-django-models
Common Django models that are used by Hut.
============ HutBaseModel
Base model that all models should inherit from.
Adds core base functionality to all models in an application.
A uuid field will be used in APIs etc. in order to hide the numerical PK.
The created_by, created_at, updated_by and created_at are all fields
used for a simple audit trail type operation.
history is a hook into https://github.com/jazzband/django-simple-history
which will track changes at an object level.
Add it to the middleware classes in your settings.py::
MIDDLEWARE = (
...,
'django_currentuser.middleware.ThreadLocalUserMiddleware',
)
[Full documentation available in the repository README]
Usage
This library is used by 2 application(s):
- flux-policy-documents-service - Django REST based web service for Sterling Policy Documents
- flux-worker-service - Worker service for Adrian Flux brand content variables.
6.24 - hut-python-cardutils
Overview
Payment card utilities.
Repository
- GitHub: https://github.com/Hut42/hut-python-cardutils
- Language: Python
- Created: 2020-03-03
- Last Updated: 2025-02-02
Documentation
django-cardutils
Payment card utilities.
[Full documentation available in the repository README]
Usage
This library is used by 1 application(s):
- short-term-api-live - Django REST based web service for Short Term Mobile app backend
6.25 - hut-python-validators
Overview
Python data normalization and validation.
Repository
- GitHub: https://github.com/Hut42/hut-python-validators
- Language: Python
- Created: 2025-06-22
- Last Updated: 2025-11-07
Latest Release
- Version: v0.5
- Published: 2025-11-07
Documentation
hut-python-validators
Python data normalization and validation for UK-specific formats.
This library provides utilities to normalize and validate common UK data formats including postcodes, vehicle registration numbers, and telephone numbers.
============ Installation
.. code-block:: bash
pip install hut-python-validators
======== Features
UK Postcodes
Normalize and validate UK postcodes according to the Royal Mail PAF format.
normalize_postcode
Normalizes a UK postcode by converting to uppercase, removing spaces, and optionally reformatting with a space before the last three characters.
.. code-block:: python
from hut_validators.postcodes import normalize_postcode
# Basic normalization (adds space)
normalize_postcode("ec1a1bb")
# Returns: 'EC1A 1BB'
# Without space
normalize_postcode("ec1a1bb", add_space=False)
# Returns: 'EC1A1BB'
# Handles existing spaces and whitespace
normalize_postcode(" EC1A 1BB ")
# Returns: 'EC1A 1BB'
**Parameters:**
* ``postcode`` (str): The postcode to normalize
* ``add_space`` (bool, optional): Whether to insert a space before the last three characters. Defaults to True.
*[Full documentation available in the repository README]*
## Usage
This library is used by 2 application(s):
- django-hut-python-validators - extensions to hut-python-validators to allow for usage in django.
- bikesure-affiliates - Bikesure Dealer Directory public frontend
6.26 - regabi-client
Overview
Python client for RegAbi microservice
Repository
- GitHub: https://github.com/Hut42/regabi-client
- Language: Python
- Created: 2024-09-19
- Last Updated: 2025-06-11
Documentation
regabi-client
Python client for RegAbi microservice
[Full documentation available in the repository README]
Usage
This library is not currently used by any documented applications.
6.27 - sources-client
Overview
Python client for sources microservice.
Repository
- GitHub: https://github.com/Hut42/sources-client
- Language: Python
- Created: 2024-09-05
- Last Updated: 2024-09-05
Documentation
sources-client
Python client for sources microservice.
[Full documentation available in the repository README]
Usage
This library is not currently used by any documented applications.
6.28 - tgsl
Overview
TGSL request / trace related SDK.
Repository
- GitHub: https://github.com/Hut42/tgsl
- Language: Python
- Created: 2022-11-05
- Last Updated: 2022-11-05
Documentation
tgsl
TGSL request / trace related SDK.
[Full documentation available in the repository README]
Usage
This library is used by 1 application(s):
- goahead-testsuite - TGSL request / response logger for TGSL service development
6.29 - tgsl-metadata
Overview
TGSL list metadata
Repository
- GitHub: https://github.com/Hut42/tgsl-metadata
- Language: Python
- Created: 2023-12-19
- Last Updated: 2024-09-05
Documentation
tgsl-metadata
TGSL list metadata
[Full documentation available in the repository README]
Usage
This library is used by 1 application(s):
- short-term-api-live - Django REST based web service for Short Term Mobile app backend
7 - Proposals
Overview
This section contains proposals for significant changes to applications, infrastructure, or architecture. Each proposal documents the rationale, impact, and implementation plan.
Active Proposals
Browse all proposals below or navigate through the sidebar.
Proposal Template
When creating a new proposal, include:
- Summary - Brief overview of the proposed change
- Rationale - Why this change is needed
- Impact - Which applications and systems are affected
- Implementation Plan - Steps to execute the proposal
- Risks - Potential issues and mitigation strategies
- Status - Draft, Under Review, Approved, Implemented, Rejected
7.1 - Edge Department Info Service Migration
Summary
Proposal for the migration and modernization of the edge-department-info-service.
Rationale
[To be filled in - reasons for this change]
Key benefits expected:
- [List expected benefits]
Affected Applications
- flux-handler-service - Django REST based web service for Department Info (opening times etc.) lookups
Impact
Services Affected
- Edge department info service
- [List additional services and dependencies]
Technical Considerations
- API compatibility with existing consumers
- Department data accuracy and synchronization
- Performance and response time requirements
- Caching strategy for department information
Data Considerations
- Department data storage and updates
- Data consistency across systems
- Data source integration
- Master data management
Implementation Plan
Phase 1: Assessment & Design
- Document current service functionality
- Identify all consumers and integration points
- Evaluate target architecture/platform
- Assess data migration requirements
- Define migration strategy
- Create proof of concept
Phase 2: Development
- Set up new infrastructure
- Implement/migrate core functionality
- Configure API endpoints
- Set up authentication and authorization
- Implement monitoring and logging
- Create comprehensive test suite
Phase 3: Migration
- Deploy to staging environment
- Integration testing with consumers
- Performance and load testing
- Data validation testing
- User acceptance testing
- Security review
- Create rollback procedures
Phase 4: Cutover
- Deploy to production
- Gradual traffic migration
- Monitor service health and performance
- Update consumer configurations
- Decommission old infrastructure
- Archive legacy documentation
Risks & Mitigation
| Risk | Impact | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|
| Service disruption | High | Gradual cutover with parallel running systems |
| Department data inconsistency | High | Thorough data validation and testing |
| Performance degradation | Medium | Load testing and capacity planning |
| Integration breakage | High | Extensive integration testing before cutover |
| Data source synchronization issues | Medium | Implement robust data sync mechanisms |
Timeline
[To be determined]
Status
Current Status: Draft
History:
- 2025-12-22: Proposal created
7.2 - Edge Sources Service Migration
Summary
Proposal for the migration and modernization of the edge-sources-service.
Rationale
[To be filled in - reasons for this change]
Key benefits expected:
- [List expected benefits]
Affected Applications
No applications currently associated with this proposal.
Impact
Services Affected
- Edge sources service
- [List additional services and dependencies]
Technical Considerations
- API compatibility with existing consumers
- Sources data accuracy and synchronization
- Performance and response time requirements
- Caching strategy for sources information
Data Considerations
- Sources data storage and updates
- Data consistency across systems
- Data source integration
- Master data management
Implementation Plan
Phase 1: Assessment & Design
- Document current service functionality
- Identify all consumers and integration points
- Evaluate target architecture/platform
- Assess data migration requirements
- Define migration strategy
- Create proof of concept
Phase 2: Development
- Set up new infrastructure
- Implement/migrate core functionality
- Configure API endpoints
- Set up authentication and authorization
- Implement monitoring and logging
- Create comprehensive test suite
Phase 3: Migration
- Deploy to staging environment
- Integration testing with consumers
- Performance and load testing
- Data validation testing
- User acceptance testing
- Security review
- Create rollback procedures
Phase 4: Cutover
- Deploy to production
- Gradual traffic migration
- Monitor service health and performance
- Update consumer configurations
- Decommission old infrastructure
- Archive legacy documentation
Risks & Mitigation
| Risk | Impact | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|
| Service disruption | High | Gradual cutover with parallel running systems |
| Sources data inconsistency | High | Thorough data validation and testing |
| Performance degradation | Medium | Load testing and capacity planning |
| Integration breakage | High | Extensive integration testing before cutover |
| Data source synchronization issues | Medium | Implement robust data sync mechanisms |
Timeline
[To be determined]
Status
Current Status: Draft
History:
- 2025-12-22: Proposal created
7.3 - Migrate Applications from Elastic Beanstalk to AWS Fargate
Summary
Proposal to migrate applications currently hosted on Elastic Beanstalk to AWS Fargate, a serverless container orchestration platform.
Rationale
[To be filled in - reasons for migrating from Elastic Beanstalk to Fargate]
Key benefits expected:
- Greater infrastructure control and flexibility
- Improved cost efficiency at scale
- Enhanced performance and resource allocation
- Better integration with AWS ecosystem
- Reduced vendor lock-in
- Improved scalability options
Affected Applications
- buying-service-al202339-live - REST based service for caravan buying
Impact
Services Affected
- All Elastic Beanstalk-hosted applications
- [List specific applications to be migrated]
Technical Considerations
- Container image creation and registry setup (ECR)
- VPC and networking configuration
- Load balancer setup (ALB/NLB)
- Service discovery and task definitions
- Auto-scaling policies
- CI/CD pipeline modifications
- Logging and monitoring infrastructure
- Secret management (AWS Secrets Manager/Parameter Store)
Infrastructure Considerations
- Database migration (Elastic Beanstalk Postgres to RDS/Aurora)
- Redis/cache migration (Elastic Beanstalk Redis to ElastiCache)
- File storage migration (S3 integration)
- Add-on replacements and alternatives
- Domain and DNS configuration
- SSL/TLS certificate management
Data Considerations
- Database backup and migration strategy
- Data consistency during migration
- Downtime requirements
- Rollback procedures
Implementation Plan
Phase 1: Assessment & Design
- Audit all Elastic Beanstalk applications and dependencies
- Document current Elastic Beanstalk add-ons and services
- Design AWS infrastructure architecture
- Map Elastic Beanstalk add-ons to AWS equivalents
- Containerize applications (if not already containerized)
- Create cost analysis and comparison
- Define migration priority and sequence
Phase 2: Infrastructure Setup
- Set up AWS accounts and IAM roles
- Configure VPC, subnets, and security groups
- Set up container registry (ECR)
- Configure ECS clusters and Fargate capacity
- Set up load balancers and target groups
- Configure CloudWatch logging and monitoring
- Set up AWS Secrets Manager
- Create infrastructure as code (Terraform/CloudFormation)
Phase 3: Application Preparation
- Create Dockerfiles for each application
- Build and test container images
- Create ECS task definitions
- Configure environment variables and secrets
- Set up CI/CD pipelines for container builds
- Implement health checks and monitoring
- Create deployment scripts
Phase 4: Data Migration
- Set up target databases (RDS/Aurora)
- Configure database replication (if applicable)
- Plan data migration windows
- Test database migration procedures
- Migrate Redis/cache data
- Migrate file storage to S3
Phase 5: Testing & Validation
- Deploy to staging/test environment
- Perform integration testing
- Load and performance testing
- Security and compliance review
- Validate monitoring and alerting
- Test disaster recovery procedures
Phase 6: Migration & Cutover
- Execute database migration
- Deploy applications to Fargate
- Update DNS records
- Monitor application health and performance
- Validate all functionality
- Address any issues
- Decommission Elastic Beanstalk applications
- Cancel Elastic Beanstalk subscriptions
Risks & Mitigation
| Risk | Impact | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|
| Extended downtime during migration | Critical | Plan careful cutover with blue-green deployment |
| Data loss during database migration | Critical | Multiple backups, test migrations, validation procedures |
| Application compatibility issues | High | Thorough testing in staging environment |
| Increased operational complexity | Medium | Comprehensive documentation, training, automation |
| Cost overruns | Medium | Detailed cost analysis, monitoring, right-sizing |
| Performance degradation | High | Performance testing, proper resource allocation |
| Loss of Elastic Beanstalk add-on functionality | Medium | Identify and implement AWS equivalents beforehand |
| CI/CD pipeline disruption | Medium | Test new pipelines before cutover |
Timeline
[To be determined]
Status
Current Status: Draft
History:
- 2025-12-22: Proposal created
7.4 - Migrate Applications from Heroku to AWS Fargate
Summary
Proposal to migrate applications currently hosted on Heroku to AWS Fargate, a serverless container orchestration platform.
Rationale
[To be filled in - reasons for migrating from Heroku to Fargate]
Key benefits expected:
- Greater infrastructure control and flexibility
- Improved cost efficiency at scale
- Enhanced performance and resource allocation
- Better integration with AWS ecosystem
- Reduced vendor lock-in
- Improved scalability options
Affected Applications
- bikesure-affiliates - Bikesure Dealer Directory public frontend
Impact
Services Affected
- All Heroku-hosted applications
- [List specific applications to be migrated]
Technical Considerations
- Container image creation and registry setup (ECR)
- VPC and networking configuration
- Load balancer setup (ALB/NLB)
- Service discovery and task definitions
- Auto-scaling policies
- CI/CD pipeline modifications
- Logging and monitoring infrastructure
- Secret management (AWS Secrets Manager/Parameter Store)
Infrastructure Considerations
- Database migration (Heroku Postgres to RDS/Aurora)
- Redis/cache migration (Heroku Redis to ElastiCache)
- File storage migration (S3 integration)
- Add-on replacements and alternatives
- Domain and DNS configuration
- SSL/TLS certificate management
Data Considerations
- Database backup and migration strategy
- Data consistency during migration
- Downtime requirements
- Rollback procedures
Implementation Plan
Phase 1: Assessment & Design
- Audit all Heroku applications and dependencies
- Document current Heroku add-ons and services
- Design AWS infrastructure architecture
- Map Heroku add-ons to AWS equivalents
- Containerize applications (if not already containerized)
- Create cost analysis and comparison
- Define migration priority and sequence
Phase 2: Infrastructure Setup
- Set up AWS accounts and IAM roles
- Configure VPC, subnets, and security groups
- Set up container registry (ECR)
- Configure ECS clusters and Fargate capacity
- Set up load balancers and target groups
- Configure CloudWatch logging and monitoring
- Set up AWS Secrets Manager
- Create infrastructure as code (Terraform/CloudFormation)
Phase 3: Application Preparation
- Create Dockerfiles for each application
- Build and test container images
- Create ECS task definitions
- Configure environment variables and secrets
- Set up CI/CD pipelines for container builds
- Implement health checks and monitoring
- Create deployment scripts
Phase 4: Data Migration
- Set up target databases (RDS/Aurora)
- Configure database replication (if applicable)
- Plan data migration windows
- Test database migration procedures
- Migrate Redis/cache data
- Migrate file storage to S3
Phase 5: Testing & Validation
- Deploy to staging/test environment
- Perform integration testing
- Load and performance testing
- Security and compliance review
- Validate monitoring and alerting
- Test disaster recovery procedures
Phase 6: Migration & Cutover
- Execute database migration
- Deploy applications to Fargate
- Update DNS records
- Monitor application health and performance
- Validate all functionality
- Address any issues
- Decommission Heroku applications
- Cancel Heroku subscriptions
Risks & Mitigation
| Risk | Impact | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|
| Extended downtime during migration | Critical | Plan careful cutover with blue-green deployment |
| Data loss during database migration | Critical | Multiple backups, test migrations, validation procedures |
| Application compatibility issues | High | Thorough testing in staging environment |
| Increased operational complexity | Medium | Comprehensive documentation, training, automation |
| Cost overruns | Medium | Detailed cost analysis, monitoring, right-sizing |
| Performance degradation | High | Performance testing, proper resource allocation |
| Loss of Heroku add-on functionality | Medium | Identify and implement AWS equivalents beforehand |
| CI/CD pipeline disruption | Medium | Test new pipelines before cutover |
Timeline
[To be determined]
Status
Current Status: Draft
History:
- 2025-12-22: Proposal created
7.5 - Migrate Applications from Heroku to Cloudflare
Summary
Proposal to migrate applications currently hosted on Heroku to Cloudflare’s edge computing platform (Workers, Pages, etc.).
Rationale
[To be filled in - reasons for migrating from Heroku to Cloudflare]
Key benefits expected:
- Edge computing with global low-latency performance
- Improved cost efficiency
- Automatic global distribution
- Built-in DDoS protection and security
- Reduced infrastructure complexity
- Better integration with Cloudflare ecosystem
- Zero cold starts (Workers)
Affected Applications
- flux-buying-pages-tour-caravan - Placeholder description
Impact
Services Affected
- All Heroku-hosted applications targeted for migration
- [List specific applications to be migrated]
Technical Considerations
- Application architecture adaptation for edge computing
- Cloudflare Workers runtime compatibility
- Request/response size limitations
- Execution time limits (CPU time constraints)
- Code bundling and module system
- API compatibility and framework support
- Stateless architecture requirements
Platform Considerations
- Cloudflare Workers vs Pages vs hybrid approach
- Database migration (D1, Durable Objects, or external)
- KV storage for caching and session data
- R2 for object storage needs
- Queue system for async processing
- Analytics and monitoring setup
- Custom domain configuration
Data Considerations
- Database compatibility and migration strategy
- Session storage and state management
- File/asset storage migration
- Data residency and compliance requirements
Implementation Plan
Phase 1: Assessment & Design
- Audit all Heroku applications and dependencies
- Evaluate application compatibility with Cloudflare platform
- Identify applications suitable for Workers vs Pages
- Design edge-native architecture
- Map Heroku add-ons to Cloudflare/external equivalents
- Assess code refactoring requirements
- Create cost analysis and comparison
- Define migration priority and sequence
Phase 2: Development Environment Setup
- Set up Cloudflare accounts and API tokens
- Configure Wrangler CLI and development tools
- Set up local development environment
- Create project structure and repositories
- Configure environment variables and secrets
- Set up Cloudflare bindings (KV, D1, R2, etc.)
Phase 3: Application Migration
- Refactor applications for edge compatibility
- Adapt middleware and frameworks to Workers runtime
- Implement database access patterns for D1/Durable Objects
- Configure KV storage for sessions/cache
- Set up R2 for file storage
- Implement logging and error handling
- Bundle and optimize application code
- Create deployment configurations
Phase 4: Data Migration
- Set up target databases (D1, external DB, or Durable Objects)
- Plan data migration strategy
- Migrate database content
- Migrate KV data
- Migrate static assets to R2 or Pages
- Validate data integrity
Phase 5: Testing & Validation
- Deploy to Cloudflare preview environments
- Integration testing
- Edge performance testing
- Geographic distribution validation
- Load testing with global traffic simulation
- Security review
- Test custom domains and SSL
Phase 6: Migration & Cutover
- Deploy to Cloudflare production
- Configure DNS and custom domains
- Gradual traffic migration via DNS/load balancing
- Monitor performance and error rates
- Validate functionality across regions
- Address any issues
- Decommission Heroku applications
- Cancel Heroku subscriptions
Risks & Mitigation
| Risk | Impact | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|
| Runtime compatibility issues | High | Thorough testing, identify incompatibilities early |
| CPU time limit exceeded | High | Optimize code, consider splitting workloads |
| Database performance on D1 | Medium | Evaluate alternative database solutions if needed |
| Cold start issues (if any) | Low | Workers have minimal cold starts, but monitor |
| Code refactoring complexity | High | Incremental migration, thorough testing |
| Loss of Heroku add-on functionality | Medium | Identify Cloudflare or external equivalents |
| Geographic data compliance | High | Understand Cloudflare’s data residency options |
| Vendor lock-in to Cloudflare | Medium | Abstract critical services where possible |
| Development workflow changes | Medium | Training and documentation for team |
Timeline
[To be determined]
Status
Current Status: Draft
History:
- 2025-12-22: Proposal created
7.6 - Migrate Exchange REST API to Serverless
Summary
Proposal to migrate the exchange REST API to a serverless architecture using the Exchange serverless stack.
Rationale
[To be filled in - reasons for migrating to serverless]
Key benefits expected:
- Improved scalability
- Reduced operational overhead
- Cost optimization through pay-per-use model
- Enhanced deployment flexibility
Affected Applications
- flux-exchange-service-al239 - Django REST based Web Service for Exchange Message workflows
Impact
Services Affected
- Exchange REST API endpoints
- [List additional services]
Technical Considerations
- API contract compatibility
- Authentication/authorization changes
- Performance characteristics
- Monitoring and logging setup
Data Considerations
- Database connection management
- State management in serverless environment
- Caching strategy
Implementation Plan
Phase 1: Assessment & Design
- Audit current REST API endpoints
- Design serverless architecture
- Evaluate AWS Lambda/serverless framework
- Define resource requirements
- Create proof of concept
Phase 2: Development
- Set up serverless infrastructure
- Implement API endpoints in serverless stack
- Configure API Gateway/routing
- Implement authentication/authorization
- Set up monitoring and logging
- Create automated tests
Phase 3: Migration
- Deploy to staging environment
- Performance testing
- Load testing
- Security review
- Create rollback plan
Phase 4: Cutover
- Deploy to production
- Update DNS/routing
- Monitor performance
- Decommission old infrastructure
Risks & Mitigation
| Risk | Impact | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|
| API downtime during migration | High | Blue-green deployment with gradual traffic shift |
| Performance degradation | Medium | Thorough load testing before cutover |
| Cold start latency | Medium | Implement provisioned concurrency for critical endpoints |
| Breaking changes to API contract | High | Maintain backward compatibility, version API |
| Increased complexity | Medium | Comprehensive documentation and runbooks |
Timeline
[To be determined]
Status
Current Status: Draft
History:
- 2025-12-22: Proposal created
7.7 - Migrate QAB Buy Web Services to Serverless
Summary
Proposal to migrate legacy Qab buy web services to a modern serverless architecture using the QabBuy serverless stack.
Rationale
[To be filled in - reasons for migrating to serverless]
Key benefits expected:
- Modernize legacy infrastructure
- Improved scalability and reliability
- Reduced maintenance burden
- Cost optimization
- Enhanced deployment practices
- Better handling of peak purchase volumes
Affected Applications
- buying-service-al202339-live - REST based service for caravan buying
Impact
Services Affected
- QAB buy/purchase web services
- [List additional services and dependencies]
Technical Considerations
- Legacy code modernization requirements
- API compatibility with existing consumers
- Integration with payment systems
- Transaction handling in serverless environment
- Performance and response time requirements
- Error handling and retry logic
Data Considerations
- Purchase data storage and retrieval
- Transaction state management
- Database access patterns
- Data consistency requirements
- Audit logging
Implementation Plan
Phase 1: Assessment & Design
- Document current buy service functionality
- Identify all consumers and integration points
- Map payment and transaction flows
- Design serverless architecture for QabBuy
- Define migration strategy for legacy code
- Assess infrastructure and security requirements
- Create proof of concept
Phase 2: Development
- Set up QabBuy serverless infrastructure
- Migrate/refactor purchase logic
- Implement serverless endpoints
- Configure API Gateway and routing
- Implement authentication and authorization
- Set up transaction handling
- Implement monitoring, logging, and alerting
- Create comprehensive test suite including transaction scenarios
Phase 3: Migration
- Deploy to staging environment
- Integration testing with consumers
- Payment system integration testing
- Performance and load testing
- Transaction failure scenario testing
- User acceptance testing
- Security and compliance review
- Create rollback procedures
Phase 4: Cutover
- Gradual traffic migration to new stack
- Monitor service health and transaction success rates
- Update consumer configurations
- Validate payment processing
- Decommission legacy buy services
- Archive legacy code and documentation
Risks & Mitigation
| Risk | Impact | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|
| Transaction failures during migration | Critical | Robust rollback plan, gradual cutover with monitoring |
| Payment processing issues | Critical | Extensive testing with payment systems, parallel running |
| Service disruption | High | Blue-green deployment with quick rollback capability |
| Legacy code complexity | High | Thorough documentation and refactoring plan |
| Integration breakage | High | Extensive integration testing before cutover |
| Data inconsistency | High | Transaction integrity testing, audit logging |
| Performance degradation | Medium | Load testing and capacity planning |
| Compliance issues | High | Security review and compliance validation |
Timeline
[To be determined]
Status
Current Status: Draft
History:
- 2025-12-22: Proposal created
7.8 - Migrate QAB Quoting Web Services to Serverless
Summary
Proposal to migrate legacy Qab quoting web services to a modern serverless architecture using the QabQuote serverless stack.
Rationale
[To be filled in - reasons for migrating to serverless]
Key benefits expected:
- Modernize legacy infrastructure
- Improved scalability and reliability
- Reduced maintenance burden
- Cost optimization
- Enhanced deployment practices
Affected Applications
No applications currently associated with this proposal.
Impact
Services Affected
- QAB quoting web services
- [List additional services and dependencies]
Technical Considerations
- Legacy code modernization requirements
- API compatibility with existing consumers
- Integration points with other systems
- Performance and response time requirements
- Session management in serverless context
Data Considerations
- Database access patterns
- Quote data storage and retrieval
- State management
- Caching requirements
Implementation Plan
Phase 1: Assessment & Design
- Document current web service functionality
- Identify all consumers and integration points
- Design serverless architecture for QabQuote
- Define migration strategy for legacy code
- Assess infrastructure requirements
- Create proof of concept
Phase 2: Development
- Set up QabQuote serverless infrastructure
- Migrate/refactor quoting logic
- Implement serverless endpoints
- Configure API Gateway and routing
- Set up authentication and authorization
- Implement monitoring and logging
- Create comprehensive test suite
Phase 3: Migration
- Deploy to staging environment
- Integration testing with consumers
- Performance and load testing
- User acceptance testing
- Security review
- Create rollback procedures
Phase 4: Cutover
- Gradual traffic migration to new stack
- Monitor service health and performance
- Update consumer configurations
- Decommission legacy web services
- Archive legacy code and documentation
Risks & Mitigation
| Risk | Impact | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|
| Service disruption | High | Gradual cutover with parallel running systems |
| Legacy code complexity | High | Thorough documentation and refactoring plan |
| Integration breakage | High | Extensive integration testing before cutover |
| Performance issues | Medium | Load testing and capacity planning |
| Data inconsistency | High | Thorough testing of quote calculations |
| Loss of domain knowledge | Medium | Document business logic during migration |
Timeline
[To be determined]
Status
Current Status: Draft
History:
- 2025-12-22: Proposal created
7.9 - Serverless Callbacks Migration
Summary
Proposal to migrate callbacks functionality to a serverless architecture.
Rationale
[To be filled in - reasons for migrating to serverless]
Key benefits expected:
- Improved scalability for callback processing
- Reduced operational overhead
- Cost optimization through pay-per-use model
- Better handling of variable callback volumes
- Enhanced reliability and retry mechanisms
Affected Applications
- flux-callme-service-al39 - Django REST based service for Callback table inserts in private VPC
- flux-callback-service - Django REST based web service for callback sending
Impact
Services Affected
- Callback handling services
- [List additional services and dependencies]
Technical Considerations
- Webhook/callback endpoint compatibility
- Event-driven architecture implementation
- Asynchronous processing requirements
- Retry and failure handling
- Message queue integration
- Timeout and execution limits
Data Considerations
- Callback data storage and logging
- Event sourcing patterns
- Audit trail requirements
- Dead letter queue handling
Implementation Plan
Phase 1: Assessment & Design
- Document current callback workflows
- Identify all callback sources and consumers
- Design event-driven serverless architecture
- Evaluate messaging/queue services (SQS, EventBridge, etc.)
- Define retry and error handling strategy
- Assess monitoring requirements
- Create proof of concept
Phase 2: Development
- Set up serverless infrastructure
- Implement event handlers and processors
- Configure API Gateway for webhook endpoints
- Set up message queues and event routing
- Implement retry logic and dead letter queues
- Set up monitoring, logging, and alerting
- Create comprehensive test suite including failure scenarios
Phase 3: Migration
- Deploy to staging environment
- Integration testing with callback sources
- Load and stress testing
- Failure scenario testing
- Latency and performance validation
- Security review
- Create rollback procedures
Phase 4: Cutover
- Deploy to production
- Gradual traffic migration
- Monitor callback processing rates and success
- Update webhook endpoint configurations
- Validate end-to-end callback flows
- Decommission old infrastructure
- Archive legacy documentation
Risks & Mitigation
| Risk | Impact | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|
| Callback delivery failures | High | Implement robust retry mechanisms and dead letter queues |
| Duplicate callback processing | Medium | Implement idempotency keys and deduplication |
| Cold start latency | Medium | Use provisioned concurrency for critical callbacks |
| Message loss during migration | High | Parallel processing with validation before cutover |
| Timeout issues for long-running callbacks | Medium | Design async processing patterns, evaluate timeout limits |
| Integration breakage | High | Extensive testing with all callback sources |
| Monitoring gaps | Medium | Comprehensive logging and alerting setup |
Timeline
[To be determined]
Status
Current Status: Draft
History:
- 2025-12-22: Proposal created
7.10 - Universal Geo Service Migration
Summary
Proposal for the migration and modernization of the universal-geo-service.
Rationale
[To be filled in - reasons for this change]
Key benefits expected:
- [List expected benefits]
Affected Applications
- flux-geo-service - Django REST based web service for GeoData lookups
- flux-geodata-service - Django REST based web service for GeoData lookups ("legacy" apps)
Impact
Services Affected
- Universal geo service
- [List additional services and dependencies]
Technical Considerations
- API compatibility with existing consumers
- Geographic data accuracy and coverage
- Performance and response time requirements
- Caching strategy for geo lookups
Data Considerations
- Geographic data storage and updates
- Data accuracy and validation
- Third-party data sources and licensing
Implementation Plan
Phase 1: Assessment & Design
- Document current service functionality
- Identify all consumers and integration points
- Evaluate target architecture/platform
- Assess data migration requirements
- Define migration strategy
- Create proof of concept
Phase 2: Development
- Set up new infrastructure
- Implement/migrate core functionality
- Configure API endpoints
- Set up authentication and authorization
- Implement monitoring and logging
- Create comprehensive test suite
Phase 3: Migration
- Deploy to staging environment
- Integration testing with consumers
- Performance and load testing
- Data validation testing
- User acceptance testing
- Security review
- Create rollback procedures
Phase 4: Cutover
- Deploy to production
- Gradual traffic migration
- Monitor service health and performance
- Update consumer configurations
- Decommission old infrastructure
- Archive legacy documentation
Risks & Mitigation
| Risk | Impact | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|
| Service disruption | High | Gradual cutover with parallel running systems |
| Geographic data accuracy issues | High | Thorough data validation and testing |
| Performance degradation | Medium | Load testing and capacity planning |
| Integration breakage | High | Extensive integration testing before cutover |
| Third-party dependency issues | Medium | Evaluate and test all external dependencies |
Timeline
[To be determined]
Status
Current Status: Draft
History:
- 2025-12-22: Proposal created
7.11 - Remove Fakertrail Application
Summary
Proposal to remove the fakertrail application from our infrastructure.
Rationale
[To be filled in - reasons for removing this application]
Affected Applications
- fakertrail - Django based HTTP Python Logger
Impact
Services Affected
- List services that will be impacted
- Downstream dependencies
Data Considerations
- Data migration requirements
- Backup and archival needs
Implementation Plan
Phase 1: Preparation
- Audit current usage
- Identify dependencies
- Create data backup
Phase 2: Migration
- Redirect traffic if needed
- Migrate critical data
Phase 3: Decommissioning
- Remove from Heroku
- Update DNS records
- Remove monitoring/alerts
- Archive documentation
Risks & Mitigation
| Risk | Impact | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|
| Loss of functionality | Medium | Document all features before removal |
| Data loss | High | Full backup before decommission |
| Broken integrations | Medium | Audit all integrations beforehand |
Timeline
[To be determined]
Status
Current Status: Draft
History:
- 2025-12-20: Proposal created
7.12 - Provider Agnostic Geo Lookup Library
| Status | Effort | Client Cost Saving |
|---|---|---|
| Draft | 20 | TBD |
Summary
Create a Python library that provides a provider-agnostic interface for geographic address lookup services. This library will support automatic failover between providers, ensuring service continuity during provider outages, and can be deployed across multiple projects and platforms (DRF, Lambda).
Rationale
The Problem
On 2026-02-04, getaddress.io experienced several hours of downtime. This caused a complete failure of the quote service flow because:
- Single Provider Dependency: The geo service currently relies exclusively on getaddress.io with no fallback mechanism
- Cross-Client Impact: This single point of failure affects multiple clients (Adrian Flux, Sterling, Bikesure) and multiple product lines (EPAs, JAF forms), amplifying the business risk
- User Experience Impact: While users could technically enter addresses manually, this option is not immediately obvious in the UI
- Business Impact: No quotes could be processed during the outage across any client or product line, directly affecting revenue
Why This Change is Needed
- Resilience: We have an avoidable single point of failure that affects multiple clients and product lines - a single provider outage takes down quote functionality across the entire business
- Code Exists: The codebase technically supports multiple providers, but only one is implemented and active
- Reusability: Other hut42 projects (Viitata, Forecaster, Katala) require similar geo lookup functionality
- Cost Optimization: Some providers like Google offer free tiers that could serve as fallback options
Proposed Solution
Python Library
A standalone Python library that:
- Abstracts Provider Implementation: Unified interface regardless of underlying provider
- Supports Multiple Providers:
- getaddress.io (primary)
- Google Places API (fallback - potentially free tier)
- Additional providers as needed
- Manual or Automatic Failover: Configurable provider switching (see phased approach below)
- Framework Agnostic: Works with DRF services and Lambda functions
- Built from Existing Code: Refactored from the current geo service codebase
Phased Approach
Phase 1 - Manual Switchover: Implement multi-provider support with manual provider switching via configuration. Service health monitoring handled externally by Uptime Robot, with manual intervention to switch providers during outages.
Phase 2 - Automatic Failover: Add built-in health checking and automatic failover management to the library, removing the need for manual intervention.
Architecture
Phase 1 - Manual Switchover
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ Geo Lookup Library │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ GeoLookupClient │
│ ├── Provider Registry │
│ ├── Provider Selector (config-driven) │
│ └── Response Normalizer │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ Providers │
│ ├── GetAddressProvider (primary) │
│ ├── GooglePlacesProvider (fallback) │
│ └── BaseProvider (abstract interface) │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
│
▼
┌──────────┐ ┌─────────────────┐
│ Geo Svc │◄───────│ Uptime Robot │
│ │ | (monitoring) │
└──────────┘ └─────────────────┘
│
▼
┌─────────────────┐
│ Manual config │
│ change to swap │
│ provider │
└─────────────────┘
Phase 2 - Automatic Failover
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ Geo Lookup Library │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ GeoLookupClient │
│ ├── Provider Registry │
│ ├── Health Checker ◄── NEW │
│ ├── Failover Manager ◄── NEW │
│ └── Response Normalizer │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ Providers │
│ ├── GetAddressProvider (primary) │
│ ├── GooglePlacesProvider (fallback) │
│ └── BaseProvider (abstract interface) │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
│ │
▼ ▼
┌──────────┐ ┌───────────┐
│ Geo Svc │ │ Geo Svc │
| [Flux] | | [Hutsoft] |
└──────────┘ └───────────┘
Key Features
| Feature | Phase | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Provider Abstraction | 1 | Unified API regardless of underlying service |
| Response Normalization | 1 | Consistent response format across all providers |
| Configurable Provider | 1 | Select active provider via configuration |
| External Health Monitoring | 1 | Uptime Robot monitors provider health |
| Manual Switchover | 1 | Change provider via config during outages |
| Metrics & Logging | 1 | Track provider performance and failures |
| Built-in Health Checker | 2 | Periodic health checks on all configured providers |
| Automatic Failover Manager | 2 | Circuit breaker pattern for automatic provider switching |
Affected Applications
Primary Integration
- Universal geo service (immediate integration)
Main Consumers (highest traffic)
- Adrian Flux, Sterling and Bikesure EPAs
- Adrian Flux and Sterling JAF forms
Other Potential Consumers
- Viitata
- Forecaster
- Katala
- Any future projects requiring geo lookup
Impact
API Compatibility
This proposal maintains 100% API compatibility with the existing geo service. No consumer application changes will be required. The library will be integrated behind the existing service interface, making this change completely transparent to Adrian Flux, Sterling, Bikesure EPAs, JAF forms, and all other consumers.
Services Affected
- Universal geo service (internal code changes for library integration)
- Quote service (indirect - improved reliability)
Technical Considerations
- API compatibility will be maintained for existing geo service consumers
- Response format normalization between different providers
- Rate limiting and quota management per provider
- Caching strategy to reduce API calls and costs
- Configuration management for API keys across environments
Data Considerations
- Different providers may return slightly different address formats
- UK-specific address formatting (getaddress.io strength)
- Postcode validation consistency across providers
Provider Analysis
getaddress.io (Current/Primary)
- Pros: UK-focused, excellent postcode lookup, current integration exists
- Cons: Single point of failure, outage yesterday
- Cost: Paid service
Google Places API (Proposed Fallback)
- Pros: Highly reliable, generous free tier, global coverage
- Cons: Less UK-specific, may require address normalization
- Cost: Free tier available (suitable for fallback volumes)
Other Options to Evaluate
- Postcodes.io (UK specific, open data)
- Ideal Postcodes
- OS Places API
Implementation Plan
Phase 1: Multi-Provider Support with Manual Switchover
1.1 Library Development
- Extract and refactor existing geo code into standalone library
- Define abstract provider interface (BaseProvider)
- Implement GetAddressProvider (port existing code)
- Implement GooglePlacesProvider
- Create response normalization layer
- Implement configurable provider selection
- Write comprehensive test suite
- Package as installable Python library
1.2 Geo Service Integration
- Install library in universal-geo-service
- Configure primary and fallback providers
- Update service to use library interface
- Integration testing
- Deploy to staging
1.3 Monitoring & Rollout
- Configure Uptime Robot to monitor provider endpoints
- Set up alerting for provider outages
- Document manual switchover procedure
- Deploy to production
- Test manual switchover process
Phase 2: Automatic Health Checking & Failover
2.1 Library Enhancement
- Implement Health Checker component
- Implement Failover Manager with circuit breaker pattern
- Add automatic provider switching logic
- Configure failover thresholds and retry policies
- Update test suite for failover scenarios
2.2 Integration & Rollout
- Update geo service to use automatic failover
- Deploy to staging
- Performance and failover testing
- Deploy to production
- Monitor automatic failover events
Wider Adoption (Post Phase 1 or 2)
- Provide library documentation and examples
- Support Viitata integration
- Support Forecaster integration
- Support Katala integration
Risks & Mitigation
| Risk | Impact | Phase | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Provider response format differences | Medium | 1 & 2 | Robust response normalization and testing |
| Increased complexity | Low | 1 & 2 | Clean abstraction layer, good documentation |
| Google free tier limits exceeded | Low | 1 & 2 | Monitor usage, upgrade plan if needed |
| Manual switchover delay | Medium | 1 | Uptime Robot alerting, documented runbook |
| Failover latency | Low | 2 | Health checks, circuit breaker pattern |
| Address accuracy differences | Medium | 1 & 2 | Thorough testing with UK addresses, consider primary-only for critical paths |
Success Metrics
Phase 1
- Ability to switch providers within minutes of detected outage
- Zero extended quote service outages due to geo provider failures
- Library adoption in at least 2 additional projects within 6 months
- Reduced operational impact from geo lookup alerts
Phase 2
- < 500ms automatic failover time when primary provider fails
- Zero manual intervention required for provider outages
- Reduced operational alerts related to geo lookups
Estimations
Phase 1: 3 days (20 hours)
| Task | Effort |
|---|---|
| Project setup, current implementation investigation, alternative provider investigation | 4 hours |
| Development build | 8 hours |
| Testing and integration | 8 hours |
Phase 2: 2 days (16 hours)
| Task | Effort |
|---|---|
| Development build | 8 hours |
| Testing and integration | 8 hours |
Status
Current Status: Draft
History:
- 2025-02-05: Proposal created following getaddress.io outage
8 - Example Page
This is a placeholder page. Replace it with your own content.
Texts can be bold, italic, or strikethrough. Links
should be blue with no underlines (unless hovered over).
There should be whitespace between paragraphs. Vape migas chillwave sriracha poutine try-hard distillery. Tattooed shabby chic small batch, pabst art party heirloom letterpress air plant pop-up. Sustainable chia skateboard art party banjo cardigan normcore affogato vexillologist quinoa meggings man bun master cleanse shoreditch readymade. Yuccie prism four dollar toast tbh cardigan iPhone, tumblr listicle live-edge VHS. Pug lyft normcore hot chicken biodiesel, actually keffiyeh thundercats photo booth pour-over twee fam food truck microdosing banh mi. Vice activated charcoal raclette unicorn live-edge post-ironic. Heirloom vexillologist coloring book, beard deep v letterpress echo park humblebrag tilde.
90’s four loko seitan photo booth gochujang freegan tumeric listicle fam ugh humblebrag. Bespoke leggings gastropub, biodiesel brunch pug fashion axe meh swag art party neutra deep v chia. Enamel pin fanny pack knausgaard tofu, artisan cronut hammock meditation occupy master cleanse chartreuse lumbersexual. Kombucha kogi viral truffaut synth distillery single-origin coffee ugh slow-carb marfa selfies. Pitchfork schlitz semiotics fanny pack, ugh artisan vegan vaporware hexagon. Polaroid fixie post-ironic venmo wolf ramps kale chips.
There should be no margin above this first sentence.
Blockquotes should be a lighter gray with a border along the left side in the secondary color.
There should be no margin below this final sentence.
First Header 2
This is a normal paragraph following a header. Knausgaard kale chips snackwave microdosing cronut copper mug swag synth bitters letterpress glossier craft beer. Mumblecore bushwick authentic gochujang vegan chambray meditation jean shorts irony. Viral farm-to-table kale chips, pork belly palo santo distillery activated charcoal aesthetic jianbing air plant woke lomo VHS organic. Tattooed locavore succulents heirloom, small batch sriracha echo park DIY af. Shaman you probably haven’t heard of them copper mug, crucifix green juice vape single-origin coffee brunch actually. Mustache etsy vexillologist raclette authentic fam. Tousled beard humblebrag asymmetrical. I love turkey, I love my job, I love my friends, I love Chardonnay!
Deae legum paulatimque terra, non vos mutata tacet: dic. Vocant docuique me plumas fila quin afuerunt copia haec o neque.
On big screens, paragraphs and headings should not take up the full container width, but we want tables, code blocks and similar to take the full width.
Scenester tumeric pickled, authentic crucifix post-ironic fam freegan VHS pork belly 8-bit yuccie PBR&B. I love this life we live in.
Second Header 2
This is a blockquote following a header. Bacon ipsum dolor sit amet t-bone doner shank drumstick, pork belly porchetta chuck sausage brisket ham hock rump pig. Chuck kielbasa leberkas, pork bresaola ham hock filet mignon cow shoulder short ribs biltong.
Header 3
This is a code block following a header.
Next level leggings before they sold out, PBR&B church-key shaman echo park. Kale chips occupy godard whatever pop-up freegan pork belly selfies. Gastropub Belinda subway tile woke post-ironic seitan. Shabby chic man bun semiotics vape, chia messenger bag plaid cardigan.
Header 4
- This is an unordered list following a header.
- This is an unordered list following a header.
- This is an unordered list following a header.
Header 5
- This is an ordered list following a header.
- This is an ordered list following a header.
- This is an ordered list following a header.
Header 6
| What | Follows |
|---|---|
| A table | A header |
| A table | A header |
| A table | A header |
There’s a horizontal rule above and below this.
Here is an unordered list:
- Liverpool F.C.
- Chelsea F.C.
- Manchester United F.C.
And an ordered list:
- Michael Brecker
- Seamus Blake
- Branford Marsalis
And an unordered task list:
- Create a Hugo theme
- Add task lists to it
- Take a vacation
And a “mixed” task list:
- Pack bags
- ?
- Travel!
And a nested list:
- Jackson 5
- Michael
- Tito
- Jackie
- Marlon
- Jermaine
- TMNT
- Leonardo
- Michelangelo
- Donatello
- Raphael
Definition lists can be used with Markdown syntax. Definition headers are bold.
Name : Godzilla
Born : 1952
Birthplace : Japan
Color : Green
Tables should have bold headings and alternating shaded rows.
| Artist | Album | Year |
|---|---|---|
| Michael Jackson | Thriller | 1982 |
| Prince | Purple Rain | 1984 |
| Beastie Boys | License to Ill | 1986 |
If a table is too wide, it should scroll horizontally.
| Artist | Album | Year | Label | Awards | Songs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Michael Jackson | Thriller | 1982 | Epic Records | Grammy Award for Album of the Year, American Music Award for Favorite Pop/Rock Album, American Music Award for Favorite Soul/R&B Album, Brit Award for Best Selling Album, Grammy Award for Best Engineered Album, Non-Classical | Wanna Be Startin’ Somethin’, Baby Be Mine, The Girl Is Mine, Thriller, Beat It, Billie Jean, Human Nature, P.Y.T. (Pretty Young Thing), The Lady in My Life |
| Prince | Purple Rain | 1984 | Warner Brothers Records | Grammy Award for Best Score Soundtrack for Visual Media, American Music Award for Favorite Pop/Rock Album, American Music Award for Favorite Soul/R&B Album, Brit Award for Best Soundtrack/Cast Recording, Grammy Award for Best Rock Performance by a Duo or Group with Vocal | Let’s Go Crazy, Take Me With U, The Beautiful Ones, Computer Blue, Darling Nikki, When Doves Cry, I Would Die 4 U, Baby I’m a Star, Purple Rain |
| Beastie Boys | License to Ill | 1986 | Mercury Records | noawardsbutthistablecelliswide | Rhymin & Stealin, The New Style, She’s Crafty, Posse in Effect, Slow Ride, Girls, (You Gotta) Fight for Your Right, No Sleep Till Brooklyn, Paul Revere, Hold It Now, Hit It, Brass Monkey, Slow and Low, Time to Get Ill |
Code snippets like var foo = "bar"; can be shown inline.
Also, this should vertically align with thisand this.
Code can also be shown in a block element.
foo := "bar";
bar := "foo";
Code can also use syntax highlighting.
func main() {
input := `var foo = "bar";`
lexer := lexers.Get("javascript")
iterator, _ := lexer.Tokenise(nil, input)
style := styles.Get("github")
formatter := html.New(html.WithLineNumbers())
var buff bytes.Buffer
formatter.Format(&buff, style, iterator)
fmt.Println(buff.String())
}
Long, single-line code blocks should not wrap. They should horizontally scroll if they are too long. This line should be long enough to demonstrate this.
Inline code inside table cells should still be distinguishable.
| Language | Code |
|---|---|
| Javascript | var foo = "bar"; |
| Ruby | foo = "bar"{ |
Small images should be shown at their actual size.

Large images should always scale down and fit in the content container.

The photo above of the Spruce Picea abies shoot with foliage buds: Bjørn Erik Pedersen, CC-BY-SA.
Components
Alerts
This is an alert.
This is an alert with a title.
This is a successful alert.
This is a warning!
This is a danger alert with a title!
Another Heading
Add some sections here to see how the ToC looks like. Bacon ipsum dolor sit amet t-bone doner shank drumstick, pork belly porchetta chuck sausage brisket ham hock rump pig. Chuck kielbasa leberkas, pork bresaola ham hock filet mignon cow shoulder short ribs biltong.
This Document
Inguina genus: Anaphen post: lingua violente voce suae meus aetate diversi. Orbis unam nec flammaeque status deam Silenum erat et a ferrea. Excitus rigidum ait: vestro et Herculis convicia: nitidae deseruit coniuge Proteaque adiciam eripitur? Sitim noceat signa probat quidem. Sua longis fugatis quidem genae.
Pixel Count
Tilde photo booth wayfarers cliche lomo intelligentsia man braid kombucha vaporware farm-to-table mixtape portland. PBR&B pickled cornhole ugh try-hard ethical subway tile. Fixie paleo intelligentsia pabst. Ennui waistcoat vinyl gochujang. Poutine salvia authentic affogato, chambray lumbersexual shabby chic.
Contact Info
Plaid hell of cred microdosing, succulents tilde pour-over. Offal shabby chic 3 wolf moon blue bottle raw denim normcore poutine pork belly.
External Links
Stumptown PBR&B keytar plaid street art, forage XOXO pitchfork selvage affogato green juice listicle pickled everyday carry hashtag. Organic sustainable letterpress sartorial scenester intelligentsia swag bushwick. Put a bird on it stumptown neutra locavore. IPhone typewriter messenger bag narwhal. Ennui cold-pressed seitan flannel keytar, single-origin coffee adaptogen occupy yuccie williamsburg chillwave shoreditch forage waistcoat.
This is the final element on the page and there should be no margin below this.